What is site directed mutagenesis?
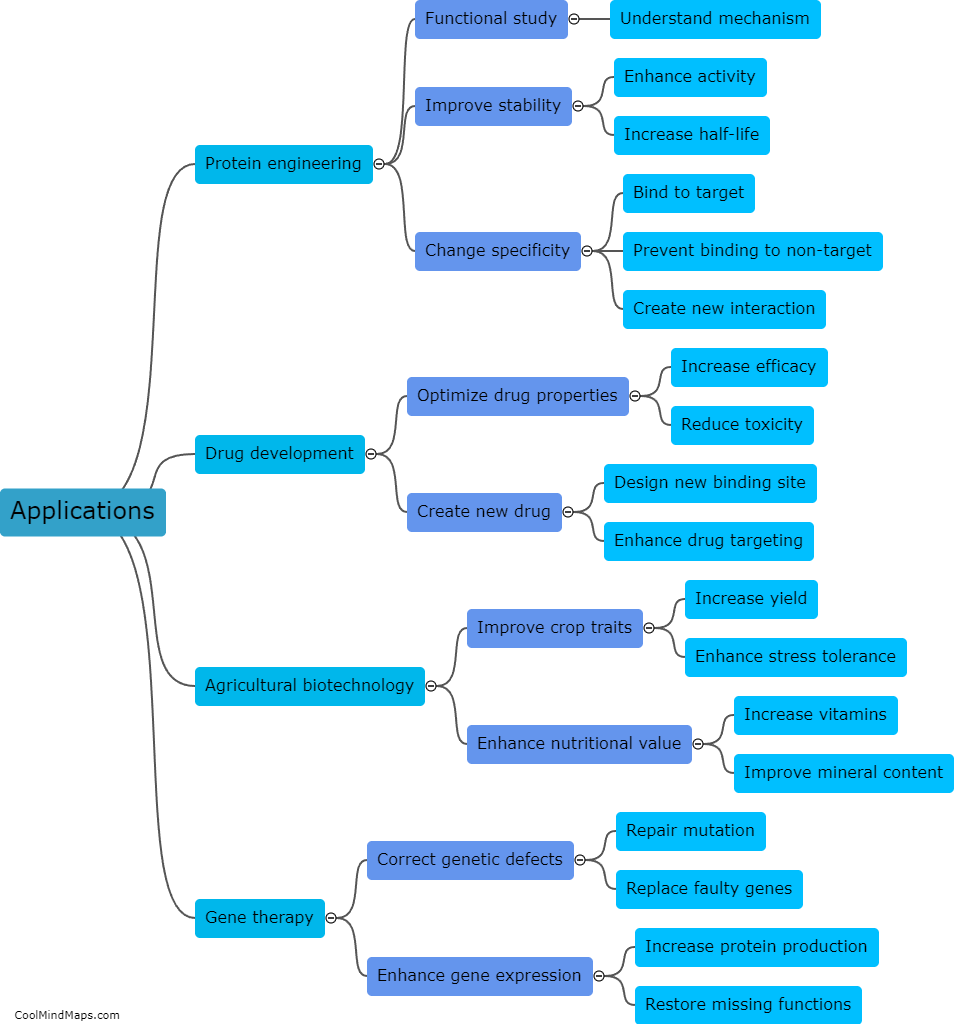
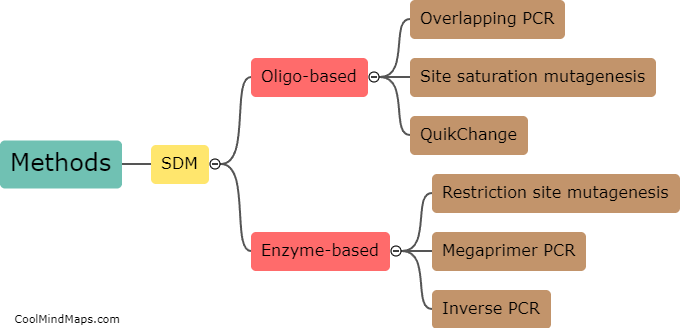
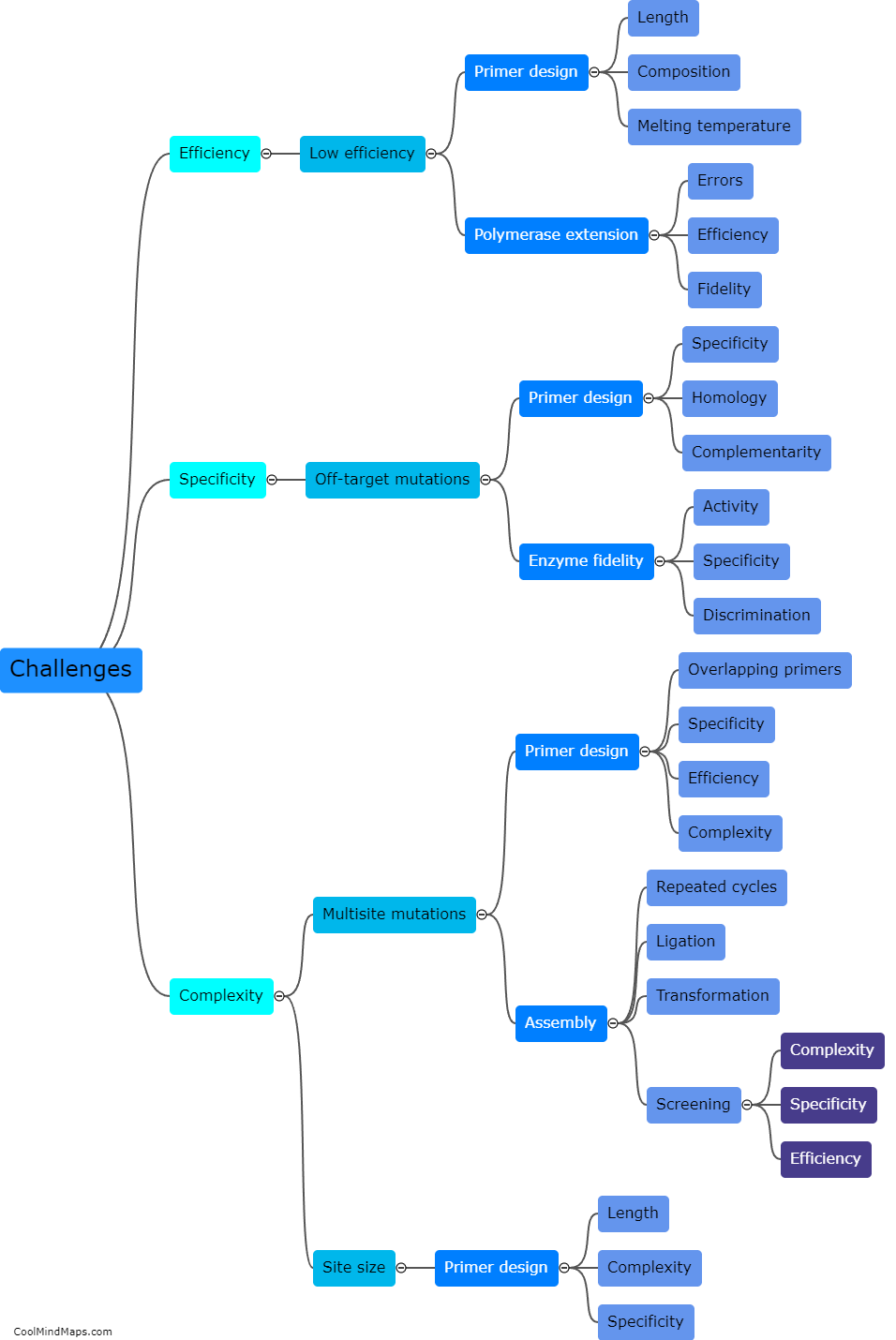
Site-directed mutagenesis is a powerful laboratory technique used to introduce specific, intentional changes, called mutations, into a DNA sequence. This process allows scientists to manipulate and study the function of genes and proteins by selectively altering certain amino acids within their sequences. With site-directed mutagenesis, researchers can create substitutions, deletions, insertions, or even combinations of mutations at desired positions in the DNA. By precisely modifying specific regions of interest, scientists can investigate the effects of these mutations in order to understand the structure-function relationship of genes and proteins, and to gain insights into disease mechanisms or develop new therapeutic strategies.

This mind map was published on 19 November 2023 and has been viewed 86 times.