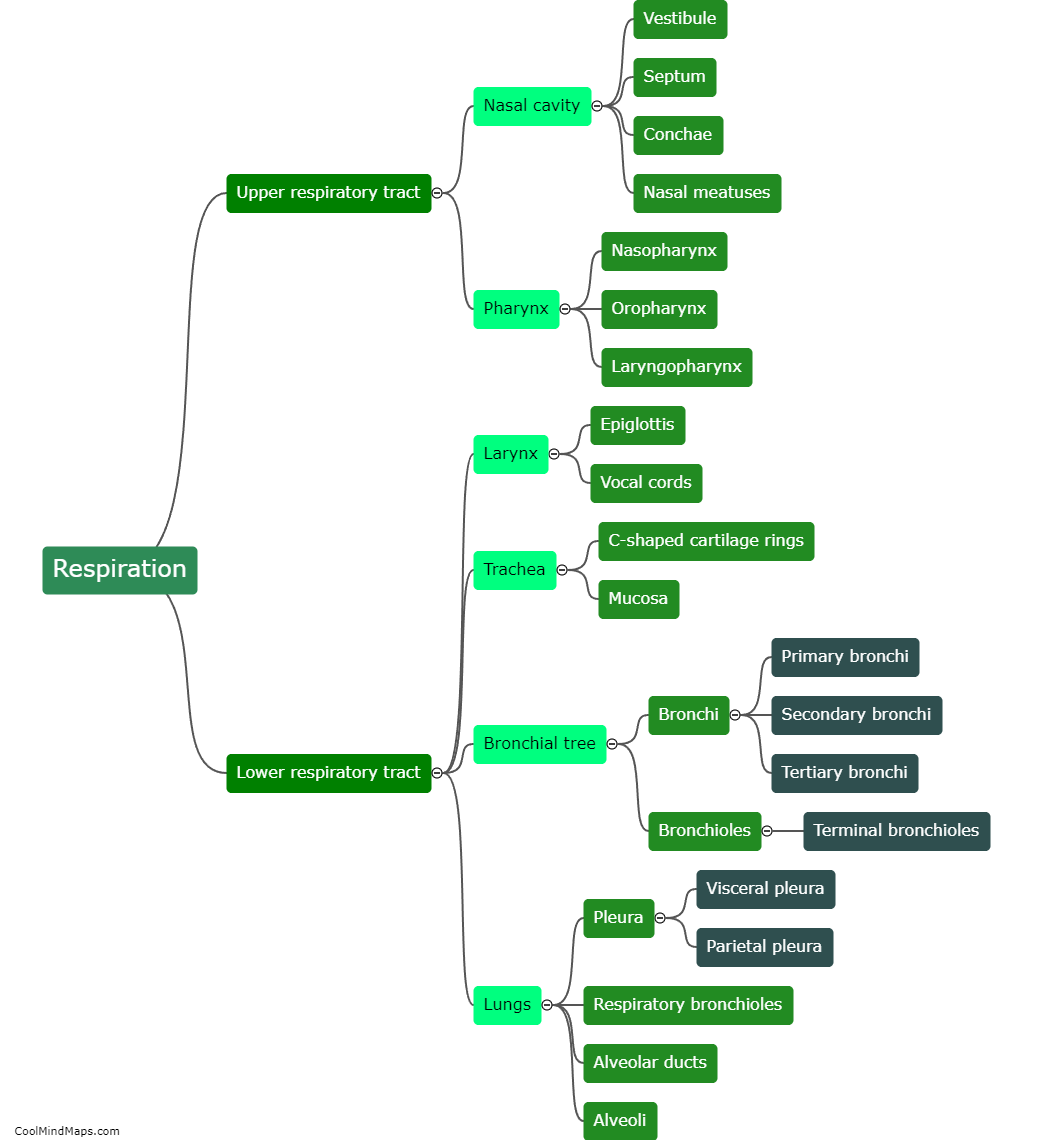
What are the main anatomical structures involved in respiration?
The main anatomical structures involved in respiration include the lungs, trachea, bronchi, and diaphragm. The lungs are the primary organs responsible for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. They consist of air sacs called alveoli where gas exchange takes place. The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, serves as the passage for air between the lungs and the outside environment. It is lined with tiny hair-like structures called cilia that help filter and remove foreign particles. The trachea branches into two bronchi, each leading to one lung. Finally, the diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the chest cavity. It contracts and relaxes during respiration, providing the necessary space for the lungs to expand and contract. Together, these anatomical structures coordinate to facilitate the vital process of respiration in humans.
This mind map was published on 8 August 2023 and has been viewed 162 times.