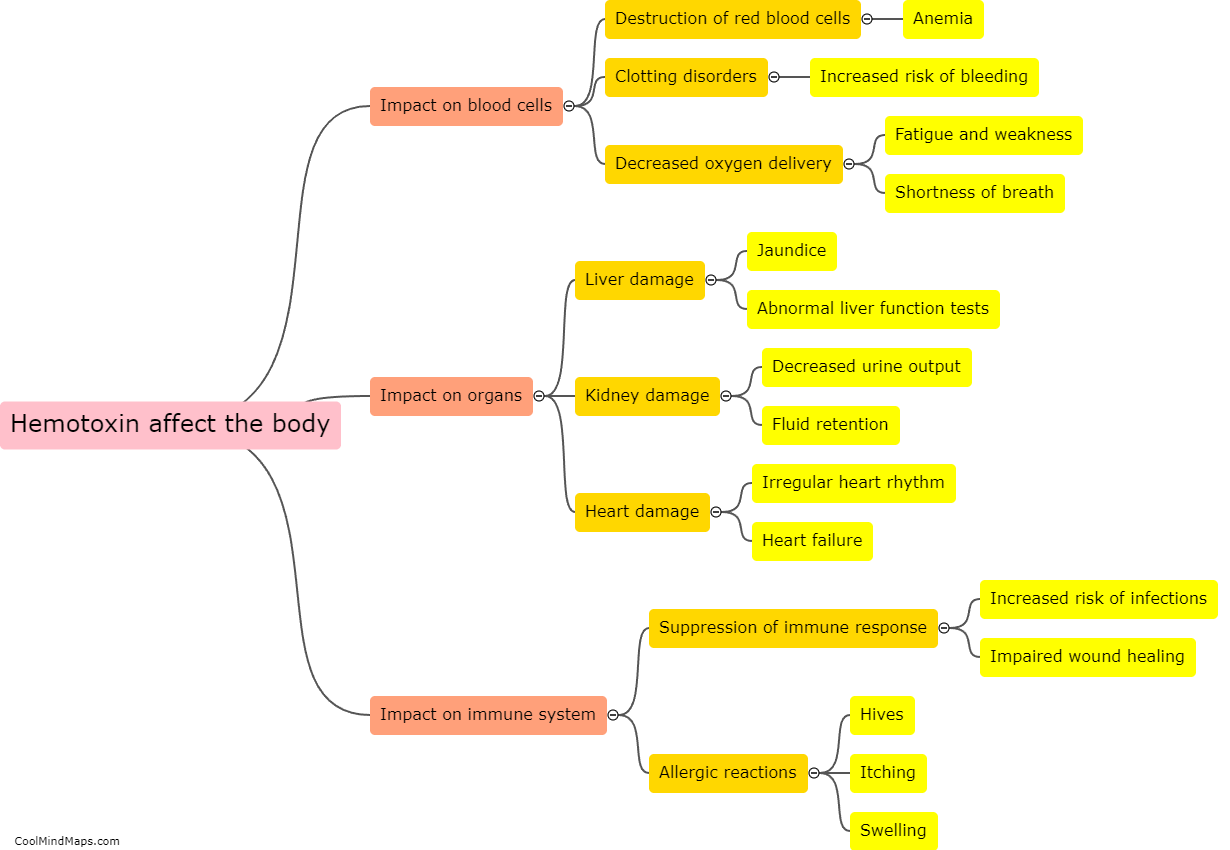
