What is asexual reproduction in plants?
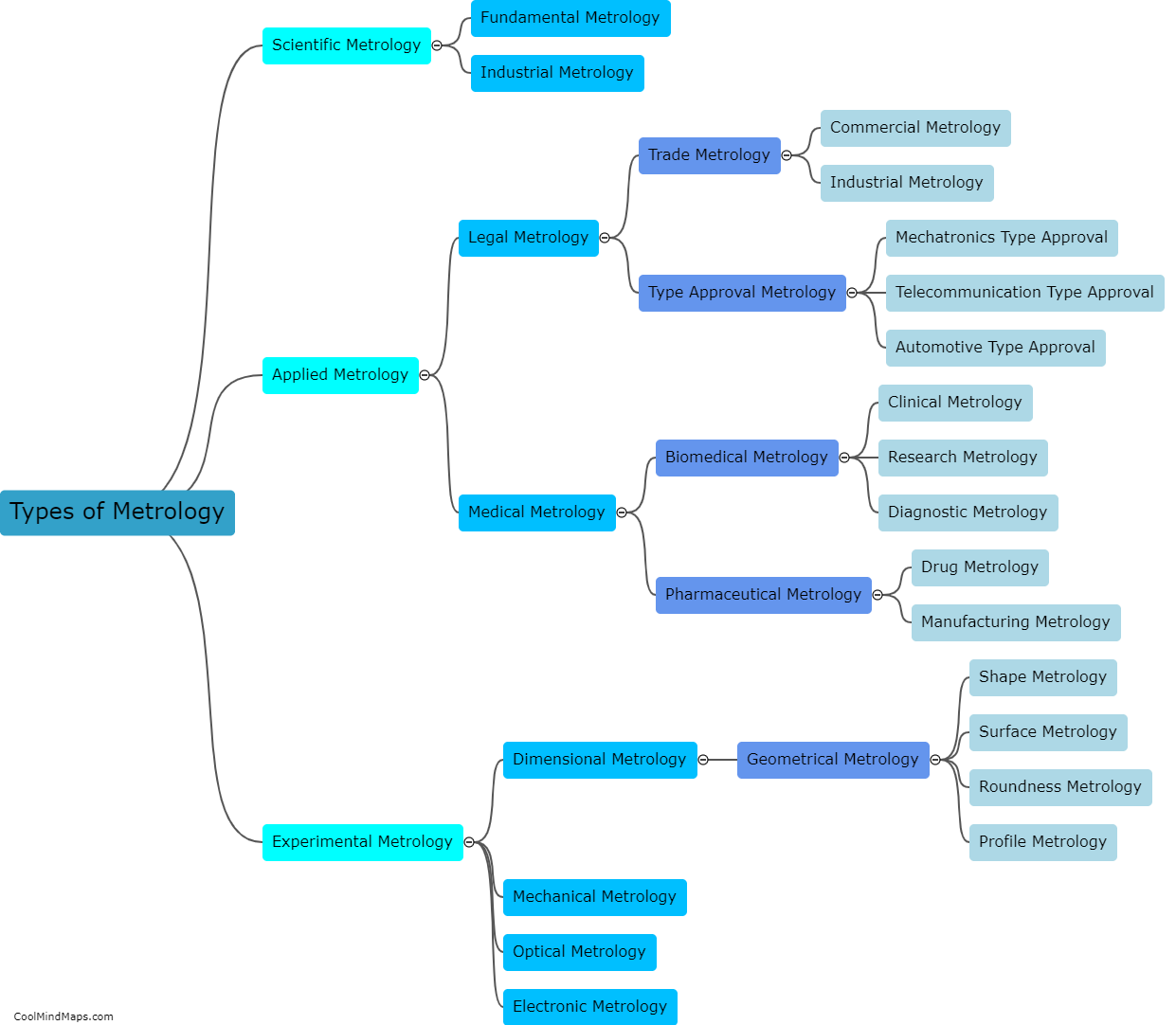
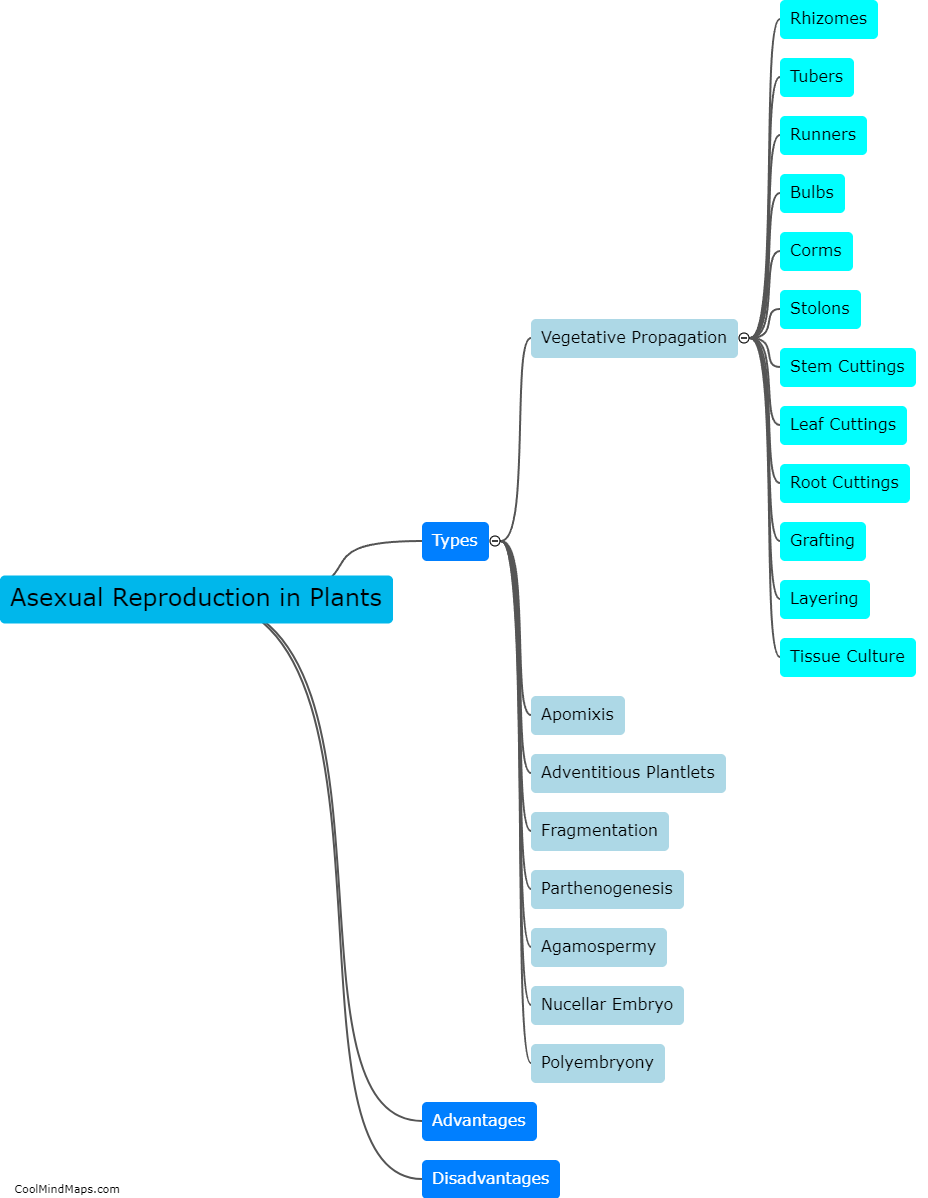
Asexual reproduction in plants refers to the process by which new plants are formed without the involvement of sexual reproduction, which typically requires the fusion of male and female gametes. In asexual reproduction, plants can create genetically identical offsprings through various mechanisms such as vegetative propagation, budding, fragmentation, and apomixis. This enables plants to rapidly and efficiently produce large numbers of new individuals with traits identical to their parent. Asexual reproduction is commonly observed in plants with specialized structures like bulbs, tubers, rhizomes, and runners, as well as in some plant species that can produce seeds without fertilization. This mode of reproduction allows plants to adapt to changing environments and colonize new areas without relying on external factors such as pollinators.
This mind map was published on 8 October 2023 and has been viewed 99 times.