How does respiration work in the human body?
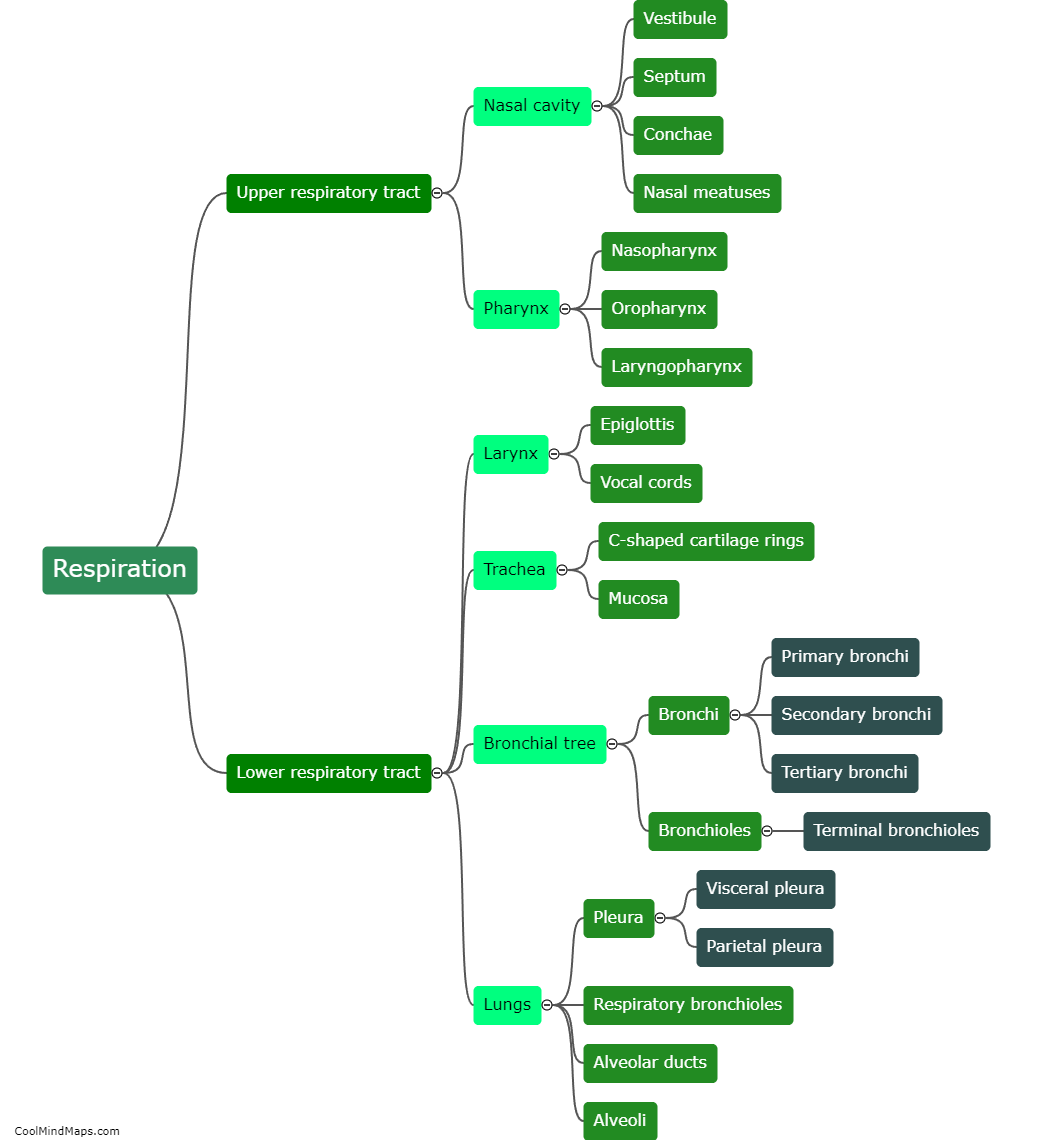
Respiration is the process through which oxygen is taken in by the human body and carbon dioxide is released. It involves multiple steps and organs working together to ensure the exchange of gases occurs efficiently. The process begins with inhalation, where the diaphragm contracts and the lungs expand, creating a negative pressure that draws in oxygen-rich air. The oxygen then passes through the bronchial tubes and into the alveoli, tiny sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place. Here, oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream and is carried by red blood cells to the body's tissues, where it is used in cellular respiration to produce energy. Simultaneously, carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration, is picked up by the red blood cells and transported back to the lungs. During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes, the lungs contract, and carbon dioxide is expelled from the body. This intricate process enables the body to constantly supply oxygen to cells and get rid of carbon dioxide, playing a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis.

This mind map was published on 8 August 2023 and has been viewed 97 times.