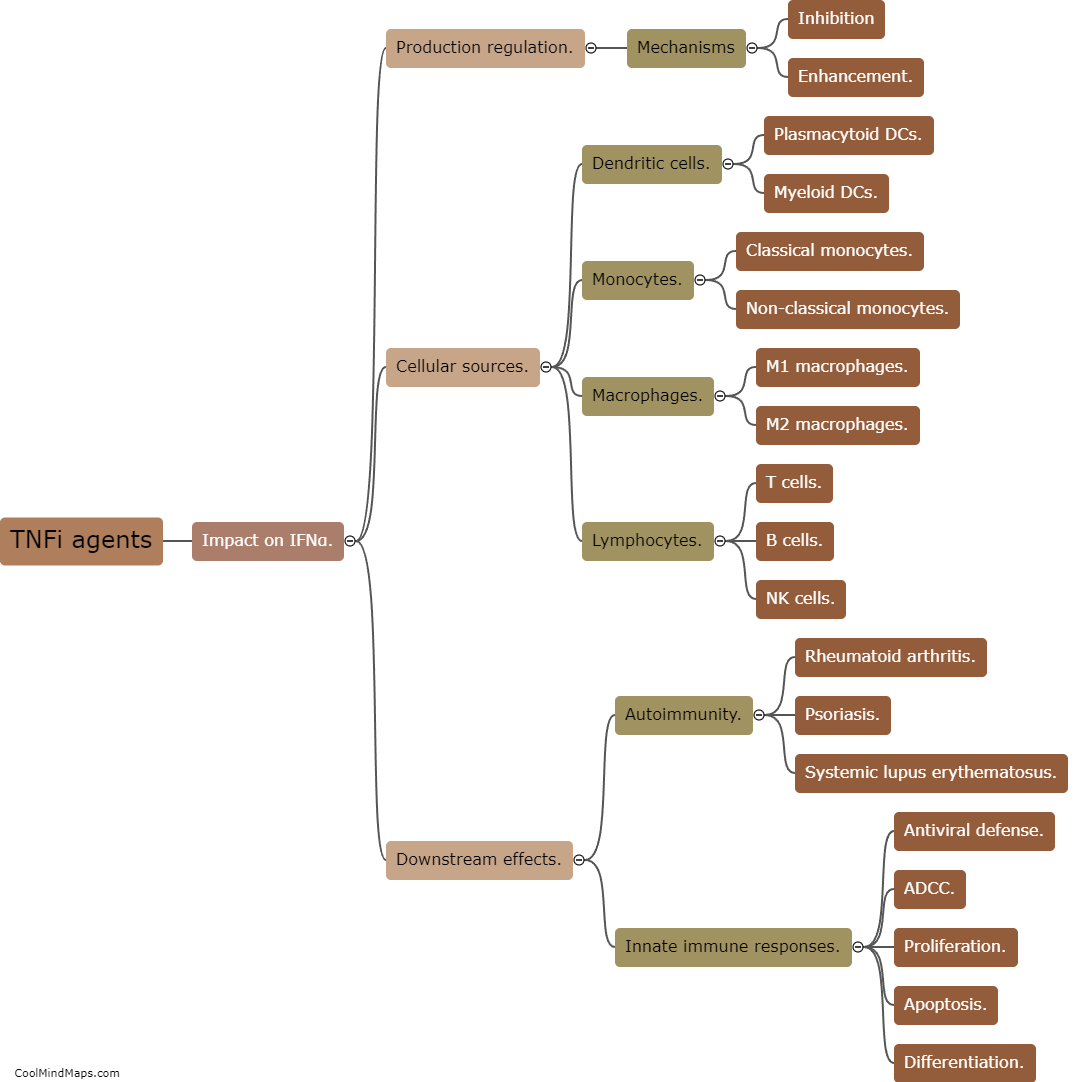
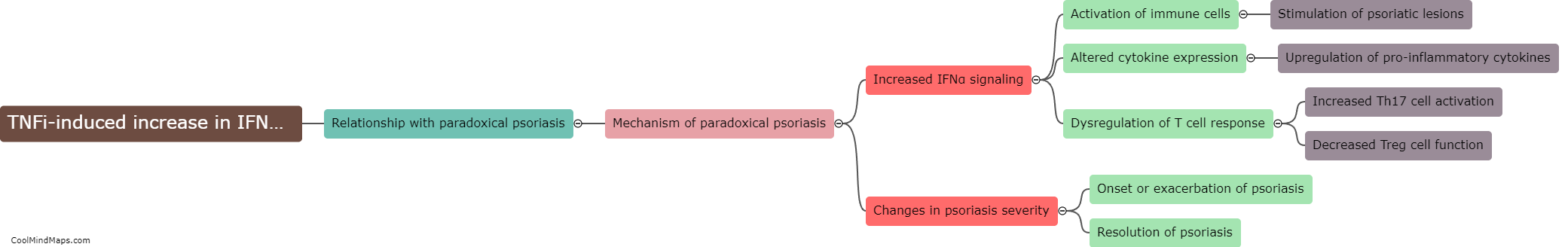
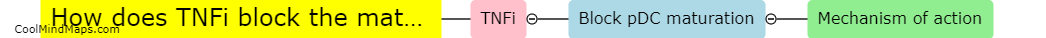How do TNF inhibitors affect pDC maturation?
TNF inhibitors, such as adalimumab or infliximab, are widely used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis due to their ability to suppress inflammation caused by excessive TNF production. These inhibitors not only target TNF but can also influence other immune cells, including plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). pDCs are a specialized subset of dendritic cells that play a crucial role in the regulation of immune responses. TNF inhibitors have been observed to modulate pDC maturation, affecting their function and phenotype. The precise mechanisms by which TNF inhibitors influence pDC maturation are not fully understood, but studies suggest that they can impair the ability of pDCs to produce type I interferons, a crucial antiviral pathway, which may contribute to their immunosuppressive effects. Further research is needed to elucidate the specific mechanisms and consequences of TNF inhibitor-mediated effects on pDC maturation.
This mind map was published on 13 July 2023 and has been viewed 111 times.