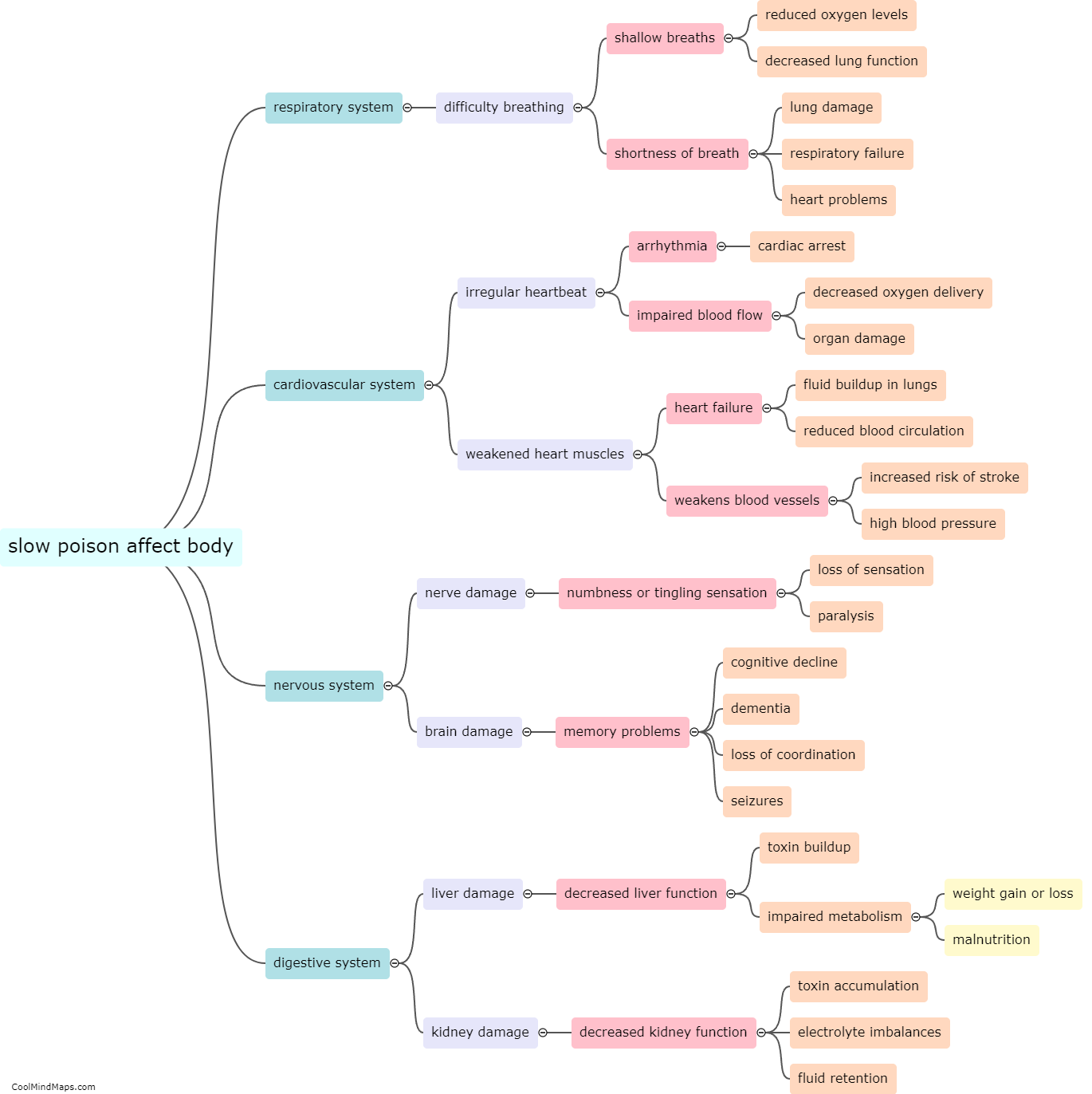
How does slow poison affect the body?
