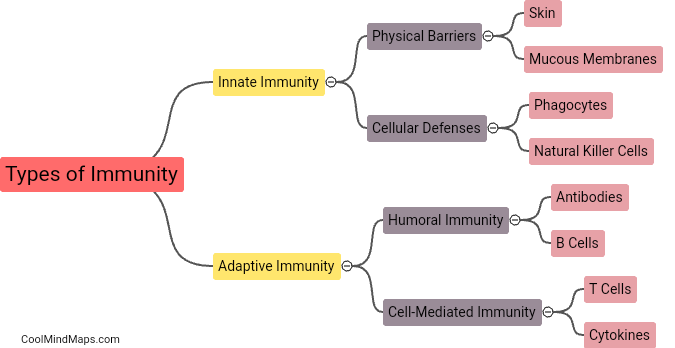
What are the different types of immunity?
Immunity refers to the body's ability to defend itself against harmful pathogens or substances that could cause diseases. There are two main types of immunity: innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity, also known as natural or non-specific immunity, is the first line of defense and provides immediate protection against a wide range of pathogens. It includes physical barriers like the skin, mucous membranes, and chemicals like stomach acid and enzymes. On the other hand, adaptive immunity, also known as acquired or specific immunity, develops over time in response to specific pathogens. It involves specialized cells, such as T and B lymphocytes, which produce specific antibodies or immune response mechanisms to target and eliminate pathogens. Adaptive immunity provides long-term protection and can also create immunological memory, allowing the body to recognize and mount a faster response to repeat exposures of the same pathogen.
This mind map was published on 25 January 2024 and has been viewed 78 times.