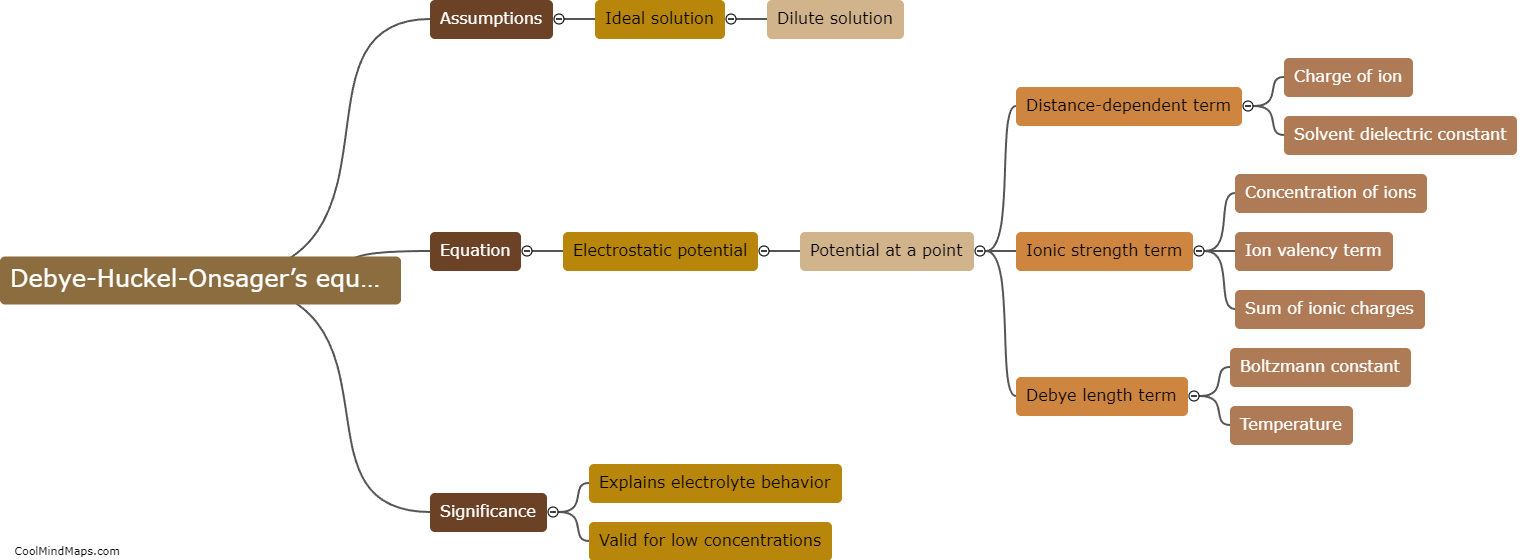
What is Debye-Huckel-Onsager’s equation?
Debye-Huckel-Onsager's equation is a mathematical equation used to describe the behavior of charged particles in a solution. It was developed by Peter Debye, Erich Huckel, and Lars Onsager in the early 20th century. The equation relates the concentration of ions in a solution to their activity coefficient, which accounts for the deviation of the behavior of these particles from idealized behavior. Specifically, the equation describes how the electrical charges of ions affect their interactions and diffusion in a solution, taking into account factors such as temperature and solvent properties. This equation has applications in various fields, including electrochemistry, biochemistry, and environmental science, helping to understand and predict the behavior of charged species in solution systems.

This mind map was published on 14 September 2023 and has been viewed 233 times.