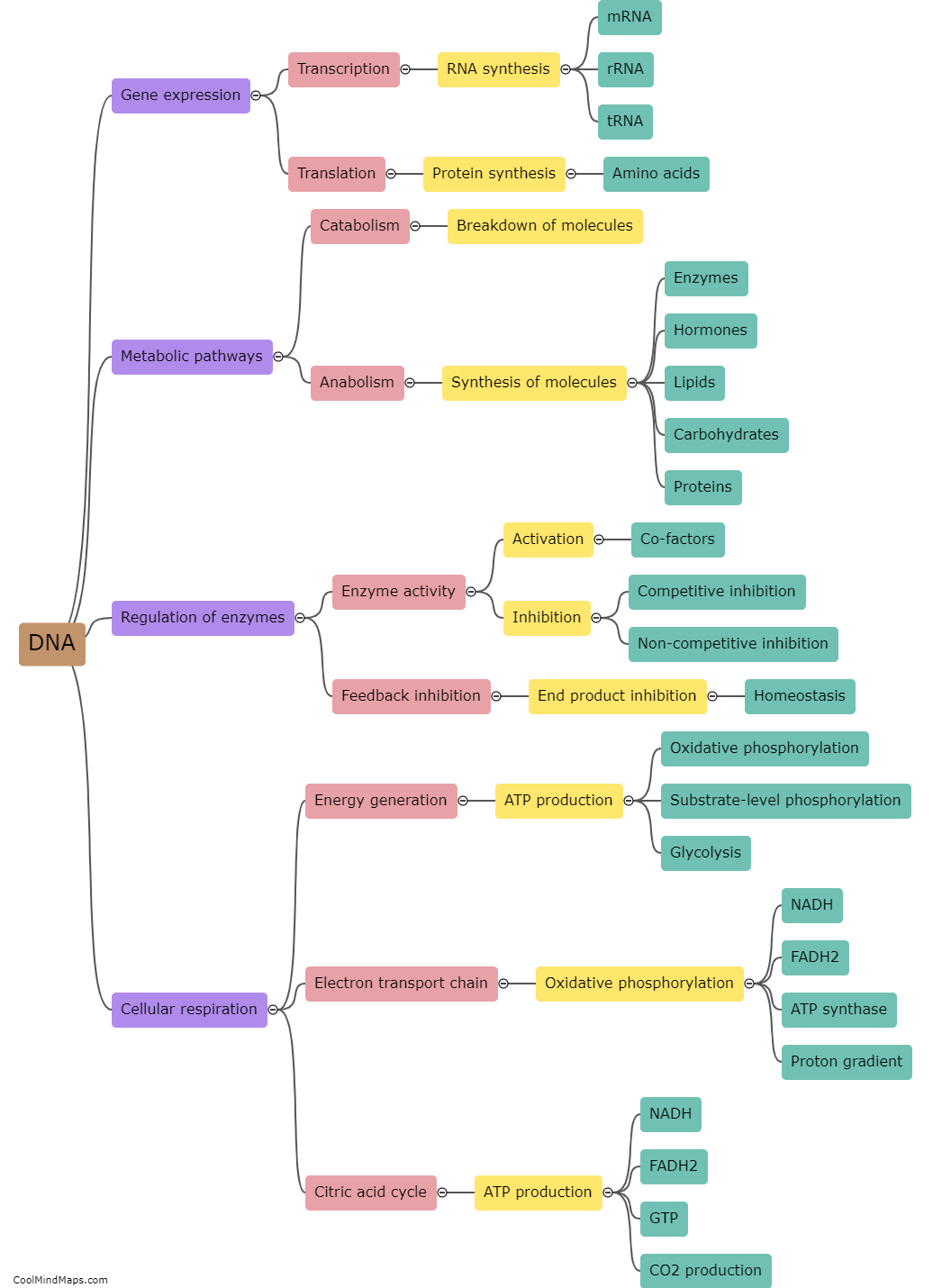
How does DNA contribute to metabolism?
