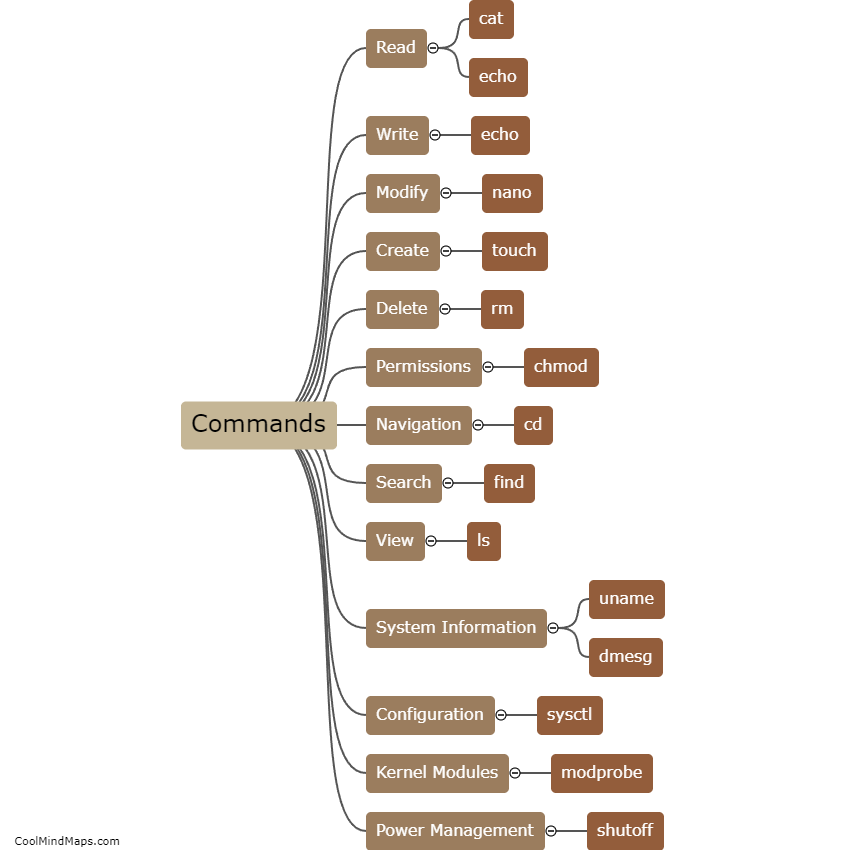
How do antibodies recognize and bind to antigens?
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system to detect and neutralize foreign substances called antigens. The recognition and binding process between antibodies and antigens is highly specific and essential for an effective immune response. Antibodies possess a specific binding site called the antigen-binding site, which corresponds to the unique shape of the antigen. This binding site comprises a variable region that can recognize and fit with the distinct structure of an antigen. The interaction occurs through multiple non-covalent bonds, such as hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and electrostatic interactions. The exquisite fit between antibodies and antigens allows antibodies to recognize a wide array of foreign substances, including toxins, viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens. Once bound, antibodies can activate various immune responses, such as neutralizing the antigen directly, attracting other immune cells to destroy it, or tagging it for elimination. The incredible specificity and versatility of antibodies in recognizing and binding to antigens are vital for the body's defense against harmful invaders.
This mind map was published on 2 January 2024 and has been viewed 91 times.