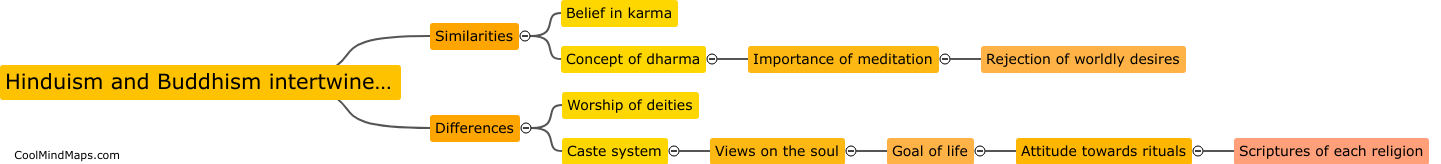
How do hydrogen cars produce electricity?
Hydrogen cars, also known as fuel cell vehicles, produce electricity through the process of electrolysis and electrochemical reactions. In these vehicles, hydrogen gas stored in high-pressure tanks is combined with oxygen from the air in a device called a fuel cell stack. The hydrogen molecules from the fuel tank are split into protons and electrons through an electrochemical reaction. The protons, which are positively charged, pass through a membrane inside the fuel cell stack, while the electrons are directed through an external circuit, creating an electric current. As the protons travel through the membrane, they combine with oxygen from the air, resulting in the formation of water vapor as the only byproduct. This continuous process generates electricity, which is used to power the electric motor in the vehicle, propelling it forward.

This mind map was published on 7 February 2024 and has been viewed 121 times.