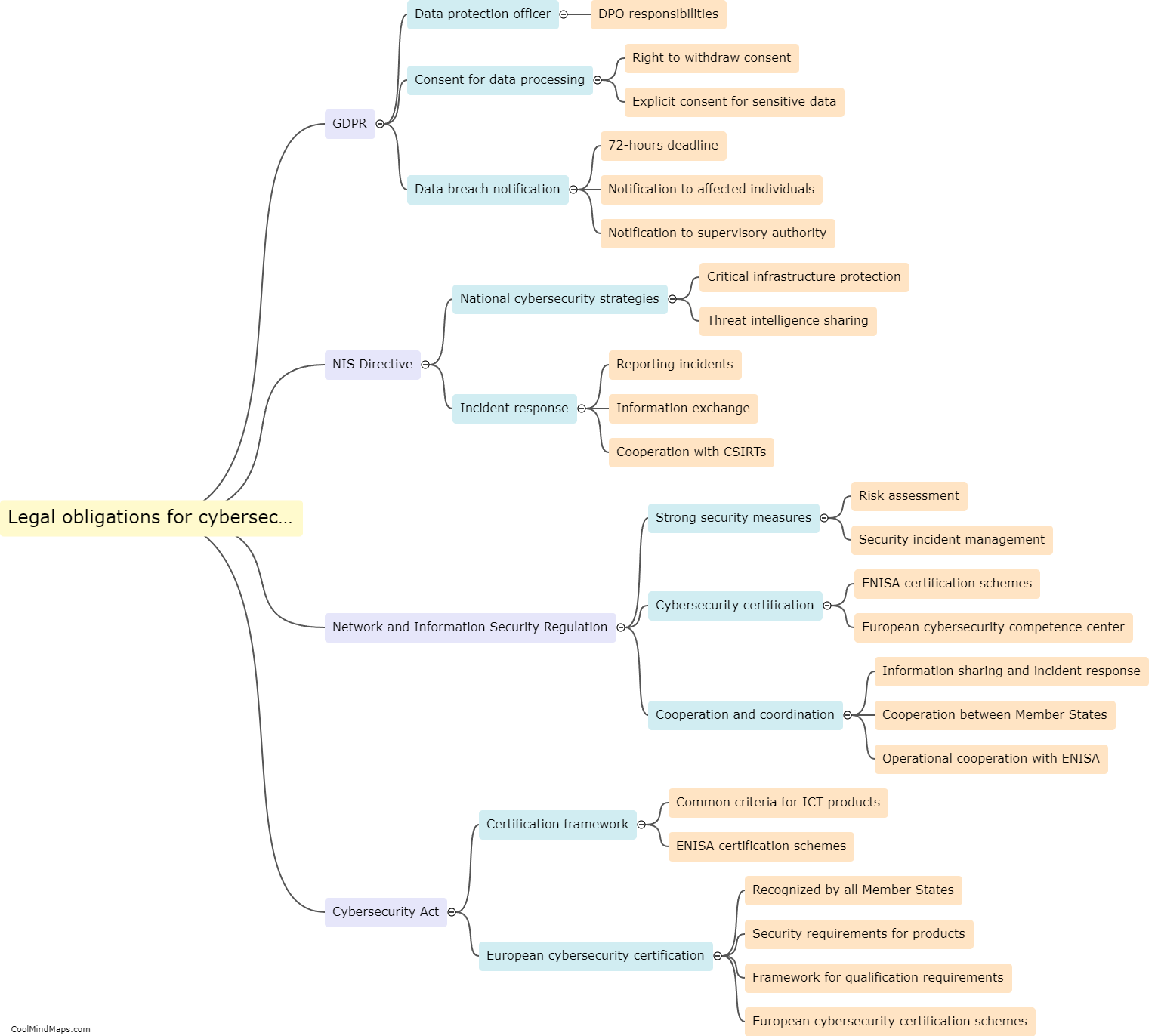
What are the legal obligations for cybersecurity in the EU?
