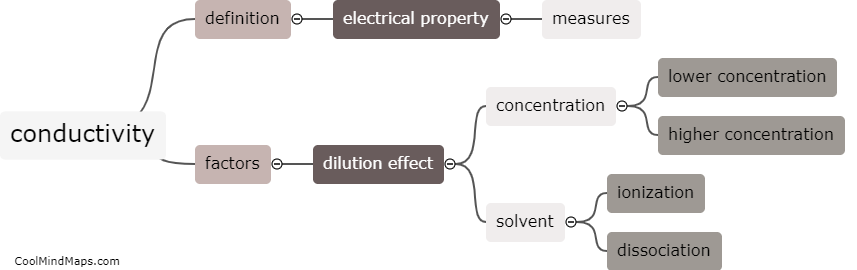
What is conductivity and how does it vary with dilution?
Conductivity refers to the ability of a substance to conduct electric current. It is a measure of how well a material allows the flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions. In the context of aqueous solutions, conductivity is primarily determined by the concentration of ions dissolved in the solution. When a substance, such as a salt, is dissolved in water, it dissociates into ions, which can carry electric charge. As the concentration of ions increases, the conductivity also increases. Therefore, conductivity is directly proportional to the concentration of ions in a solution. When a solution is diluted with more solvent (usually water), the concentration of ions decreases, leading to a decrease in conductivity. The relationship between conductivity and dilution is such that as the solution becomes more diluted, the conductivity decreases.
This mind map was published on 31 August 2023 and has been viewed 113 times.