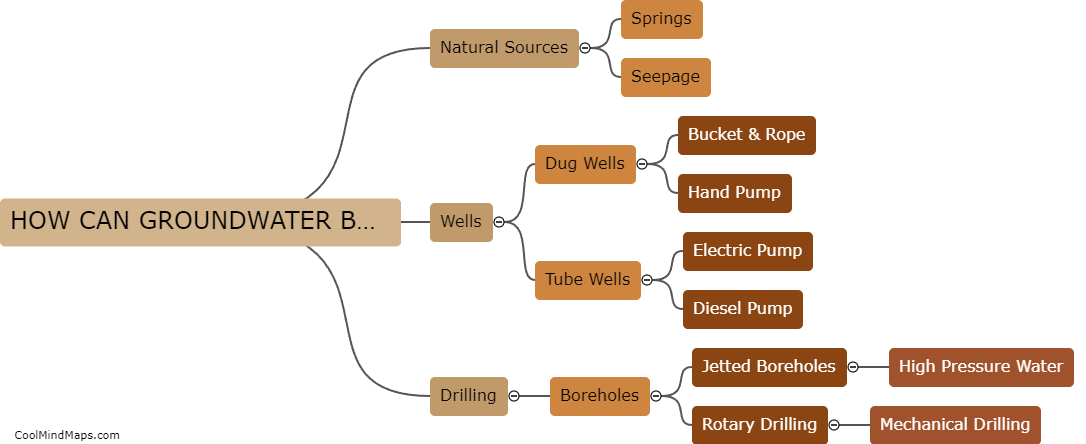
Where does groundwater come from?
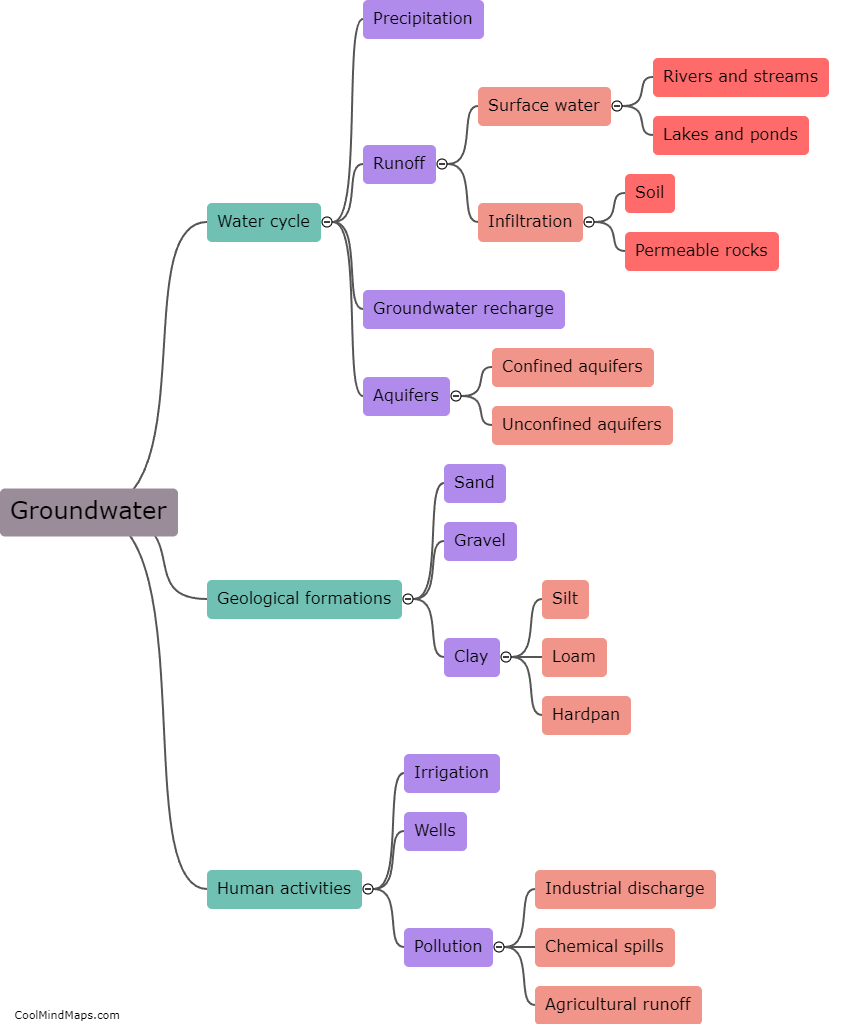
Groundwater is the water that fills the spaces between particles of sand, gravel, and rocks beneath the Earth's surface. It originates from different sources, primarily precipitation in the form of rain or snow. When it rains, water infiltrates into the ground, partly absorbed by plants, surface waters, and evaporating back into the atmosphere. However, a significant portion seeps through the soil and reaches the porous spaces underground, becoming groundwater. This process, known as recharge, replenishes underground aquifers, which act as natural storage tanks for this valuable resource. In addition to precipitation, groundwater can also come from rivers, lakes, and other surface water bodies that penetrate the ground through seepage or by flowing into underground reservoirs called springs. Overall, groundwater is a vital component of the Earth's water cycle, playing a crucial role in maintaining ecosystems and serving as a primary water source for wells and springs.
This mind map was published on 27 November 2023 and has been viewed 101 times.