What factors affect drag in fluid mechanics?
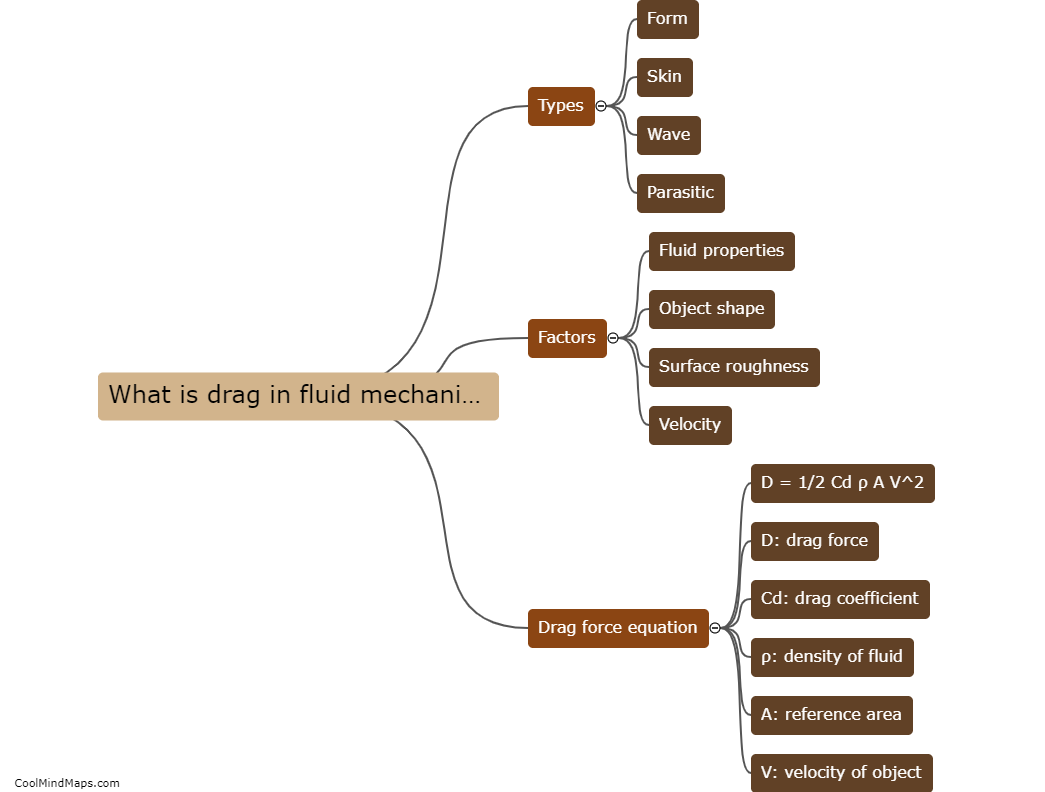
In fluid mechanics, drag refers to the resistive force that acts on an object as it moves through a fluid medium such as air or water. Several factors come into play that affect drag, with the most significant being the shape of the object and its surface roughness. The shape determines how fluid flows around the object and influences the formation of boundary layers, which are thin layers of fluid adjacent to the object's surface. A streamlined or aerodynamic shape reduces drag as it allows for smoother and more laminar flow. Conversely, irregular shapes create turbulence and increase drag. Surface roughness can also impact drag by disrupting the flow of fluid over the object and generating more turbulence. Additionally, the density and viscosity of the fluid, as well as the object's size and speed, play a role in determining the magnitude of drag forces.

This mind map was published on 4 July 2023 and has been viewed 98 times.