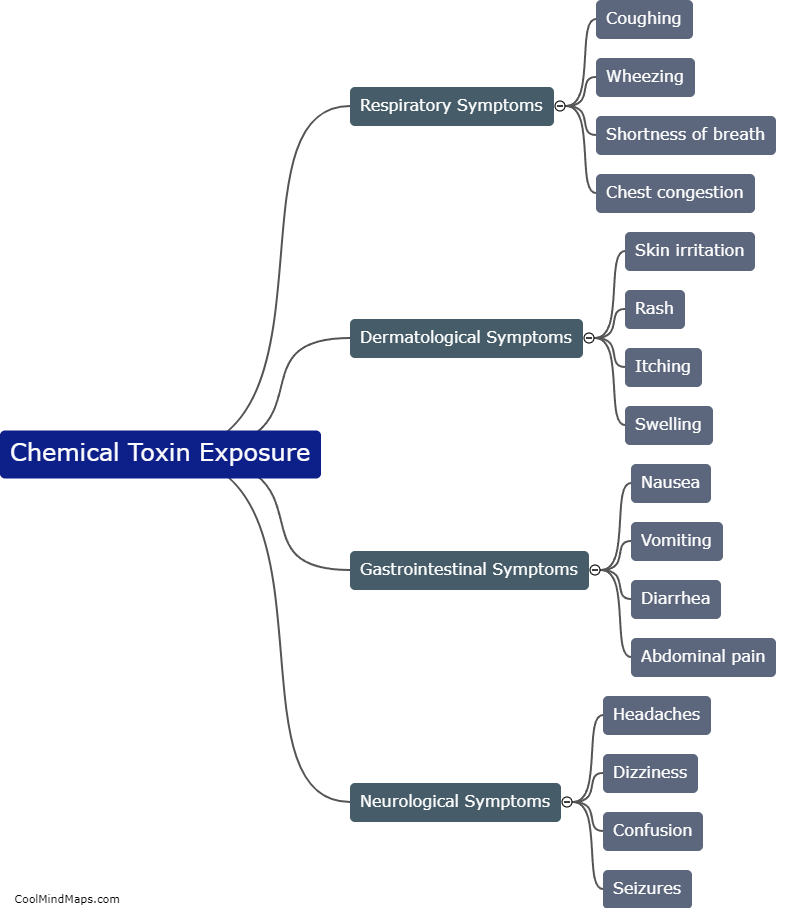
How do bacterial toxins damage cells?
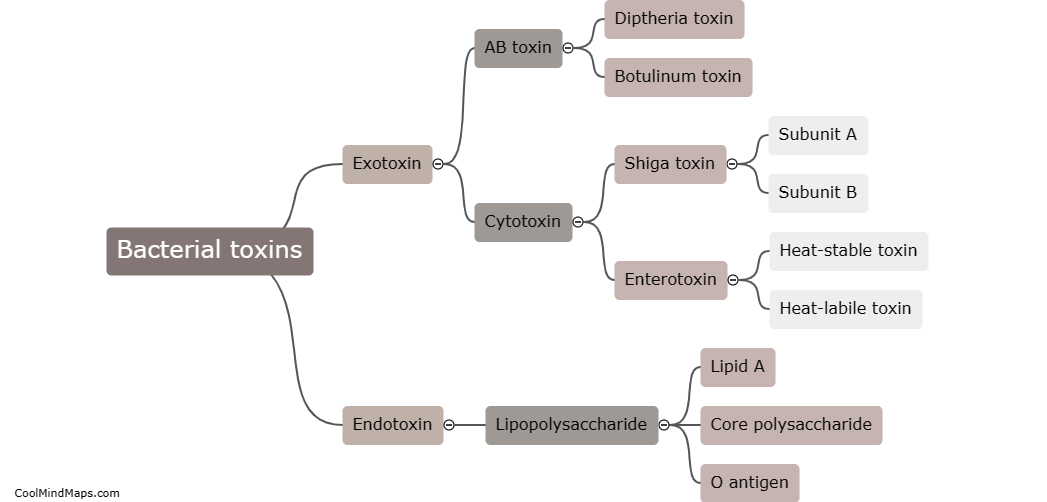
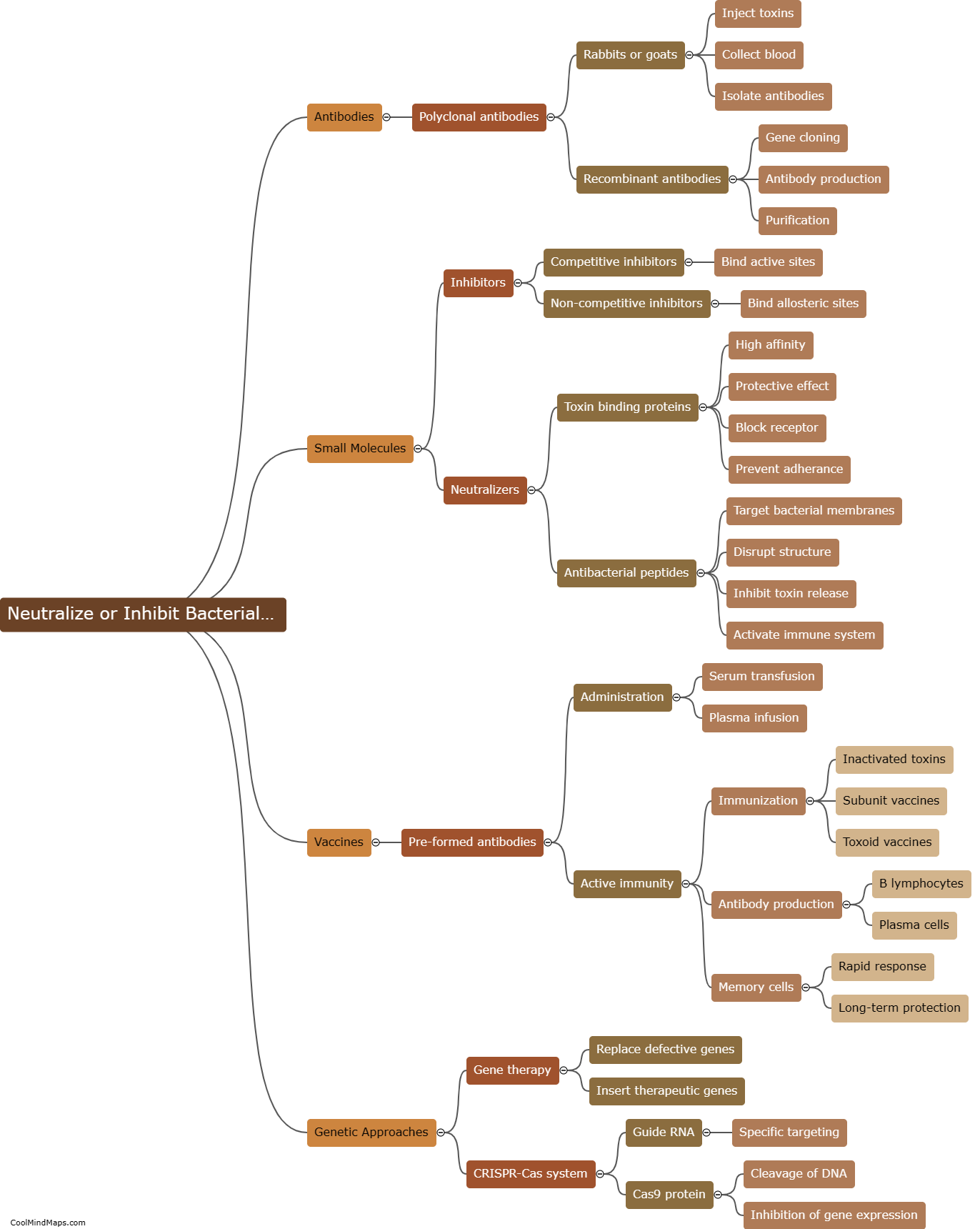
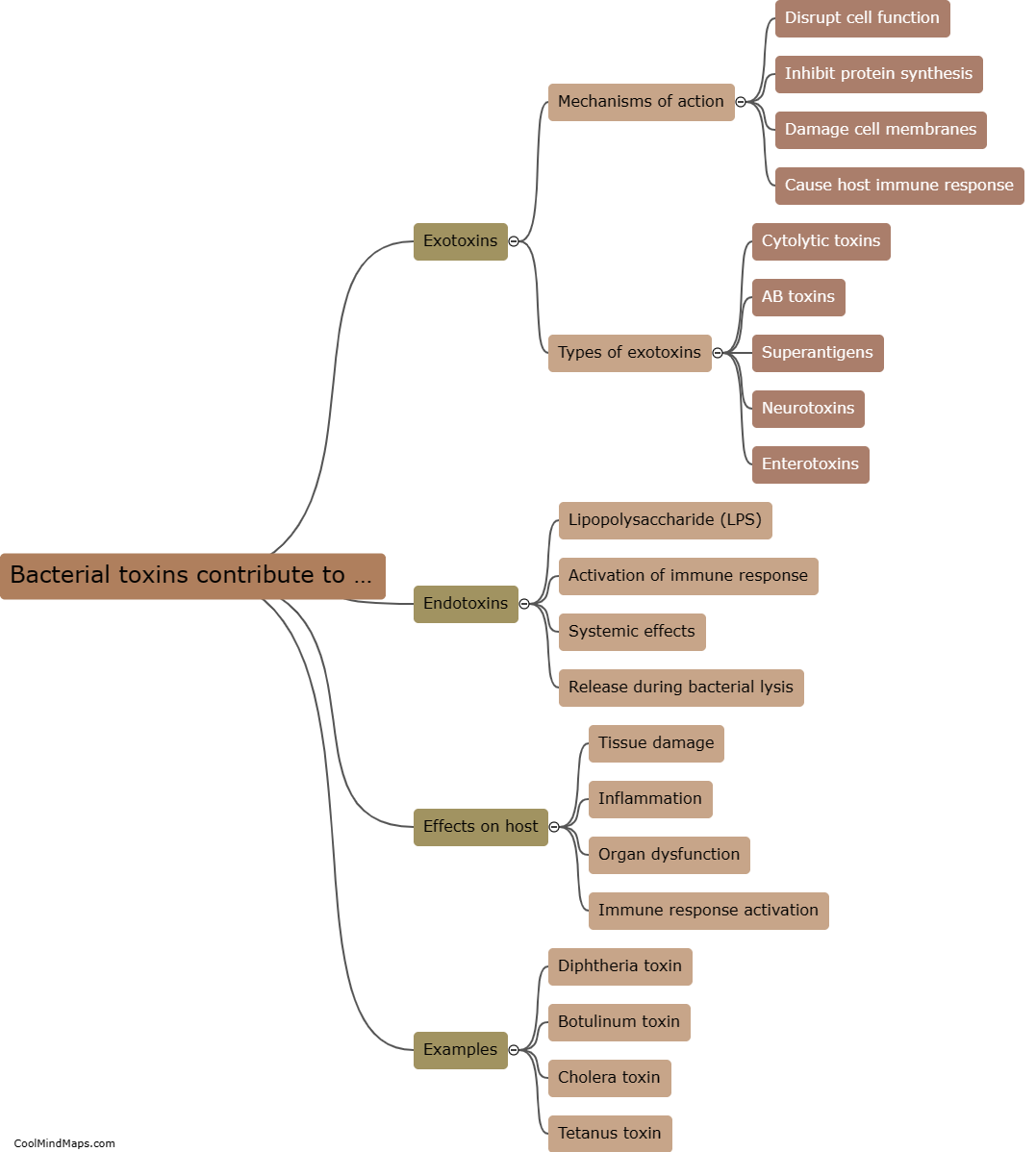
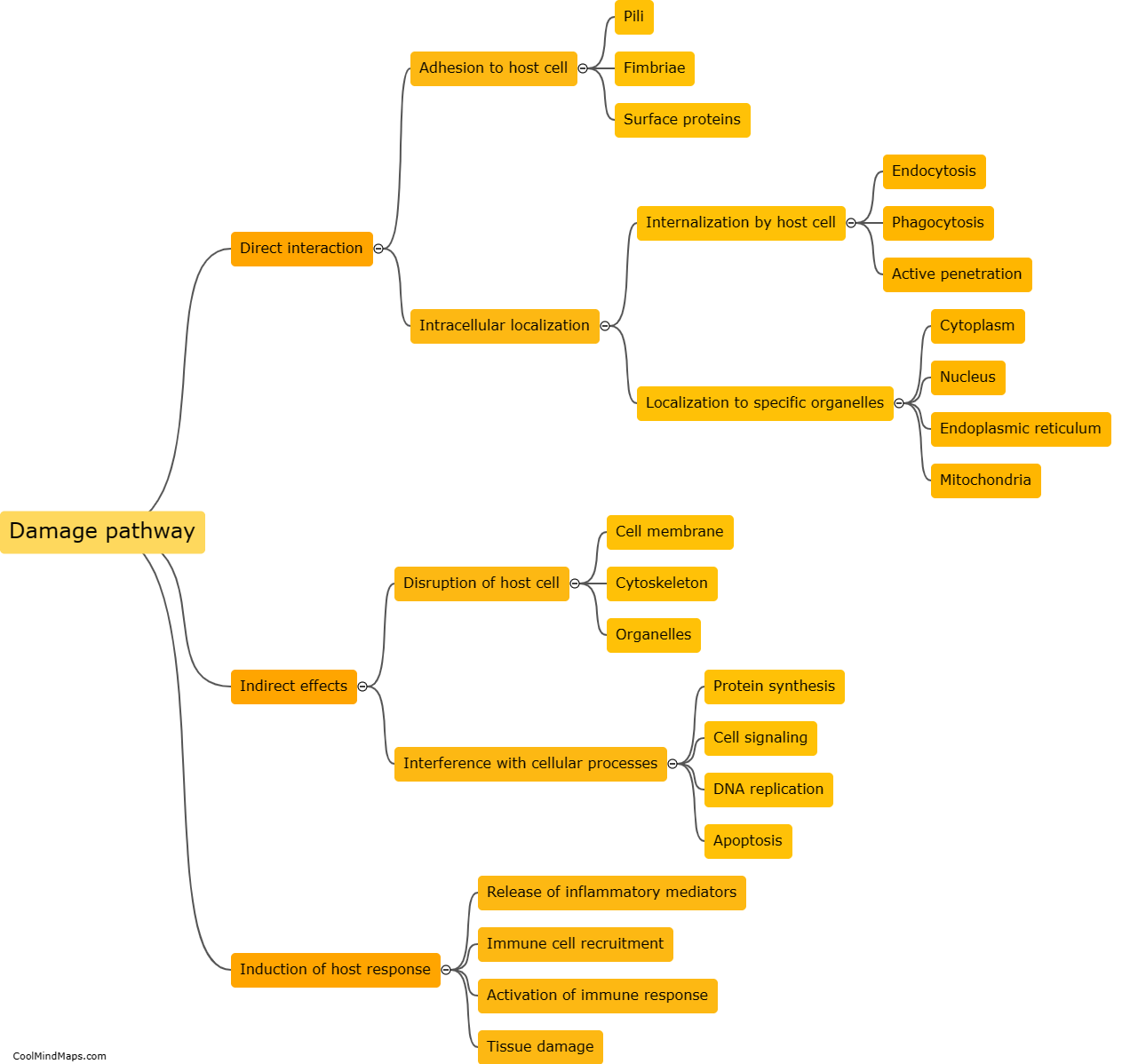
Bacterial toxins are produced by certain types of bacteria and have the ability to damage cells in various ways. One mechanism by which bacterial toxins damage cells is through the disruption of the cell membrane. Some toxins, like pore-forming toxins, create holes in the cell membrane, leading to loss of cell integrity and leakage of cellular contents. Other toxins, such as phospholipases, can break down the phospholipid molecules that make up the cell membrane, resulting in membrane damage. Additionally, bacterial toxins may interfere with cellular processes by inactivating essential enzymes or proteins, disrupting signal transduction pathways, or inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death). This damage caused by bacterial toxins can have severe consequences, including tissue damage, organ failure, and the development of disease symptoms.
This mind map was published on 3 December 2023 and has been viewed 158 times.