How does time dilation occur in the special theory of relativity?
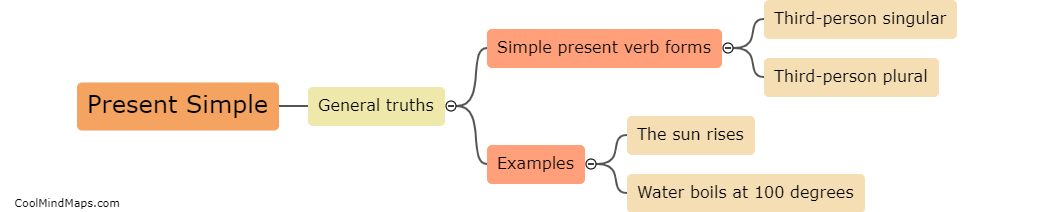
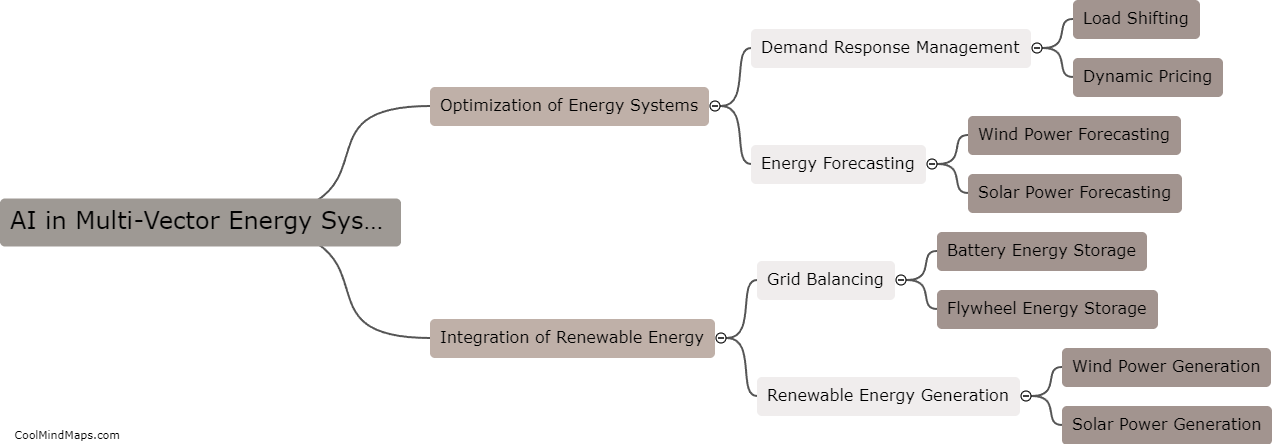
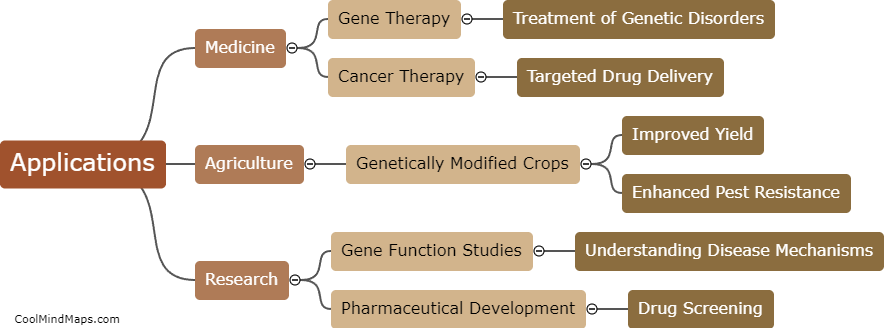
Time dilation occurs in the special theory of relativity when an object is moving relative to an observer at a significant fraction of the speed of light. According to Einstein's theory, time is not a fixed concept but rather depends on the relative motion between two observers. When an object moves closer to the speed of light, time for that object appears to slow down from the perspective of a stationary observer. This effect, known as time dilation, occurs because the faster an object moves, the more time it takes for light signals to reach an observer. As a result, the moving object experiences time passing slower compared to the observer who is at rest. This phenomenon has been experimentally verified and is a fundamental concept in understanding the implications of motion and relative velocities in the special theory of relativity.

This mind map was published on 6 December 2023 and has been viewed 91 times.