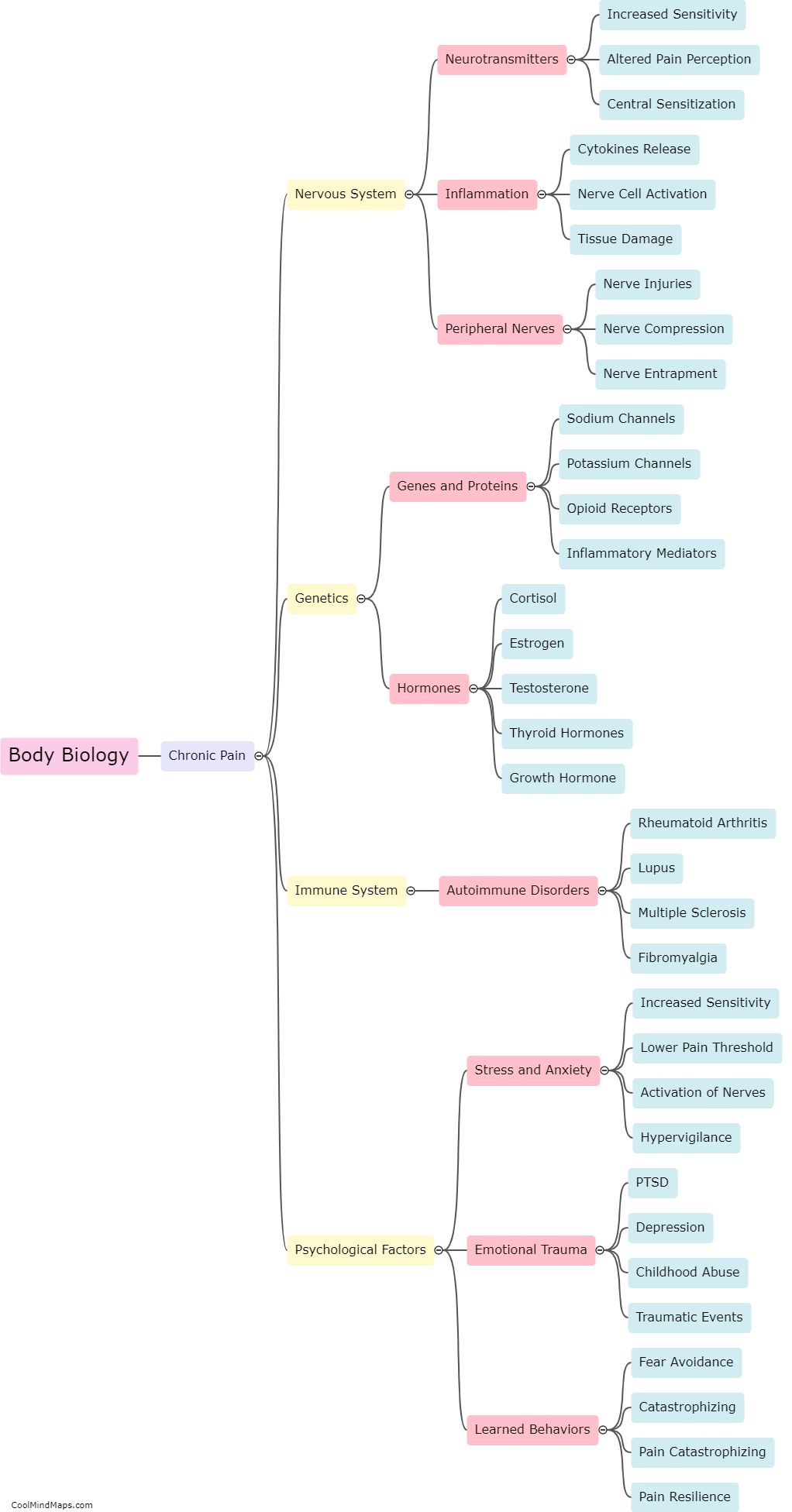
How does the biology of the body contribute to chronic pain?
