How do eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells?
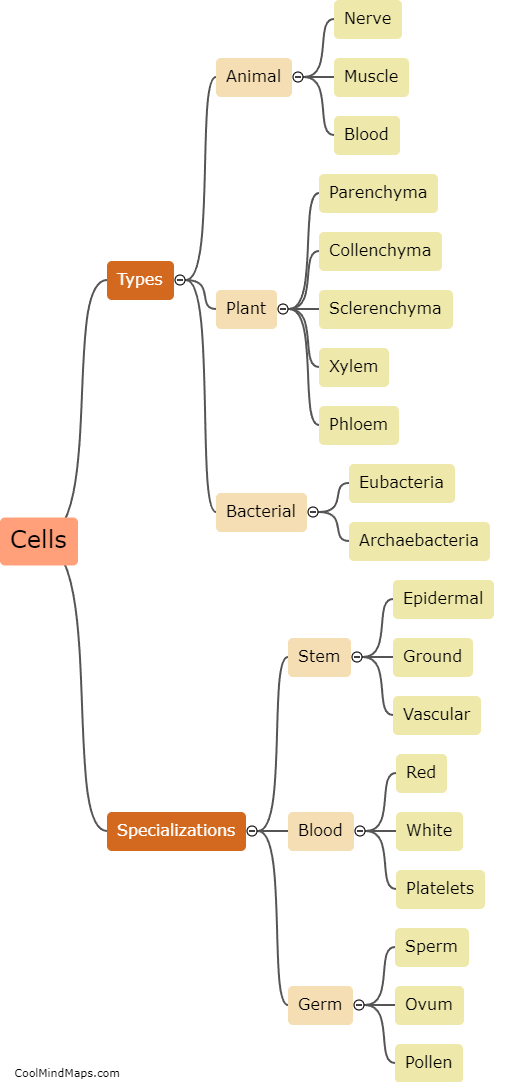
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are two distinct types of cells that differ in several fundamental ways. Eukaryotic cells are typically larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. One key difference is the presence of a nucleus in eukaryotic cells, which houses the genetic material, while prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus. Another major difference is that eukaryotic cells possess membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, which enable them to carry out specialized functions. In contrast, prokaryotic cells lack these membrane-bound organelles and instead have simpler structures like ribosomes and a single circular DNA molecule. Furthermore, eukaryotic cells can be found in multicellular organisms, whereas prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms or bacteria. These distinctions highlight the evolutionary and structural differences between these two types of cells.

This mind map was published on 26 October 2023 and has been viewed 122 times.