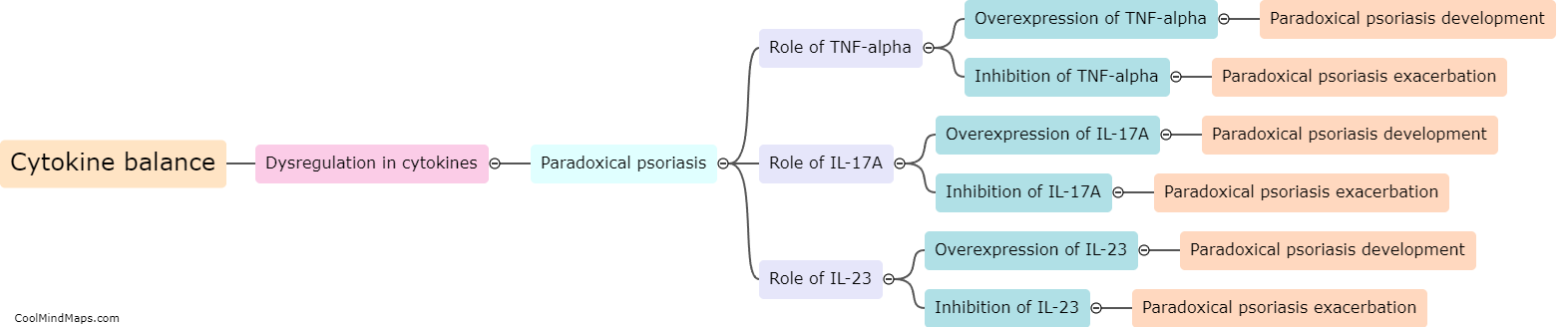
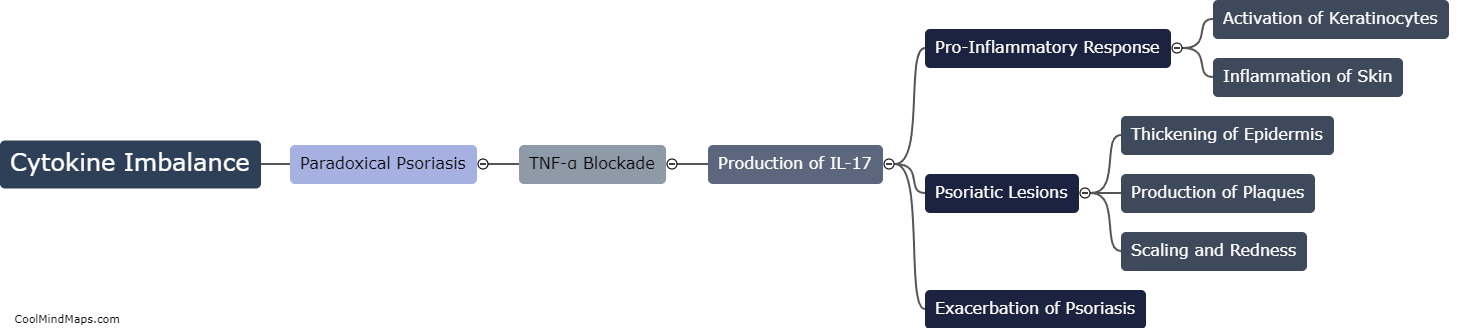
What is the mechanism of Inparadoxical psoriasis?
In paradoxical psoriasis, the regular use of certain medications, typically used to treat autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn's disease, leads to the development or worsening of psoriasis symptoms. The exact mechanism underlying this phenomenon is not yet fully understood. However, it is believed that the medication-induced disturbance of the immune system plays a crucial role. These medications, such as tumor necrosis factor blockers or interleukin inhibitors, are designed to suppress specific immune responses. However, in some cases, this immune suppression can lead to an overcompensation or rebound effect, triggering an upregulation of inflammatory pathways involved in psoriasis. This results in the paradoxical emergence or exacerbation of psoriasis symptoms in patients who are being treated for other autoimmune conditions. Further research is necessary to fully elucidate the intricacies of this mechanism and develop effective strategies for managing paradoxical psoriasis.
This mind map was published on 12 July 2023 and has been viewed 153 times.