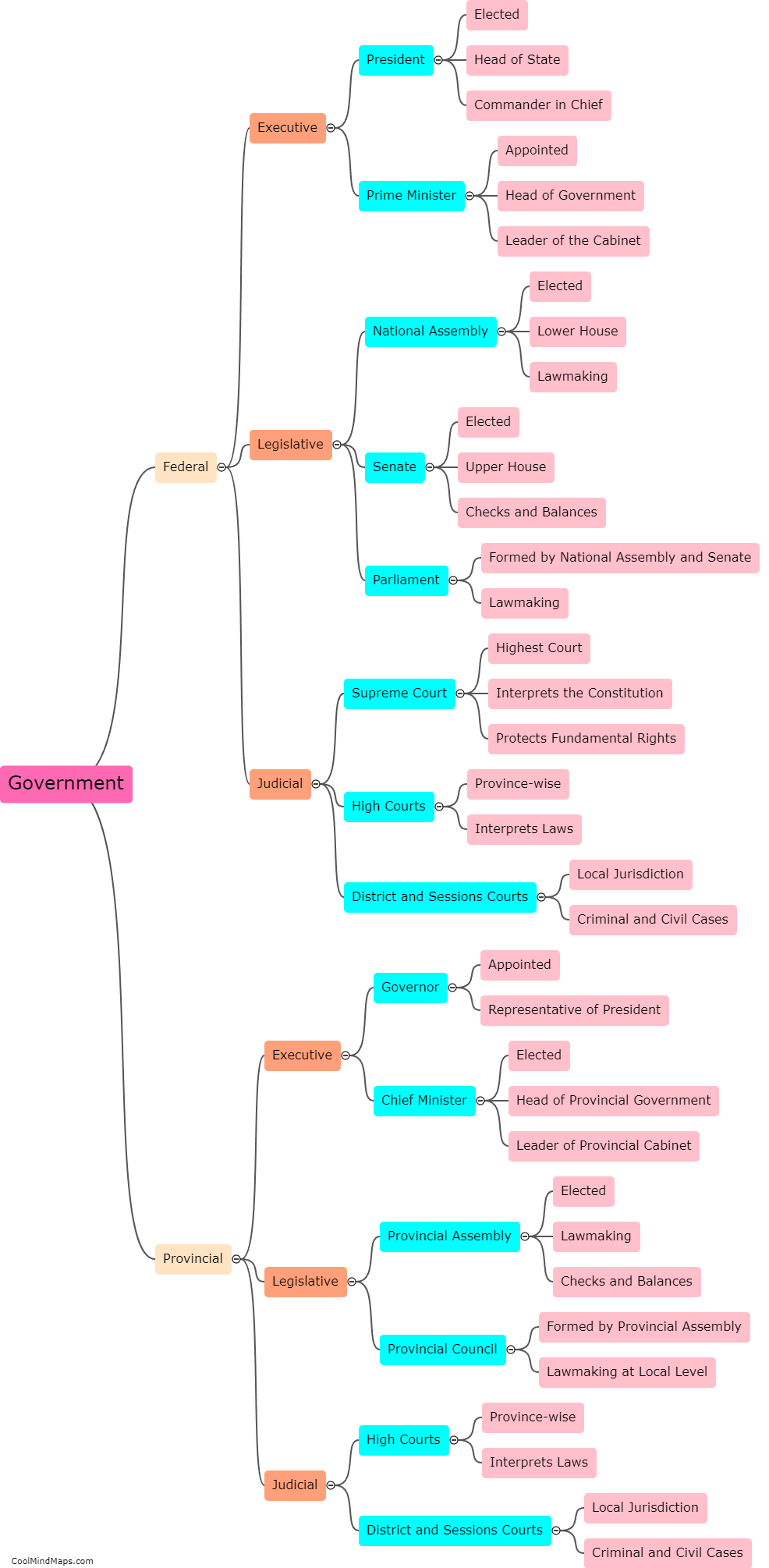
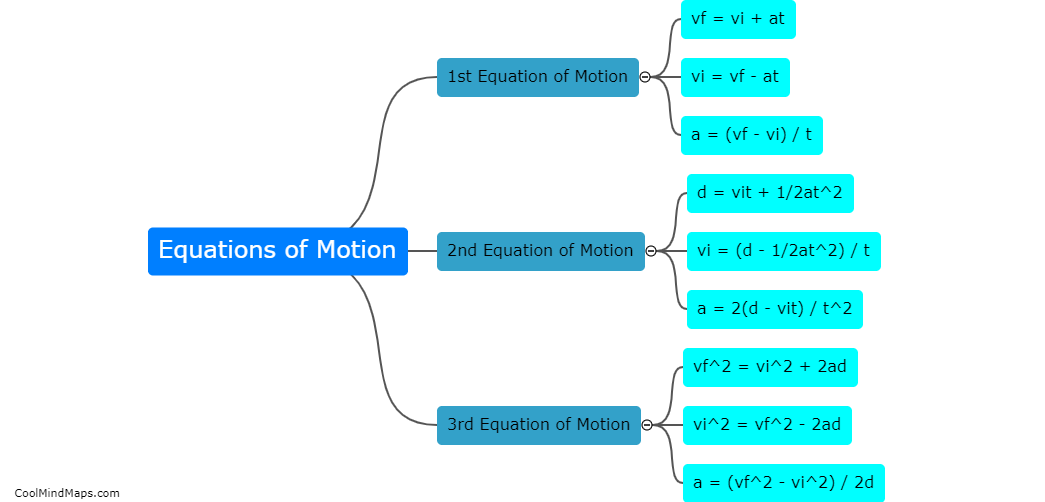
What are the equations of motion in Galileo's theory?
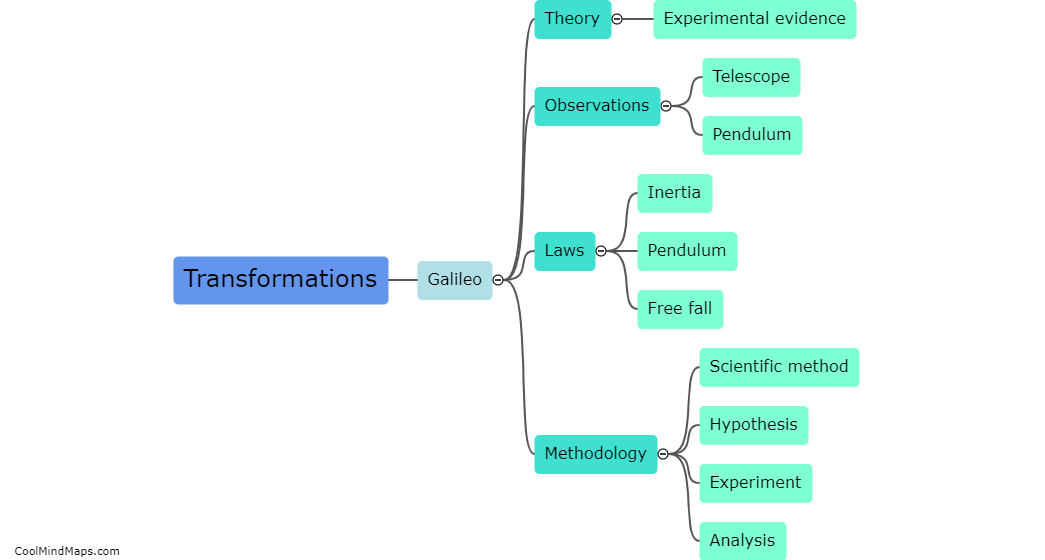
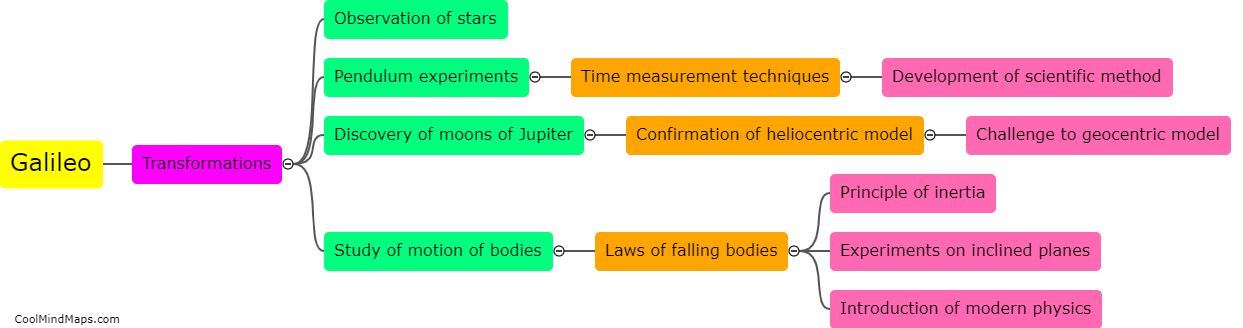
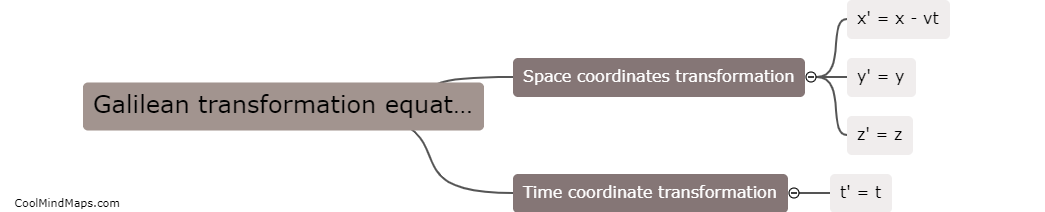
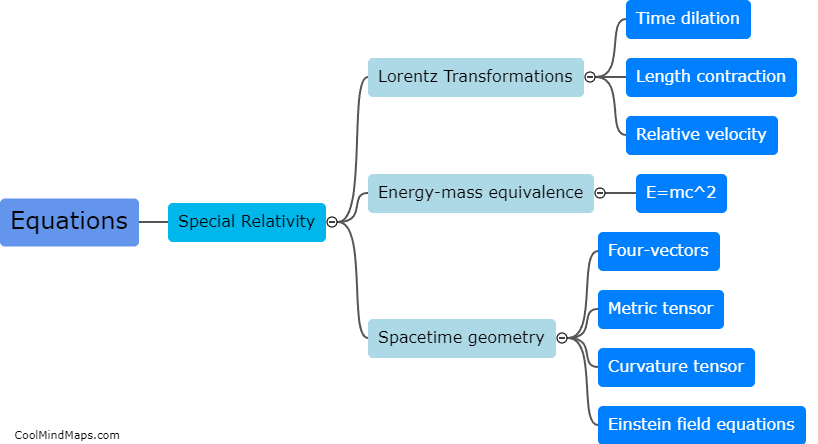
In Galileo's theory, the equations of motion explain how objects move under the influence of gravity and other forces. Galileo proposed that objects fall to the ground at the same rate regardless of their mass, revolutionizing our understanding of gravity. He derived the equation of motion for a freely falling object, stating that the distance traveled by an object in free fall is directly proportional to the square of the time it takes to fall. This equation, known as the equation of motion for uniform acceleration, is given as y = 1/2gt^2, where y is the distance, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and t is the time. It is worth noting that Galileo's theory only considered motion in a vacuum, neglecting air resistance. Nonetheless, his equations laid the foundation for further advancements in the field of physics.
This mind map was published on 5 October 2023 and has been viewed 103 times.