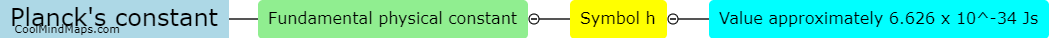How does DNS lookup work?
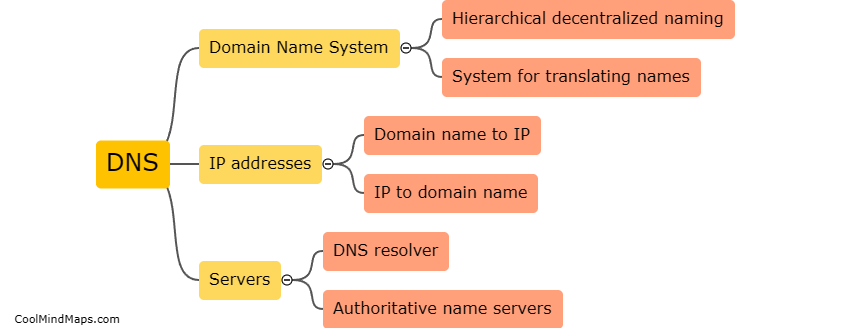
DNS lookup works by translating a human-readable domain name (such as example.com) into an IP address that computers can use to connect to the requested website or service. When a user enters a domain name into their web browser, the browser sends a request to a DNS resolver, which then queries a series of DNS servers to find the corresponding IP address. This process involves multiple steps, starting with a query to the root DNS servers, then to the authoritative DNS server for the domain, and finally returning the IP address to the user's browser. DNS lookup is essential for navigating the internet and accessing websites, email servers, and other online services.

This mind map was published on 13 July 2024 and has been viewed 70 times.