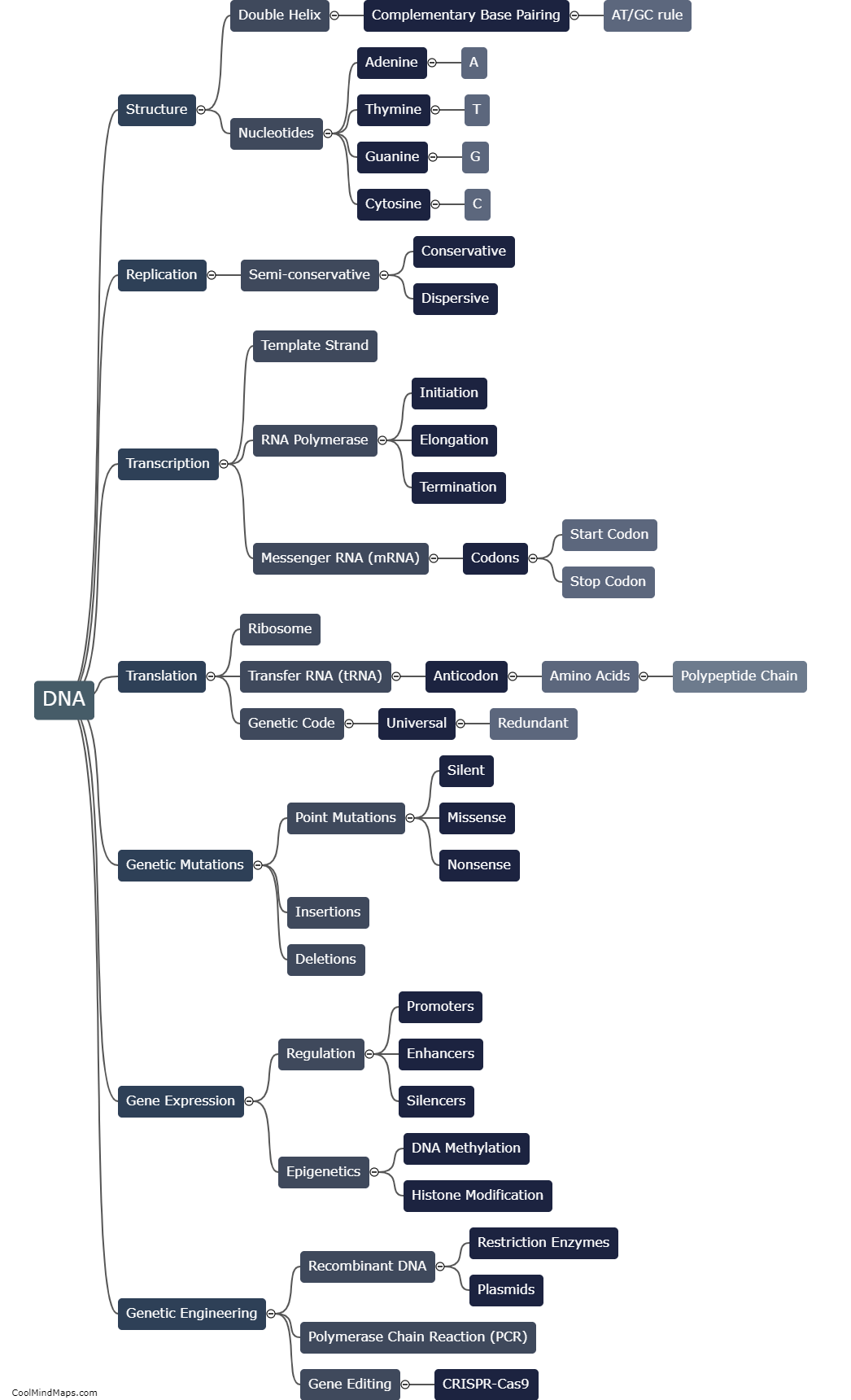
DNA is essential for metabolism as it plays a crucial role in providing the instructions required for the synthesis of enzymes and other proteins involved in metabolic processes. Genes, which are sections of DNA, contain the codes for specific proteins that are responsible for catalyzing chemical reactions within cells. These proteins, called enzymes, are involved in various metabolic pathways, including the breakdown of nutrients, energy production, and the synthesis of molecules necessary for cell functioning. DNA acts as the blueprint for the production of these enzymes, ensuring that the necessary proteins are synthesized in the correct quantities and at the appropriate times to maintain optimal metabolic activity. In this way, DNA contributes to metabolism by regulating and controlling the various biochemical reactions that occur within cells.
This mind map was published on 22 November 2023 and has been viewed 104 times.