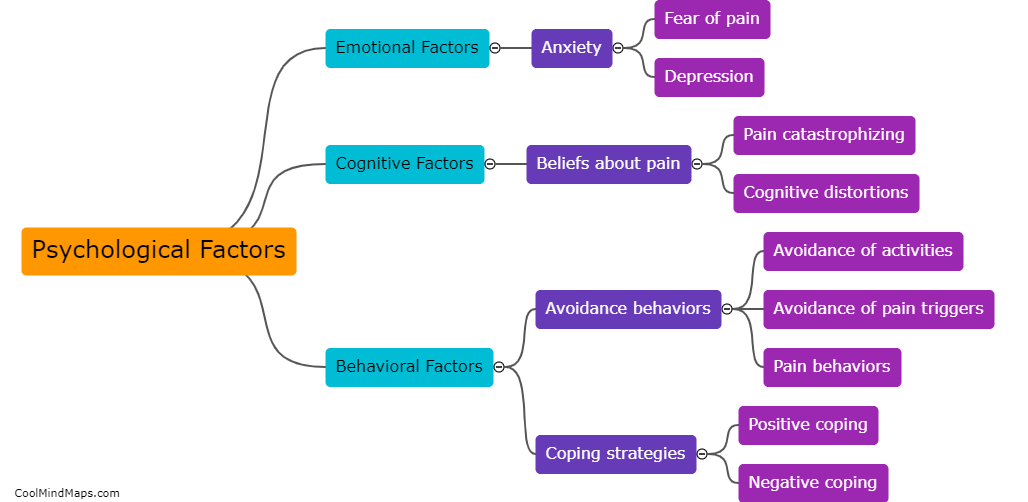
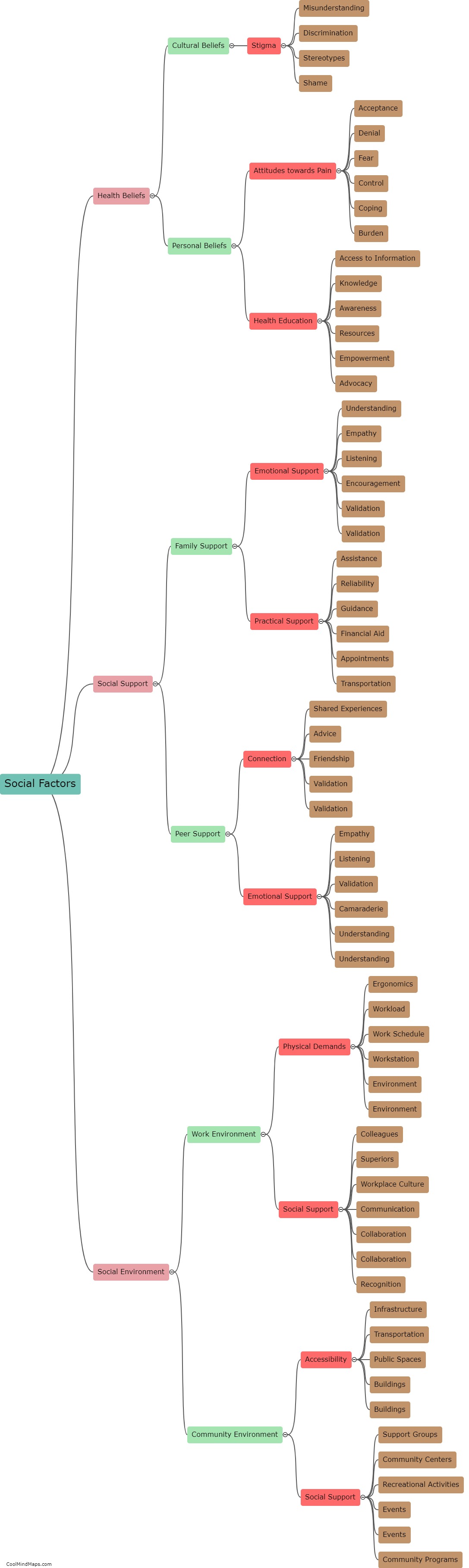
Chronic pain, a persistent and debilitating condition, is influenced by various factors, including the biology of the body. The human body has a complex network of nerves, tissues, and cells that play a crucial role in the perception and transmission of pain. When an injury or illness occurs, specialized nerve cells called nociceptors detect the painful stimuli and transmit signals to the brain. However, in cases of chronic pain, these nerve cells can become hyperactive, sending continuous pain signals even when the initial cause of pain has resolved. Additionally, chronic pain can also arise due to changes in the structure and function of the nervous system, such as an increase in the number of pain receptors or alterations in the release and reception of neurotransmitters. Such biological processes contribute to the persistence and amplification of pain, making chronic pain a multidimensional issue that requires comprehensive management approaches.
This mind map was published on 2 December 2023 and has been viewed 88 times.