How did the British colonize India?
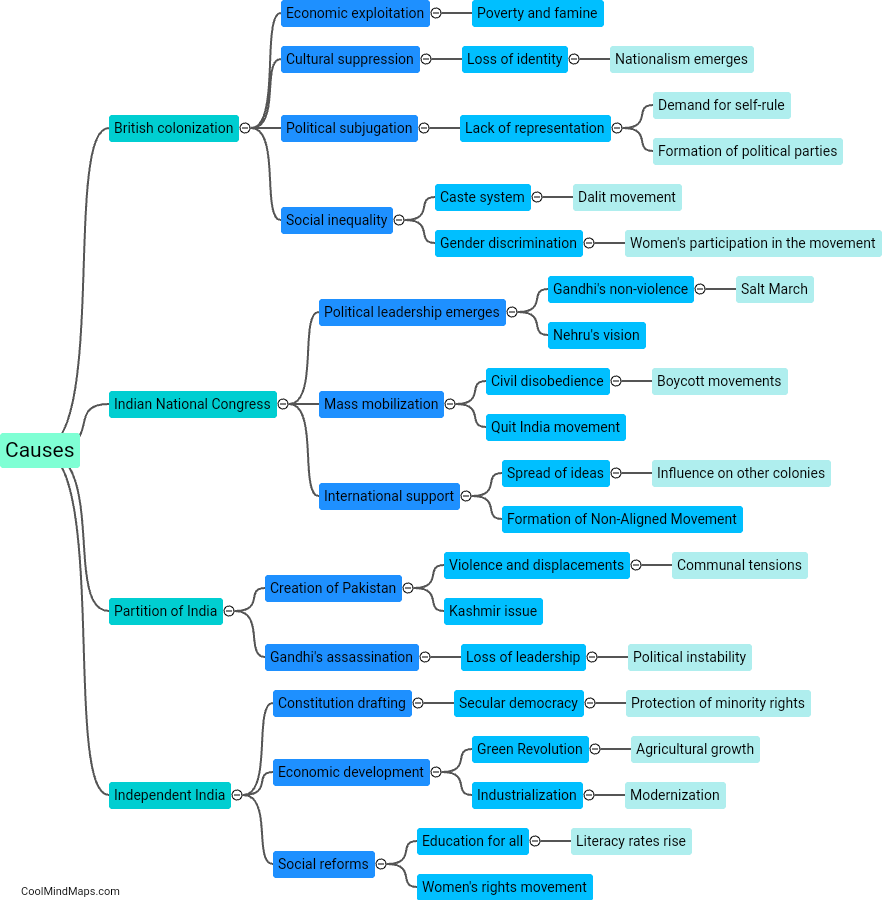
The British colonization of India began in the early 17th century with the establishment of trading posts by the East India Company. Initially, the British were primarily interested in India as a source of valuable spices and textiles. However, over time, they expanded their foothold in the region by forging alliances with local rulers and engaging in military campaigns. The Battle of Plassey in 1757 marked a significant turning point, with the British gaining control over Bengal. This was followed by a series of wars and treaties that gradually extended British influence across the subcontinent. The British exploited internal conflicts and divisions within Indian society, employing a policy of divide and rule to maintain their dominion. Economic exploitation, cultural imposition, and political repression characterized British rule in India until a widespread movement for independence emerged in the 20th century.

This mind map was published on 9 October 2023 and has been viewed 105 times.