How do drosophila perceive and detect pheromones?
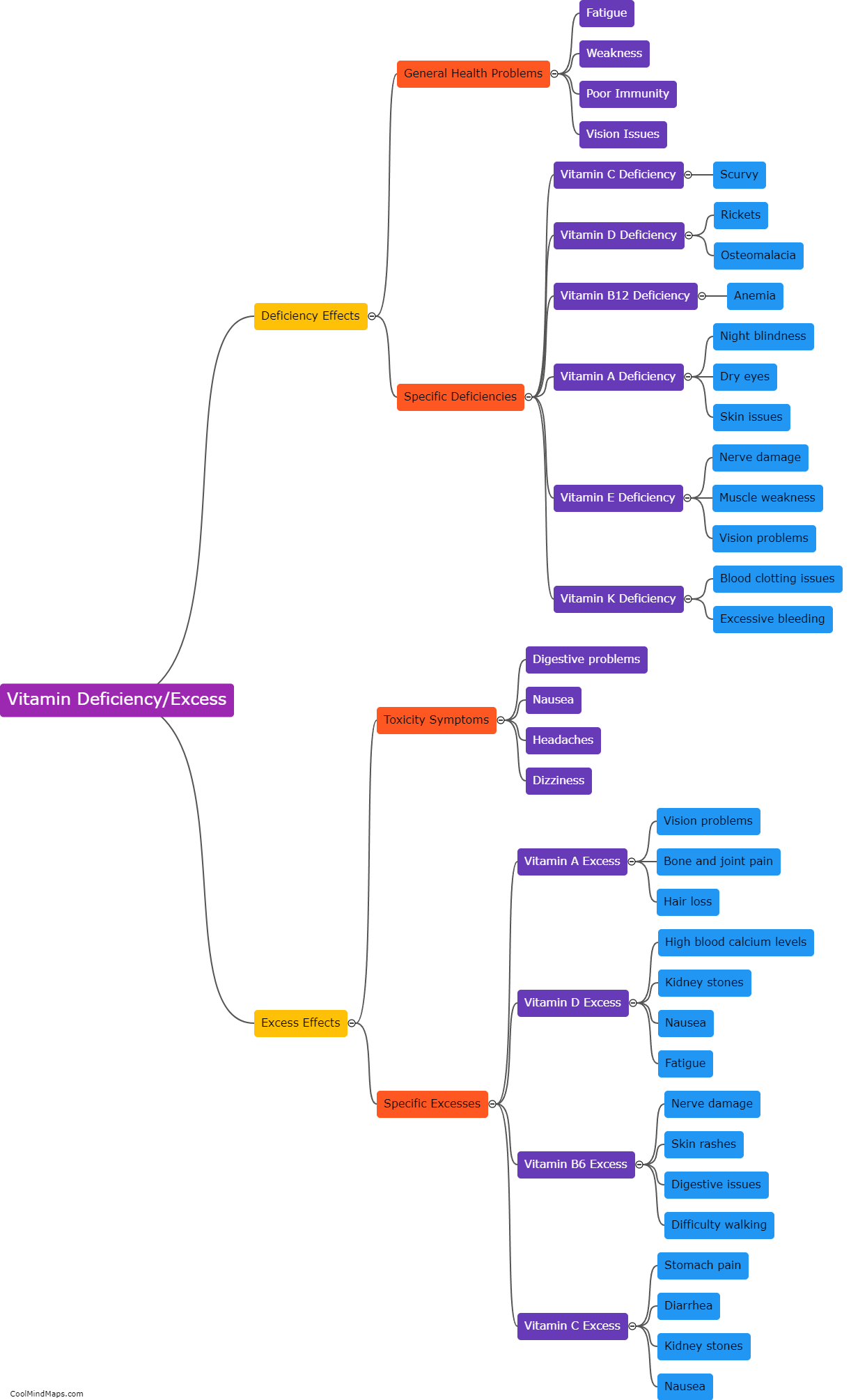
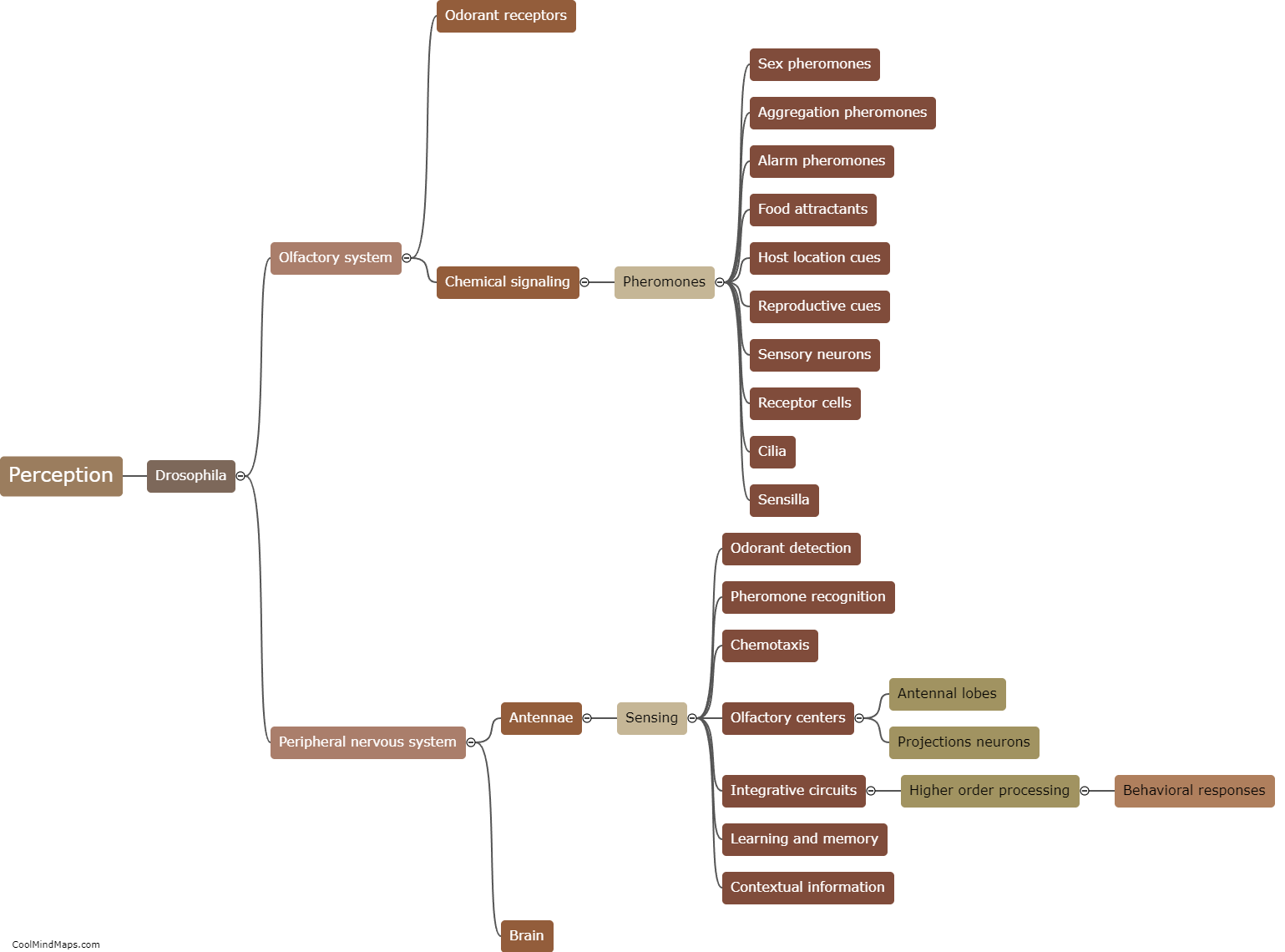
Drosophila, commonly known as fruit flies, are highly adept at perceiving and detecting pheromones, which are chemical signals used for different forms of communication between individuals. The perception and detection of pheromones in Drosophila involve a complex process. Firstly, odorant receptors located on the sensory neurons in their antennae play a crucial role in detecting pheromones. These receptors are activated when specific pheromone molecules bind to them, triggering various signaling pathways within the sensory neurons. This activation results in the transmission of electrical signals to the brain, where further processing and interpretation of the pheromone information takes place. Drosophila also possess specialized neurons called pheromone-sensing neurons that specifically respond to certain pheromones, indicating a level of specificity in their detection system. Overall, the abilities of Drosophila to perceive and detect pheromones demonstrate the remarkable sophistication of their olfactory system and their reliance on these chemical cues for social interactions and mating behaviors.
This mind map was published on 19 September 2023 and has been viewed 97 times.