How does the central bank control money supply?
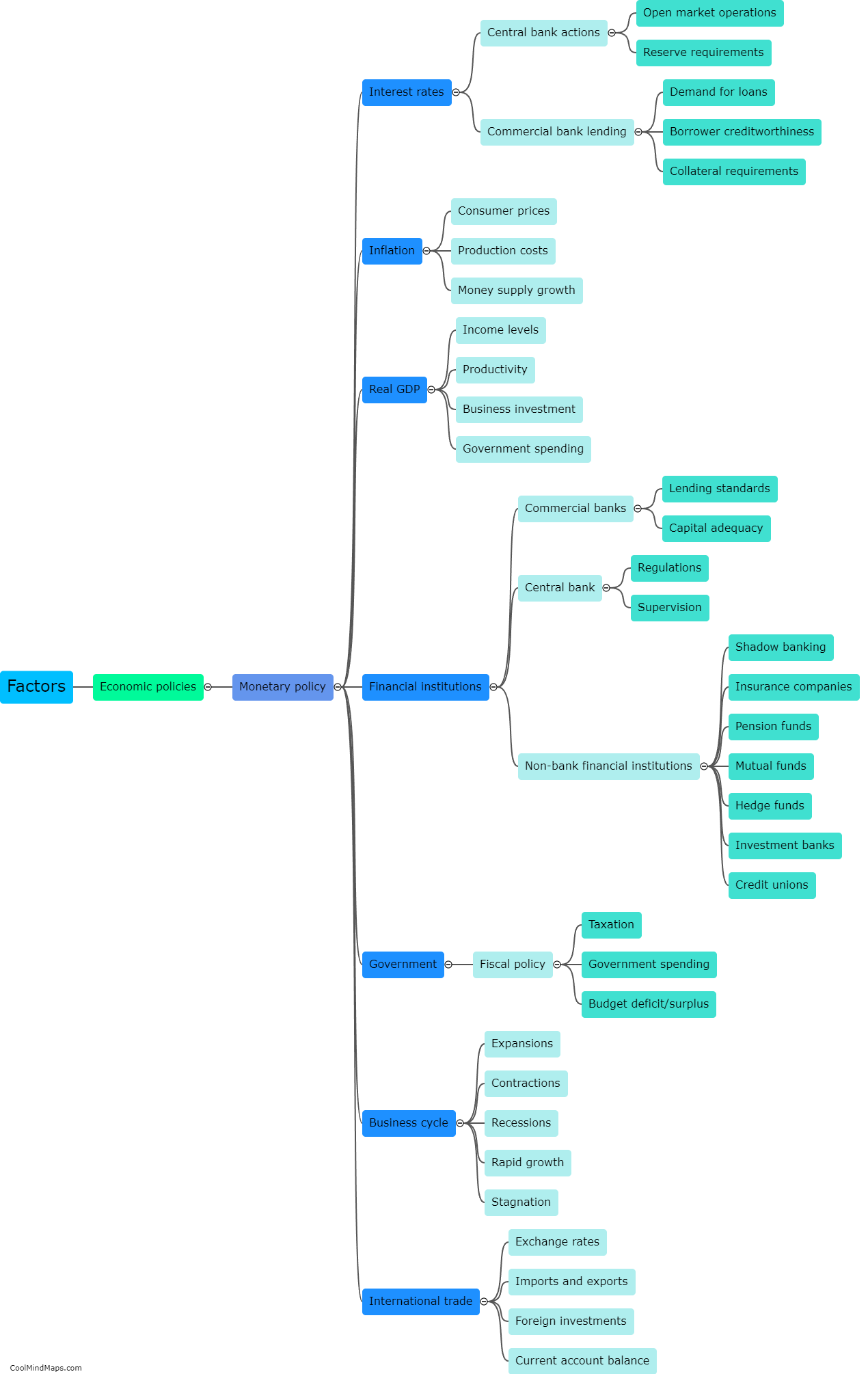
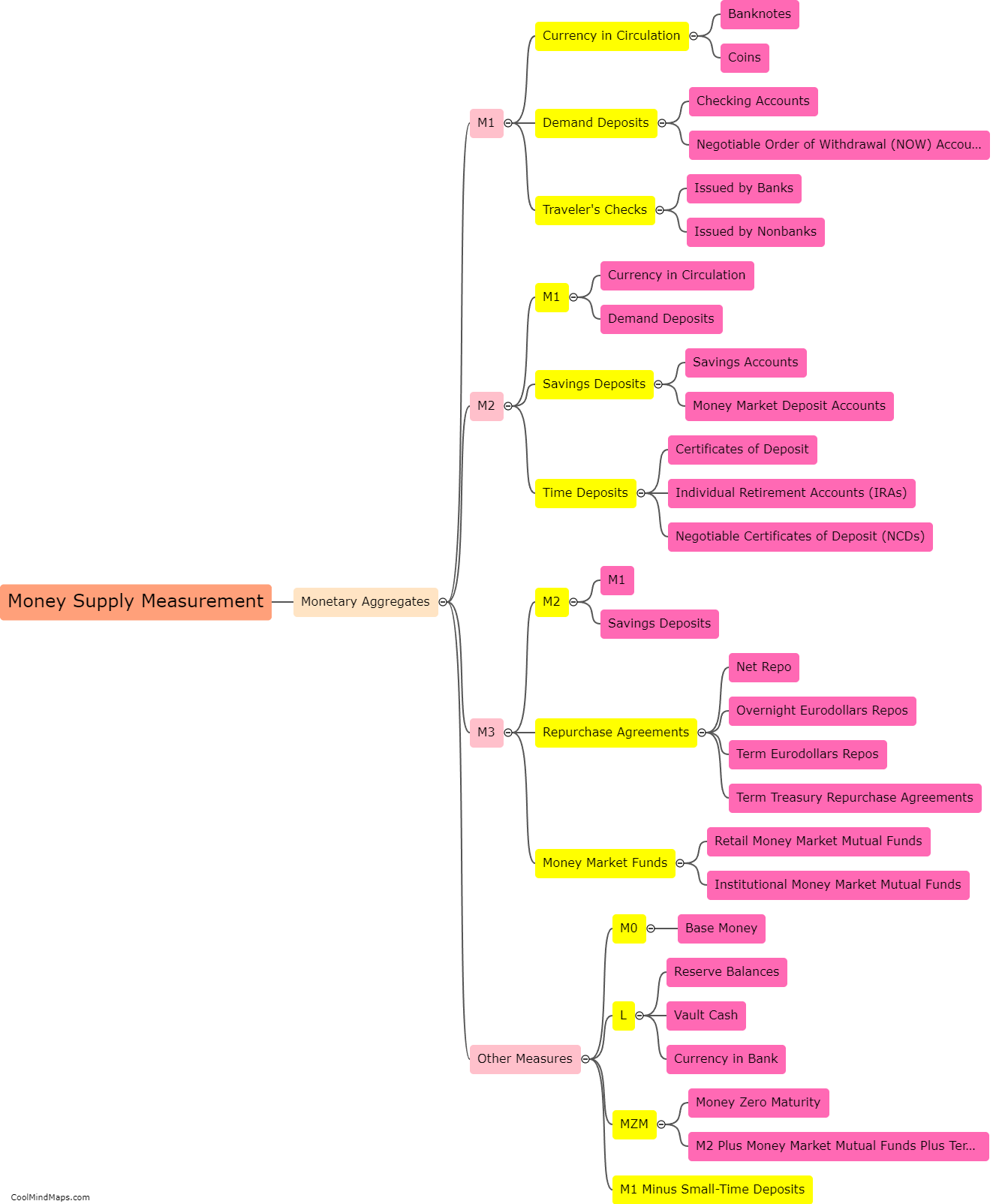
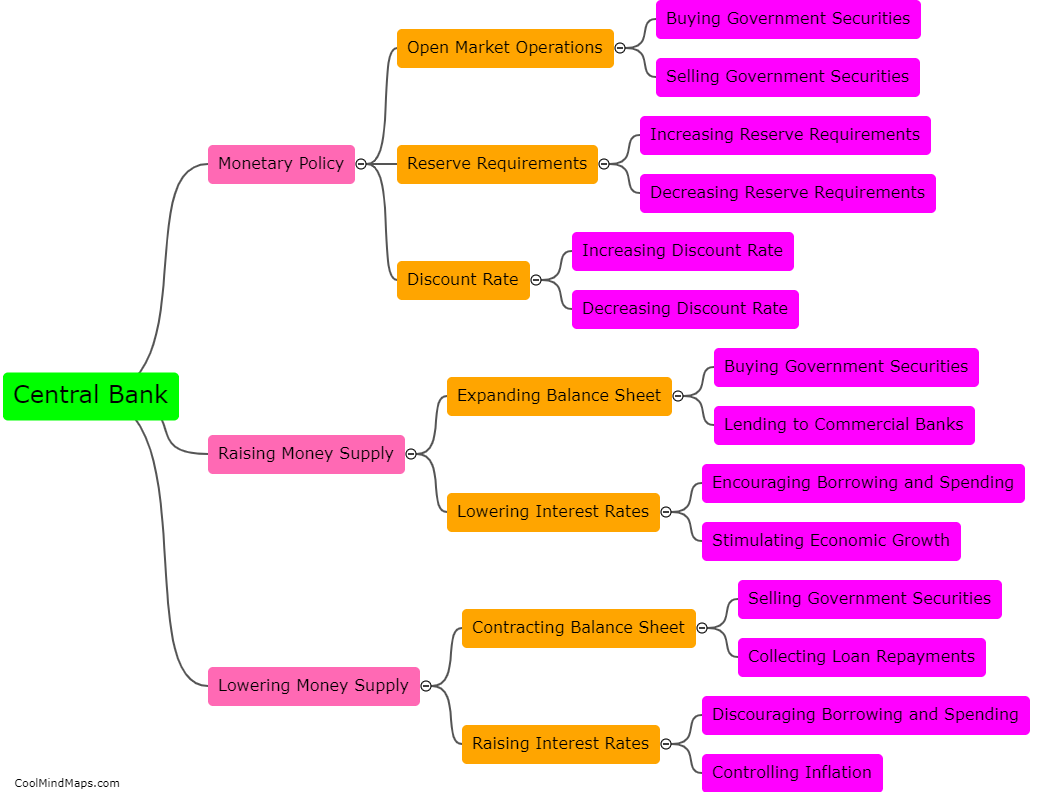
The central bank controls money supply through various tools and mechanisms. One of the key ways is through open market operations, where the central bank buys or sells government securities, such as bonds, to commercial banks and other financial institutions. By purchasing these securities, the central bank injects money into the economy, increasing the money supply, and vice versa. Another method is through reserve requirements, where the central bank sets a certain percentage of deposits that commercial banks must hold as reserves. By increasing or decreasing these requirements, the central bank can influence the ability of banks to lend and create money. Additionally, the central bank can use the policy interest rate as a tool to influence money supply. By raising or lowering this rate, the central bank can control the cost of borrowing, which in turn affects the level of lending and spending in the economy. These measures are employed by the central bank to ensure price stability, manage inflation, and stimulate or slow down economic growth.
This mind map was published on 17 September 2023 and has been viewed 107 times.