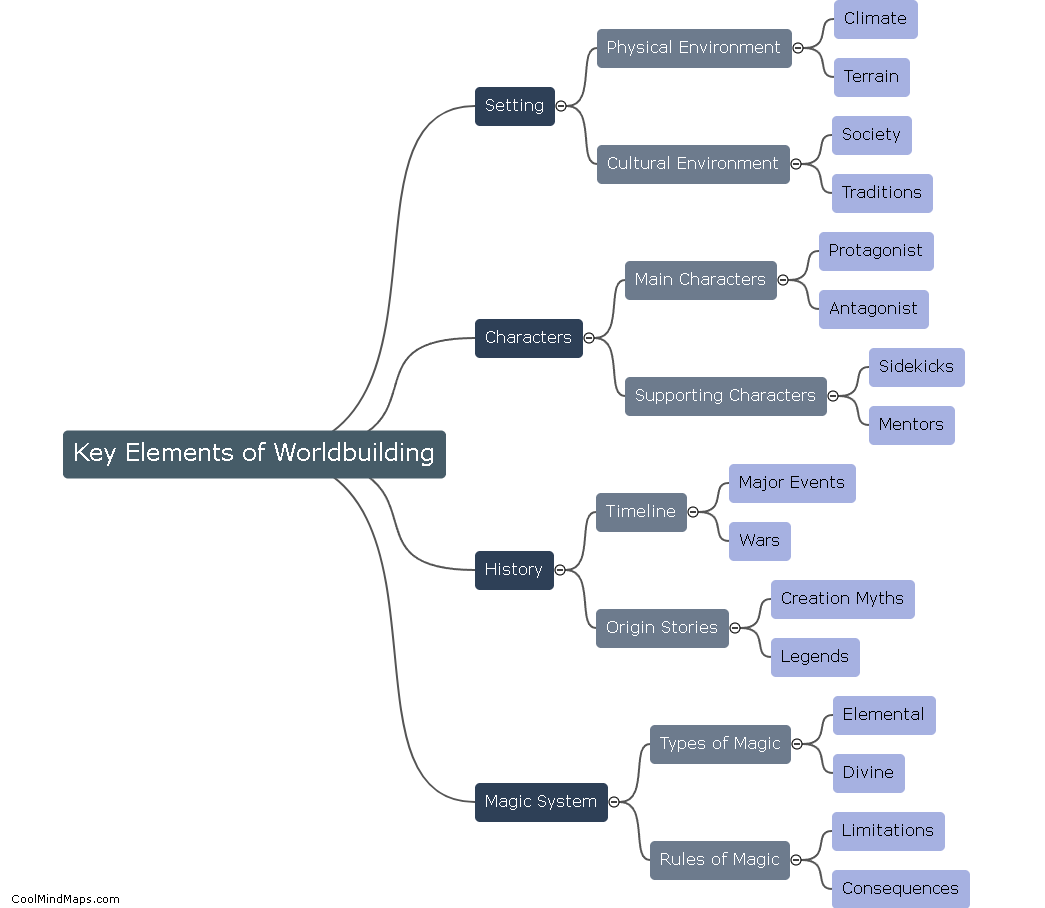
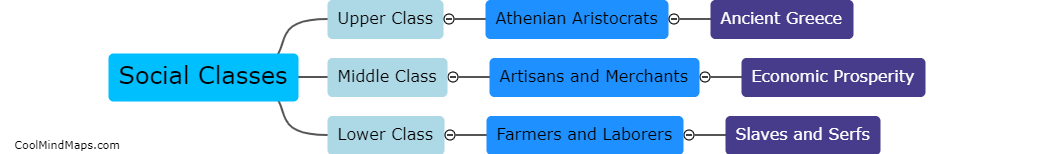
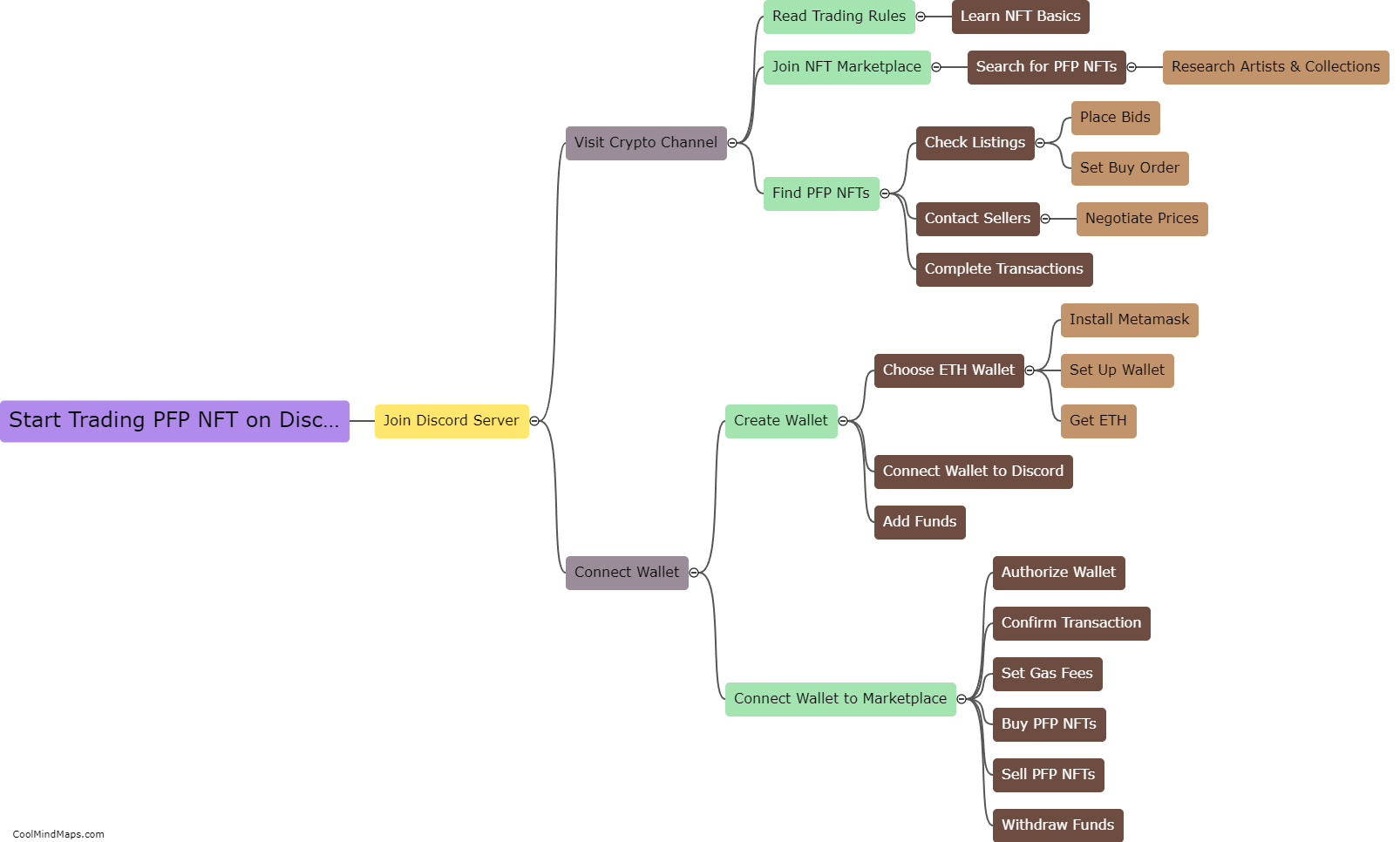
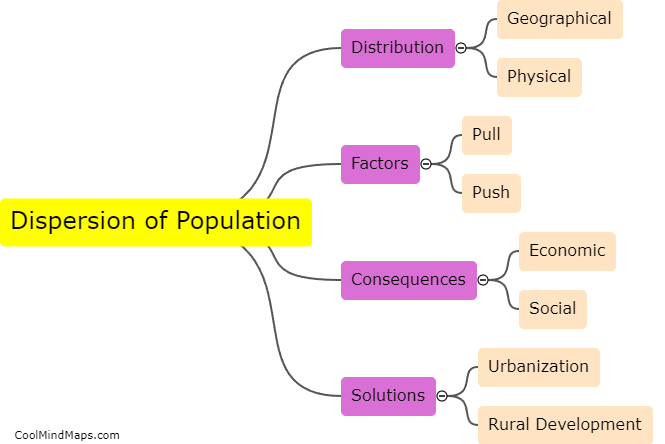
What is dispersion of population?
Dispersion of population refers to the way people are distributed across a geographical area. It can be measured in terms of the concentration of people in urban or rural areas, or in terms of the average distance between individuals. Factors that affect dispersion of population include economic opportunities, geographical features, transportation infrastructure, and social or cultural factors. Dispersion of population has significant consequences for resource management, economic development, and social well-being, and is an important consideration in urban planning, public policy, and demographic analysis.
This mind map was published on 22 May 2023 and has been viewed 125 times.