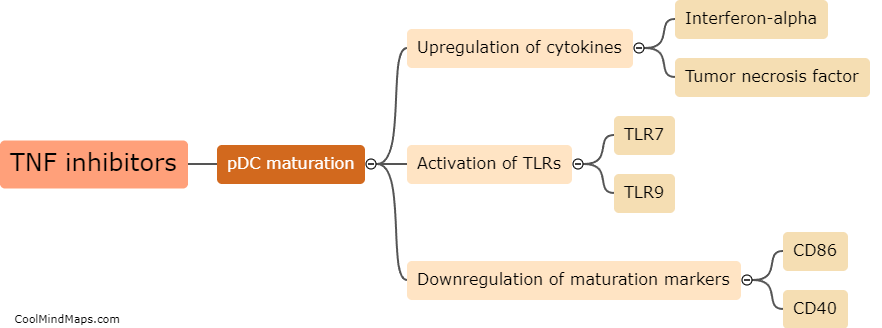
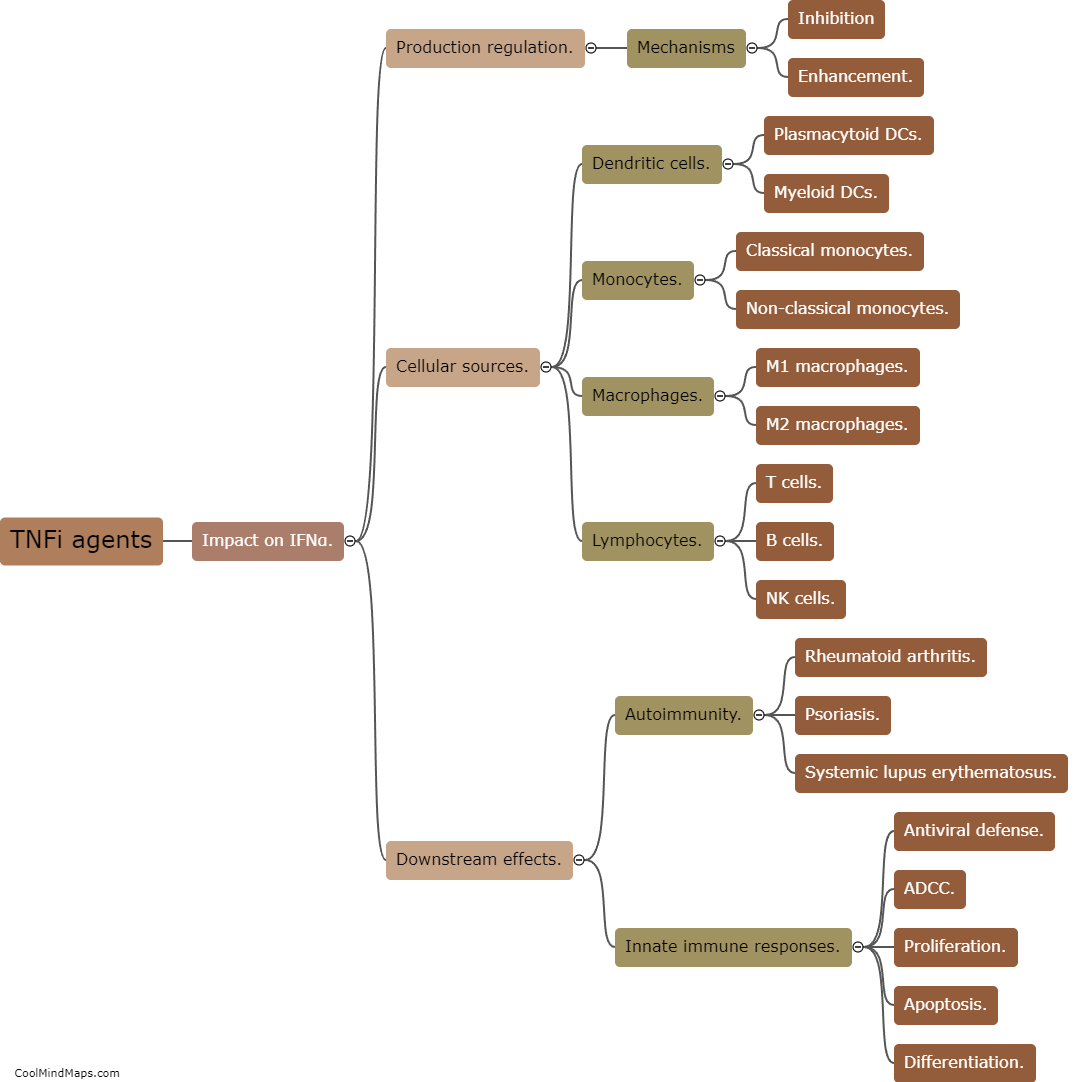
Can a significant increase in IFNα response alone cause paradoxical psoriasis?
