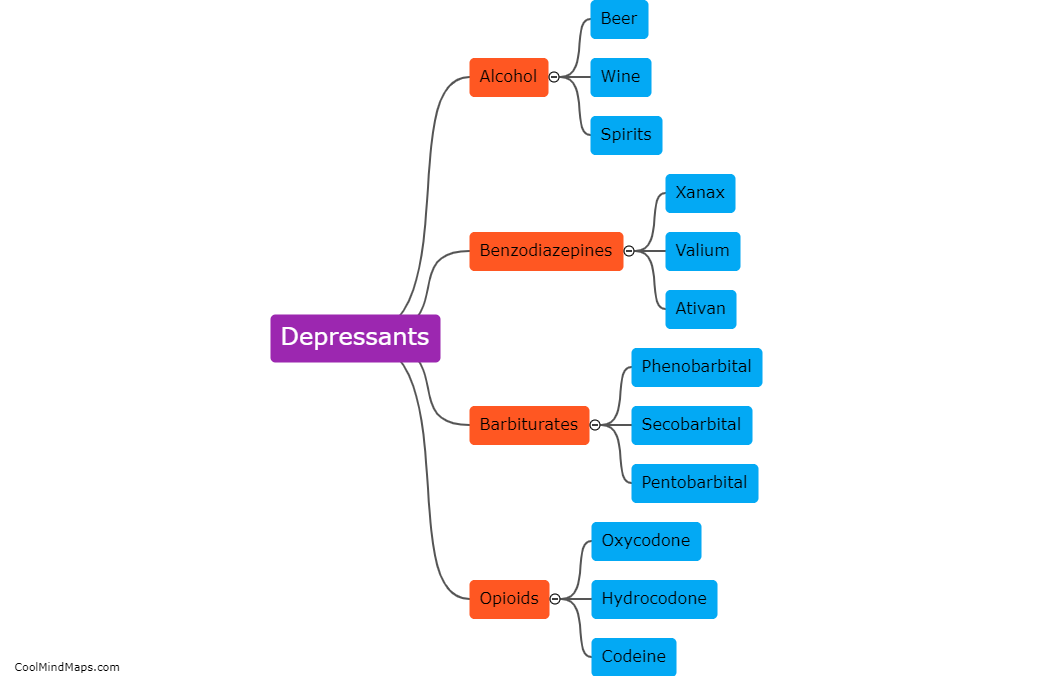
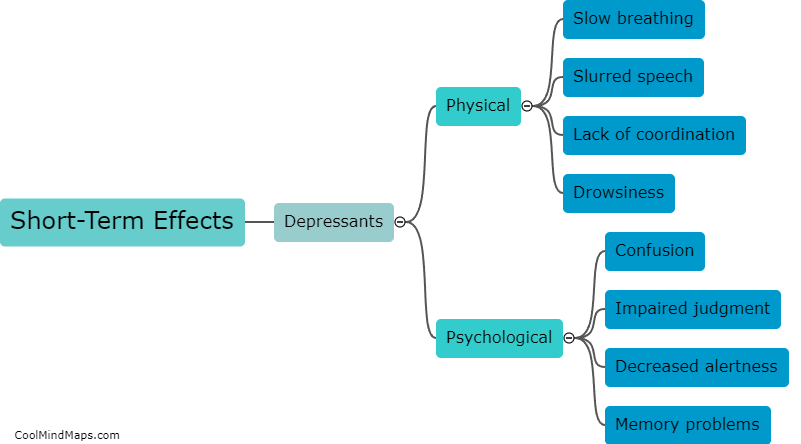
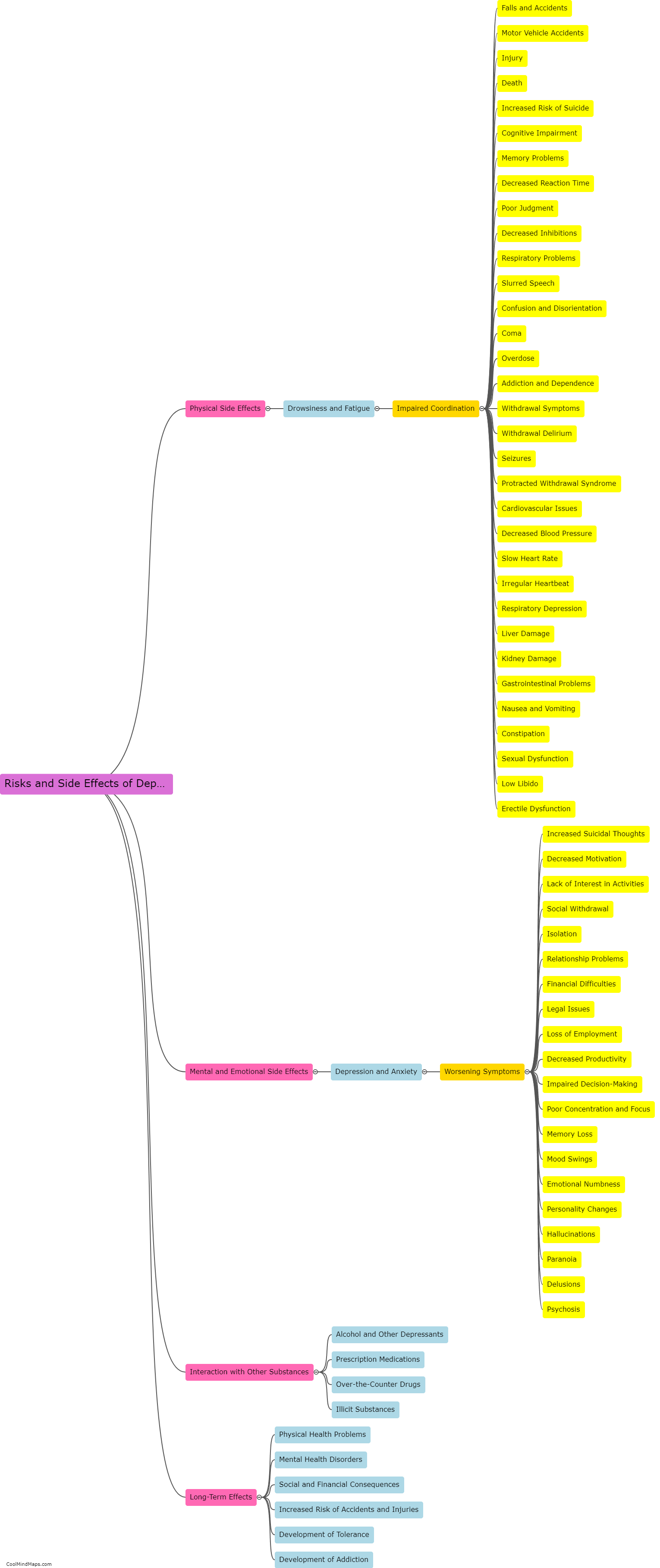
How do depressants affect the central nervous system?
Depressants, such as alcohol, benzodiazepines, and barbiturates, act on the central nervous system (CNS) by slowing down its activity. These substances enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that reduces the transmission of nerve signals throughout the CNS. By increasing the effects of GABA, depressants decrease the overall brain activity, leading to relaxation, sedation, and a slowdown of mental and physical processes. However, prolonged use or abuse of depressants can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to addiction, tolerance, and harmful effects on cognitive and motor functions.

This mind map was published on 6 December 2023 and has been viewed 89 times.