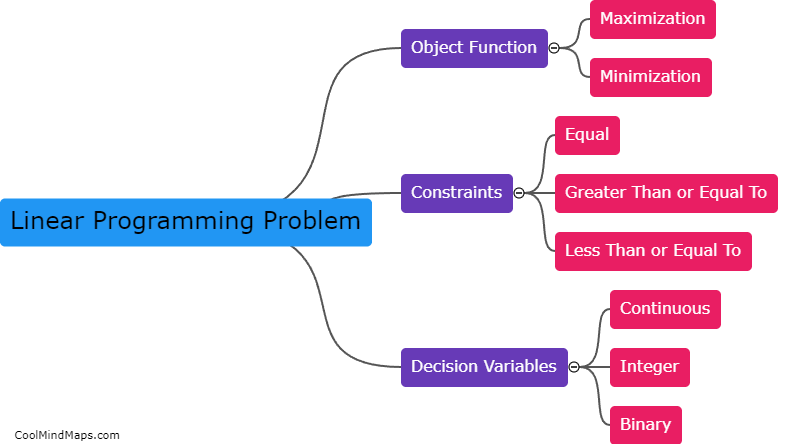
What are the components of a linear programming problem?
A linear programming problem consists of three main components: the objective function, the constraints, and the decision variables. The objective function represents the goal of the problem, such as maximizing profit or minimizing costs. The constraints are limitations on the decision variables, such as production capacity or available resources. The decision variables are the unknown quantities that need to be determined, such as the number of units to produce or the amount of resources used. Linear programming problems can be modeled mathematically using these components to find the optimal solution that satisfies all constraints while maximizing or minimizing the objective function.
This mind map was published on 16 May 2023 and has been viewed 100 times.