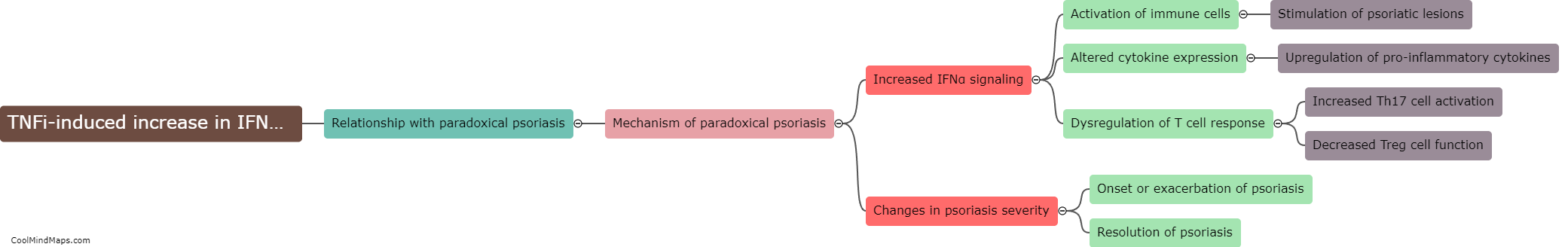
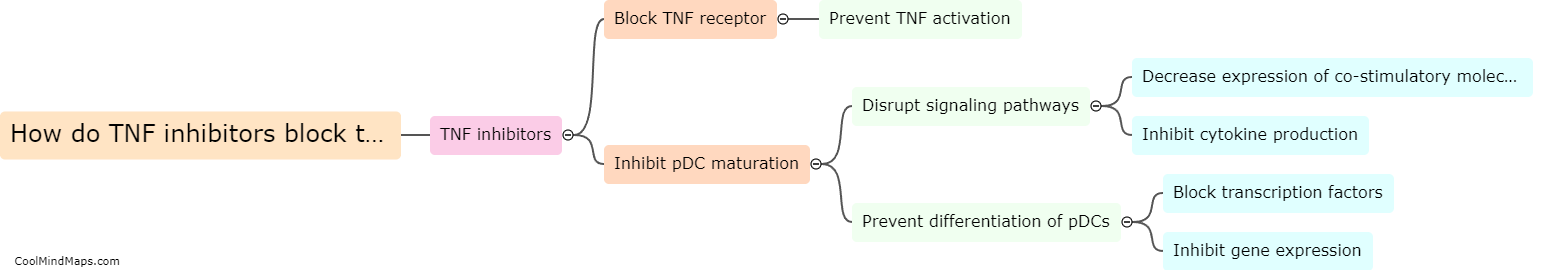
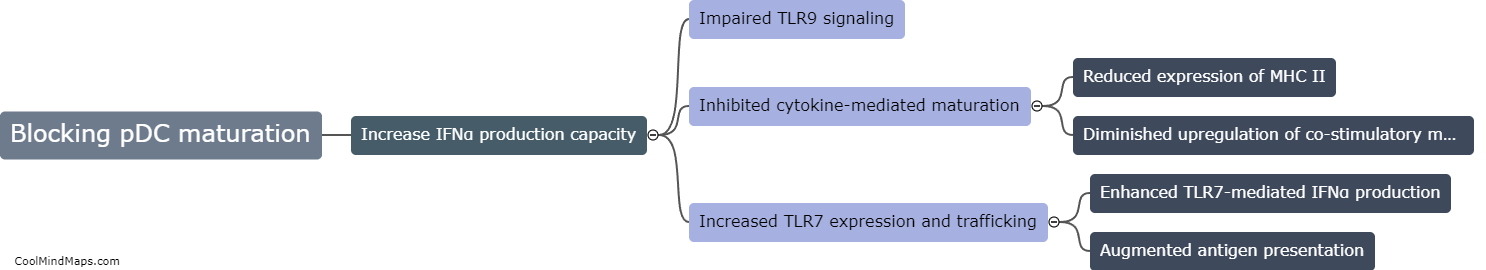
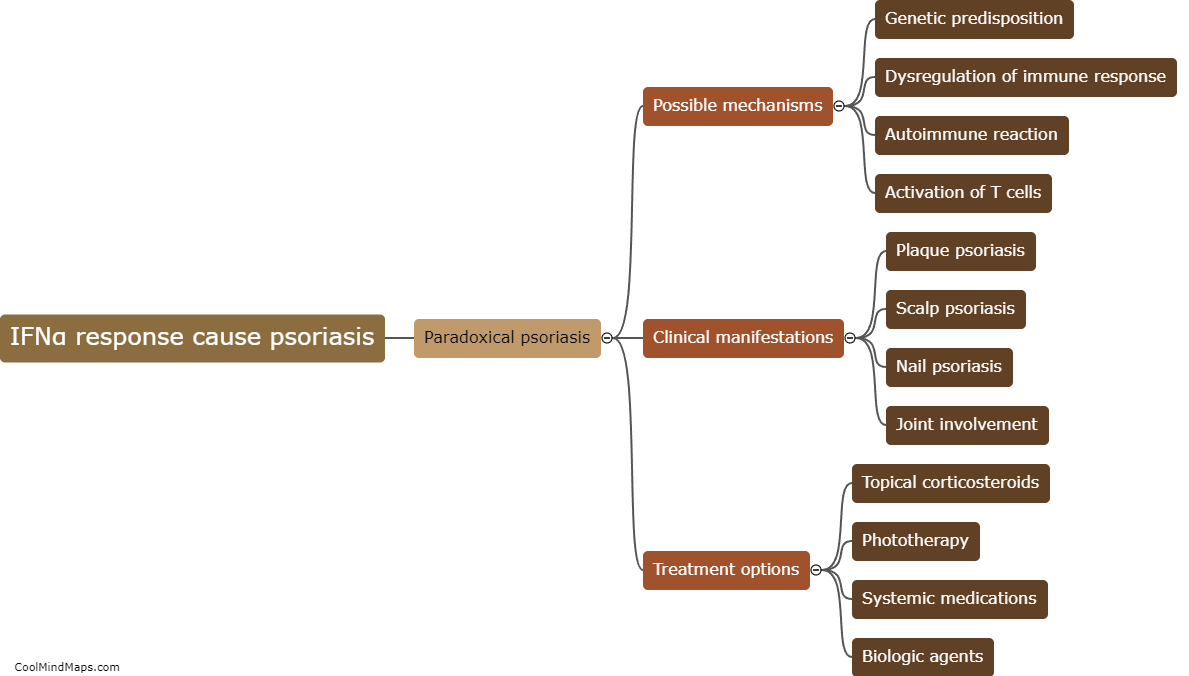
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by red, scaly patches that can be itchy and painful. Paradoxical psoriasis refers to the paradoxical worsening or development of psoriasis following treatment with certain immunomodulatory medications. While the exact mechanisms underlying paradoxical psoriasis are not fully understood, research suggests that a dysregulated immune response, particularly an abnormal increase in interferon-alpha (IFNα) signaling, may play a role in its pathogenesis. IFNα is a cytokine involved in the immune response against viral infections. Studies have shown that higher levels of IFNα can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. However, it is important to note that a significant increase in IFNα response alone may not be sufficient to cause paradoxical psoriasis, as other factors, including the individual's genetic susceptibility, immune system functioning, and concurrent treatments, may also contribute to the development of this condition. Further research is needed to unravel the complex interactions between IFNα and psoriasis, and to identify potential therapeutic strategies to manage paradoxical psoriasis in patients receiving immunomodulatory treatments.
This mind map was published on 13 July 2023 and has been viewed 269 times.