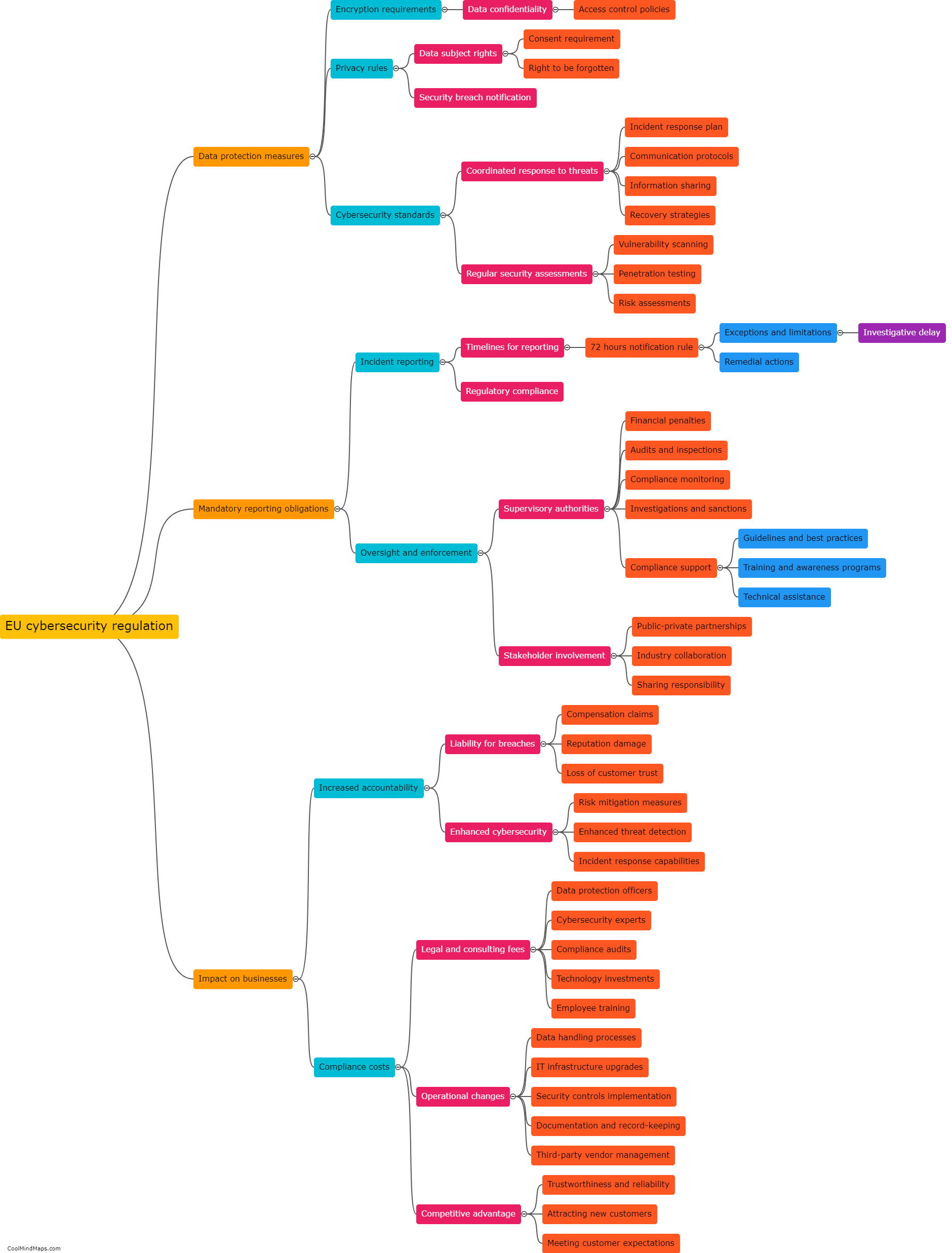
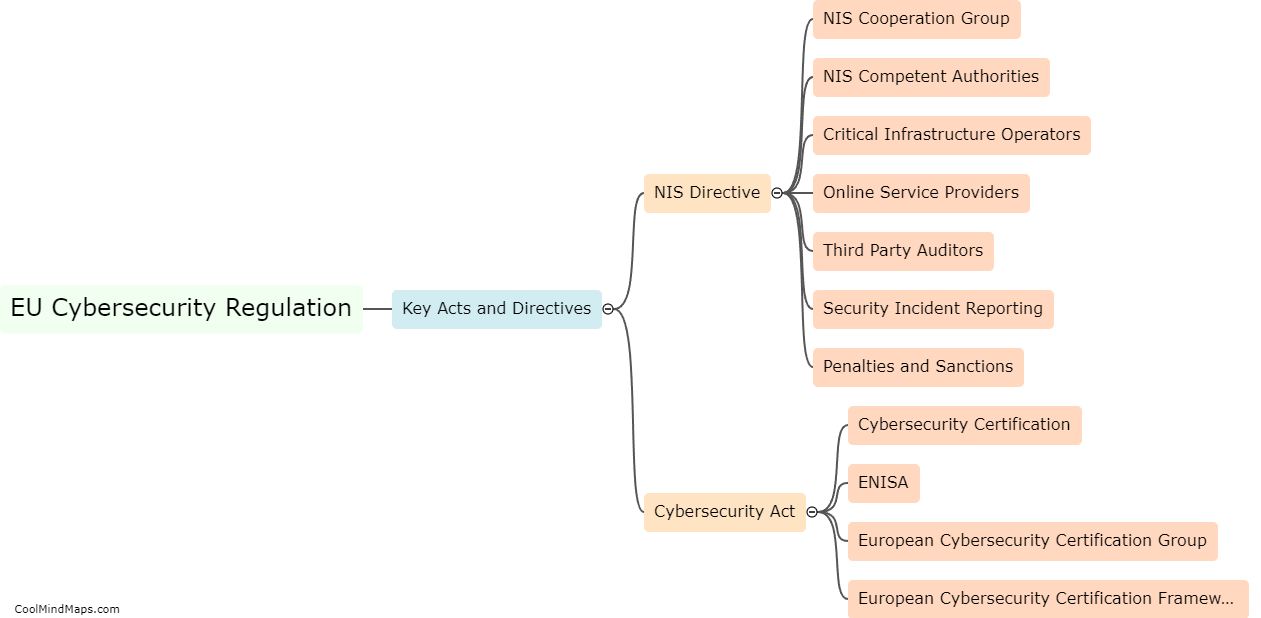
In the European Union (EU), there are several legal obligations that businesses and organizations must comply with to ensure cybersecurity. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which came into effect in 2018, is one of the primary legislations governing cybersecurity in the EU. GDPR requires organizations to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of personal data. It emphasizes the need for measures such as encryption, regular security assessments, and incident response plans. Additionally, the Network and Information Security (NIS) Directive requires operators of essential services and digital service providers to establish robust cybersecurity measures and report significant cyber incidents to relevant authorities. The EU also promotes cybersecurity through frameworks like the Cybersecurity Act and the EU Cybersecurity Certification Framework, aiming to ensure the security and trustworthiness of digital products and services. Compliance with these regulations is essential for organizations to protect personal data, maintain customer trust, and avoid hefty fines or legal consequences.
This mind map was published on 16 September 2023 and has been viewed 106 times.