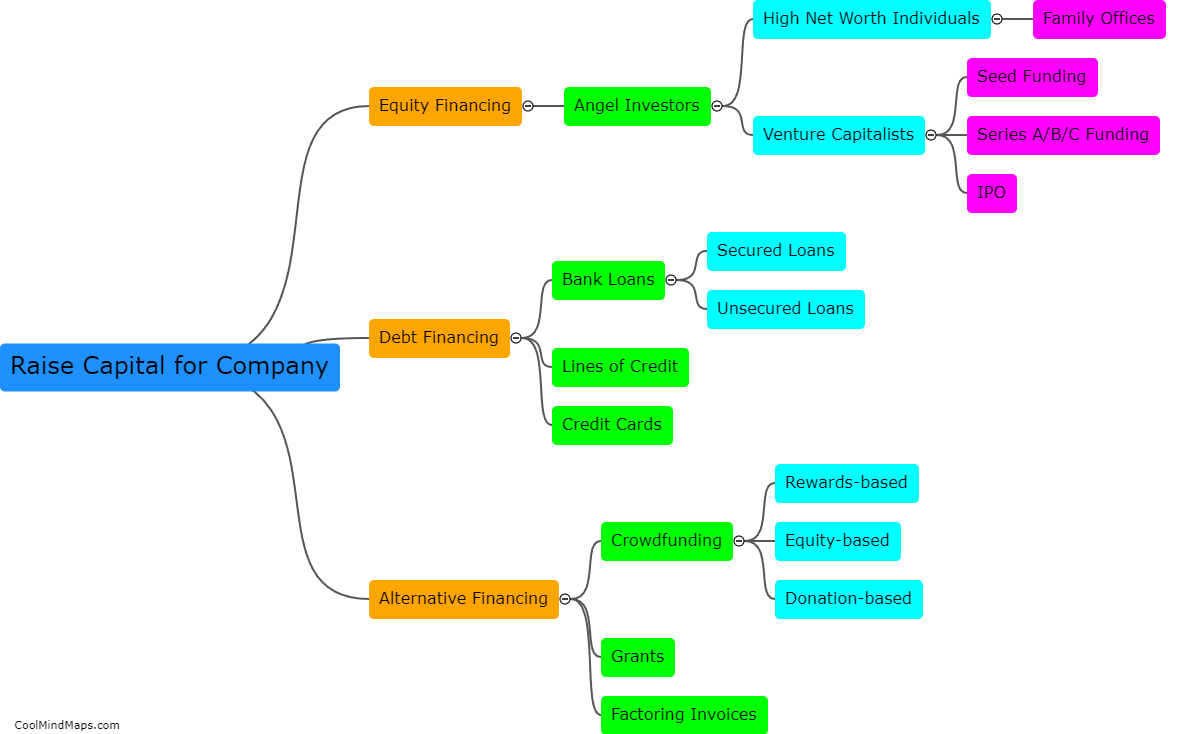
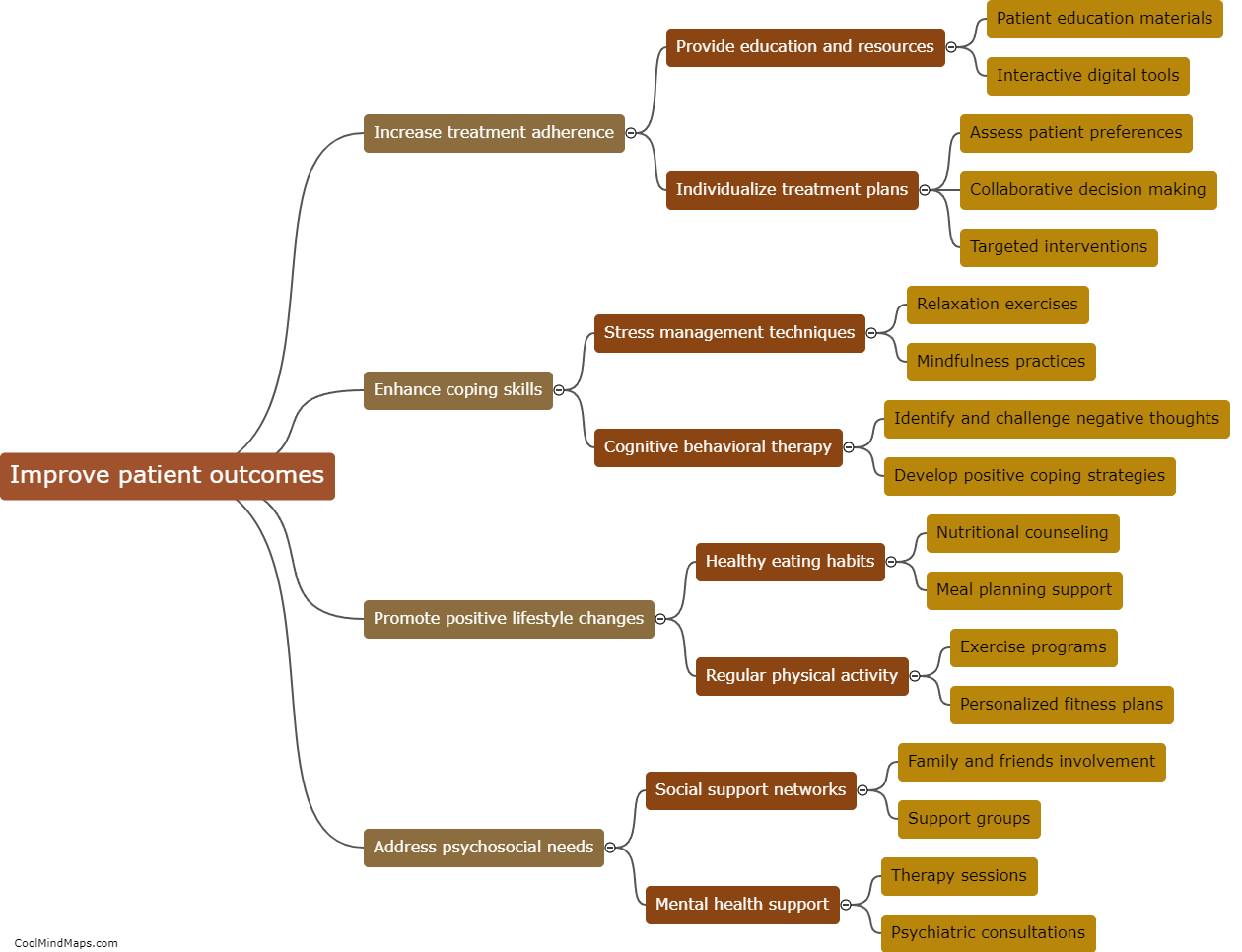
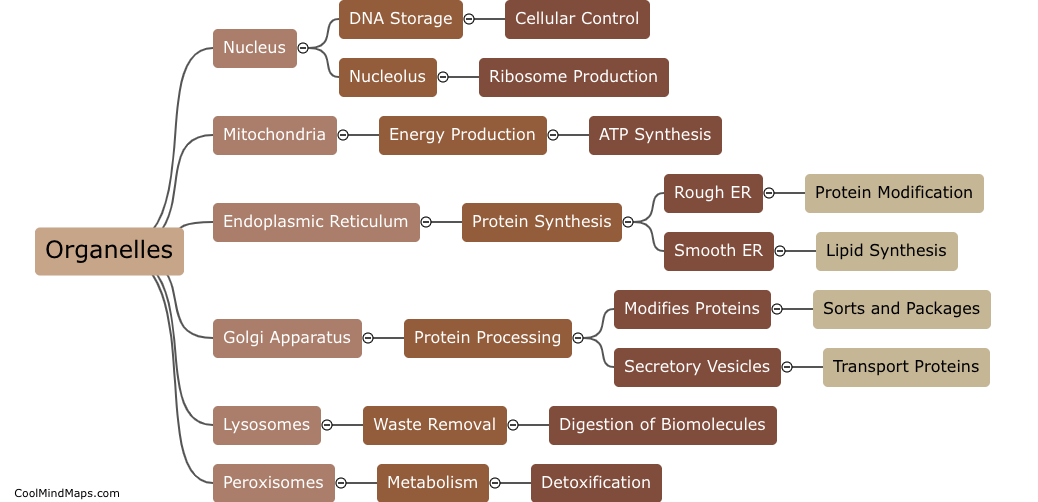
What are the six main organelles found within a human (eukaryotic) cell and what is their function?
The human (eukaryotic) cell contains several key organelles that play crucial roles in maintaining the cell's structure, function, and overall well-being. These include the nucleus, which houses the cell's genetic material and controls cellular activities; the mitochondria, which generate energy through cellular respiration; the endoplasmic reticulum, responsible for protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification; the Golgi apparatus, which processes, modifies, and packages proteins for transport; the lysosomes, involved in intracellular digestion and waste removal; and the cytoskeleton, a network of protein filaments that provides structure, support, and facilitates cell movement. Each organelle contributes to the proper functioning and overall integrity of the cell, ensuring its survival and ability to carry out essential functions.
This mind map was published on 10 October 2023 and has been viewed 101 times.