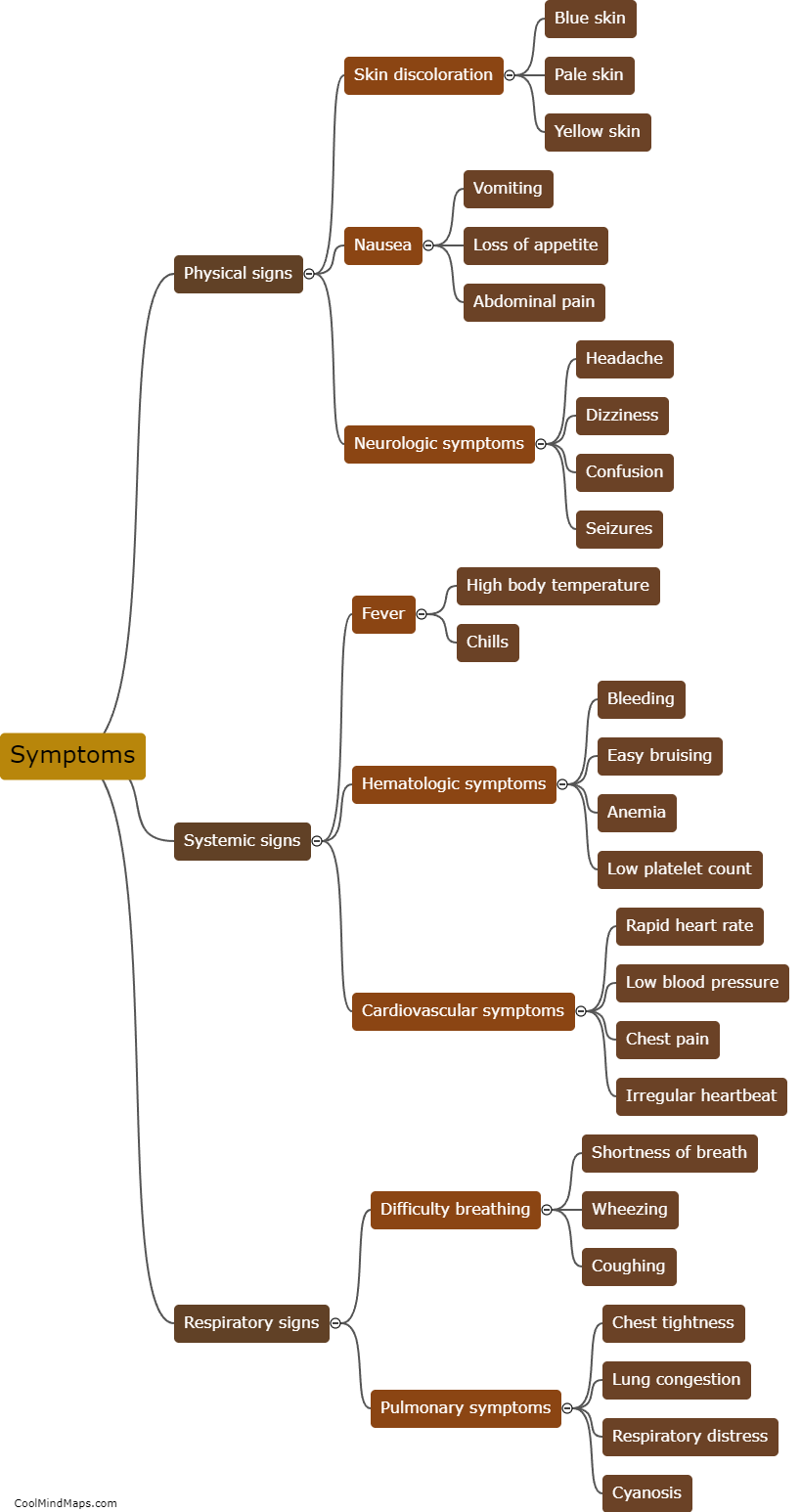
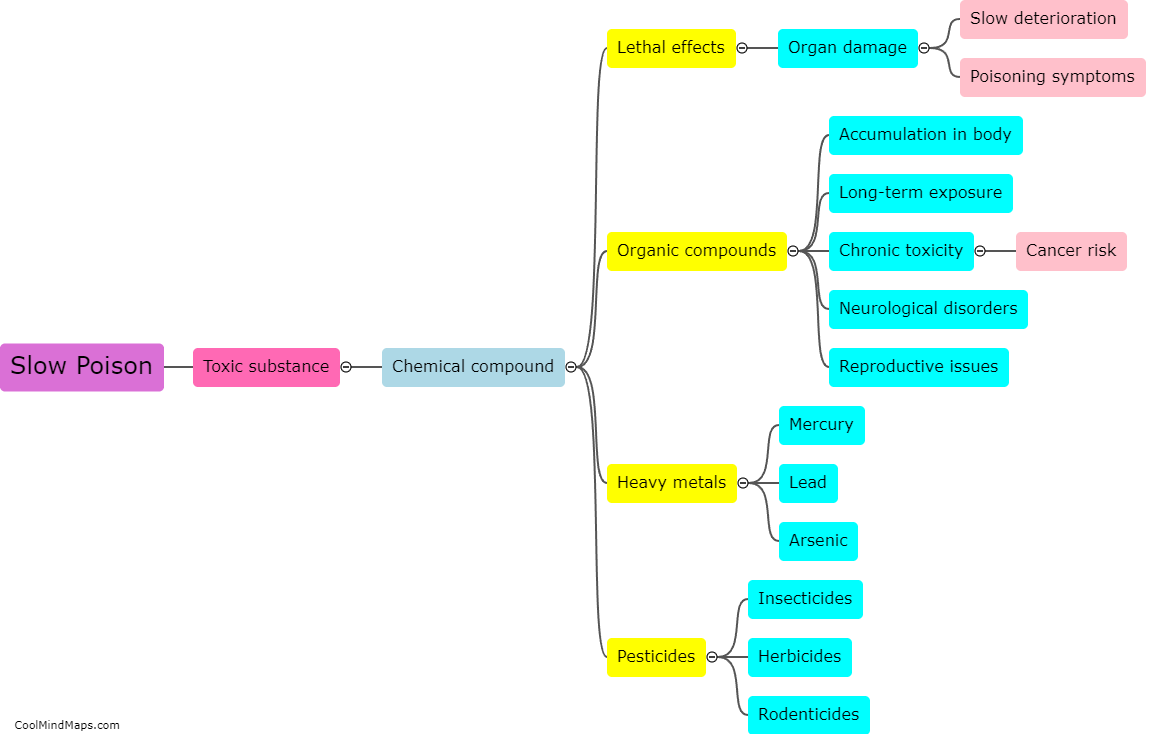
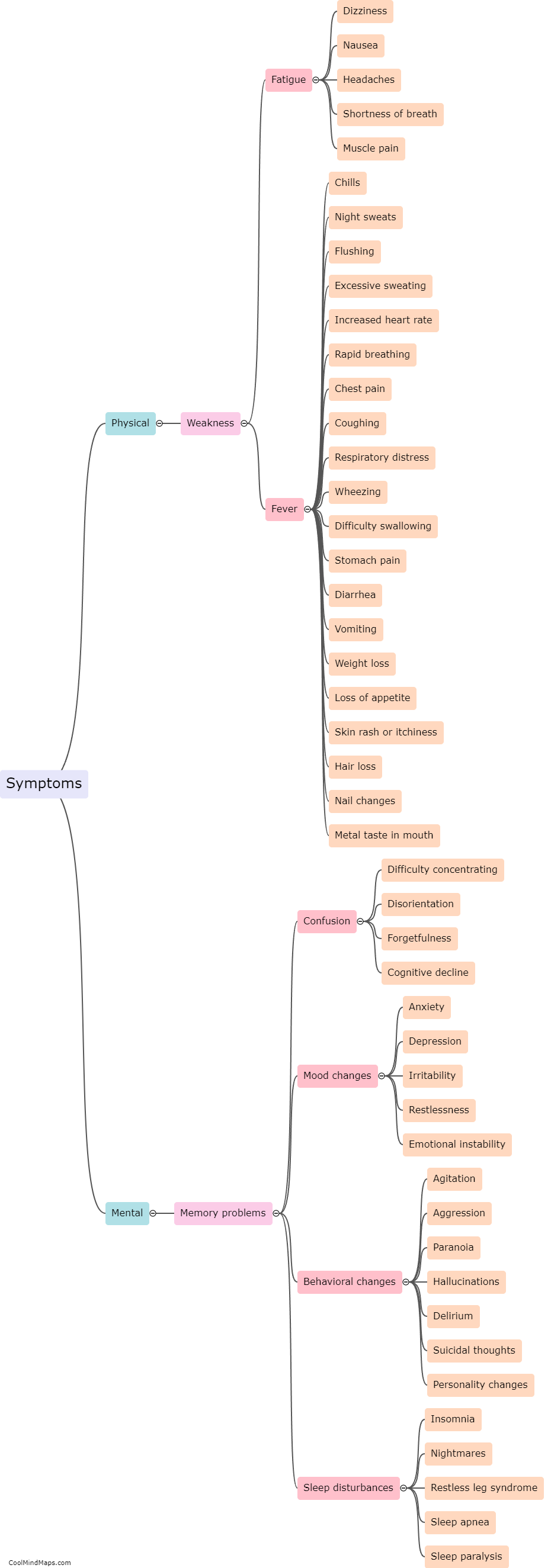
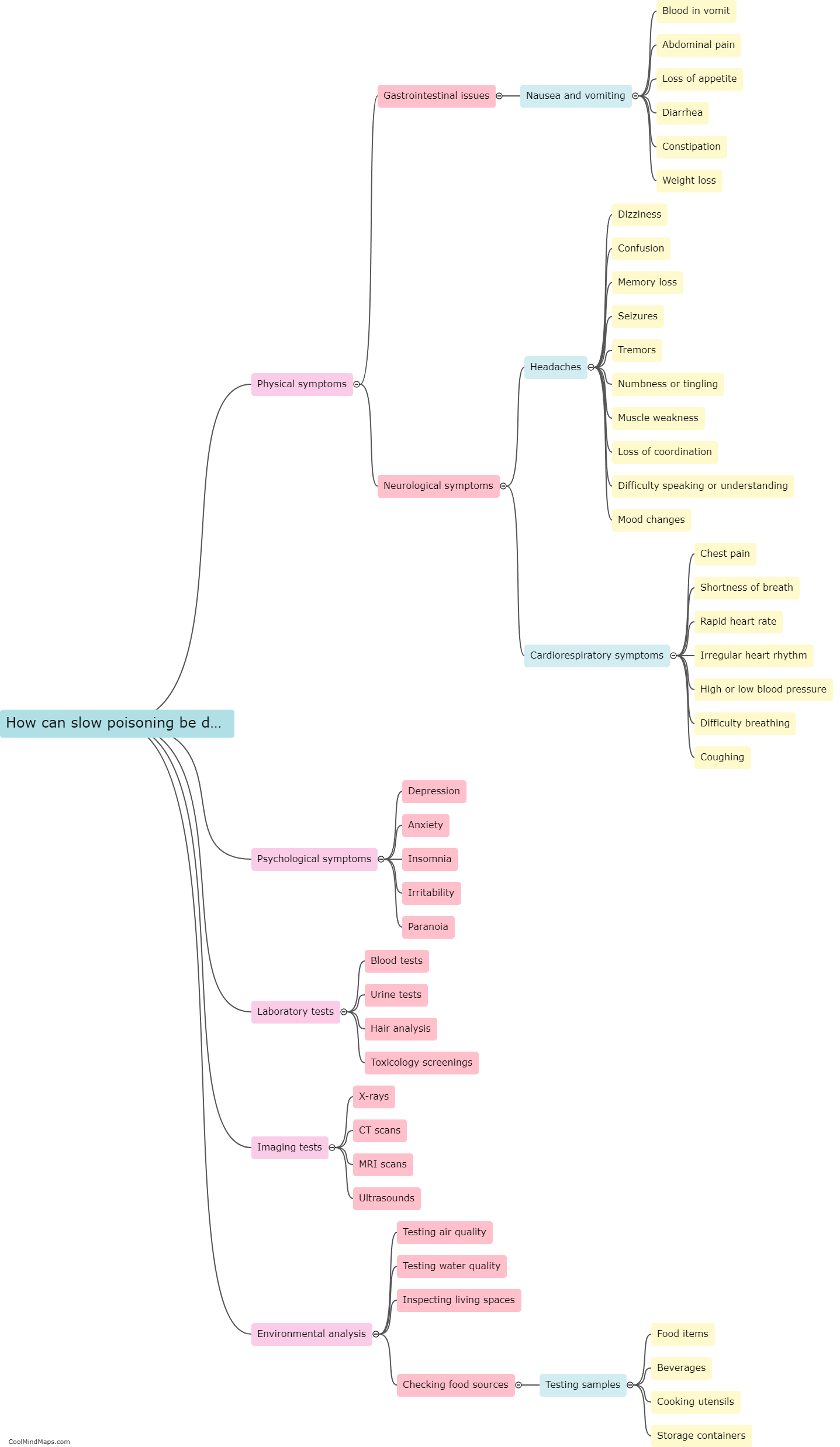
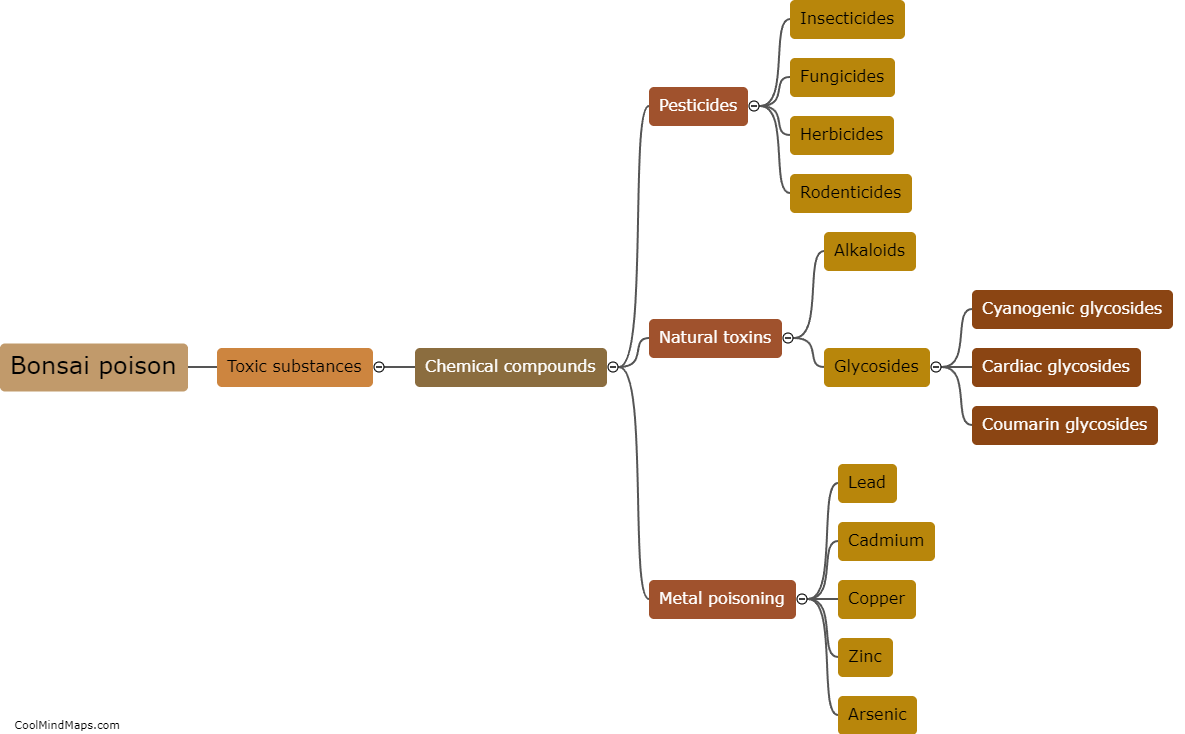
Slow poison refers to the gradual ingestion of toxic substances that can have harmful effects on the body over an extended period. Unlike acute poisoning, which occurs immediately after exposure to a high dose of poison, slow poisoning occurs when toxins build up in the body over time. Slow poison can negatively affect various biological systems and organs, leading to a range of symptoms and health issues. Depending on the type of poison and the length and intensity of exposure, common effects may include chronic fatigue, respiratory problems, liver and kidney damage, gastrointestinal issues, neurological disorders, immune system dysfunction, and even an increased risk of developing cancers. The body's ability to detoxify and eliminate these toxins is often overwhelmed, resulting in long-term consequences on overall health and well-being.
This mind map was published on 19 December 2023 and has been viewed 76 times.