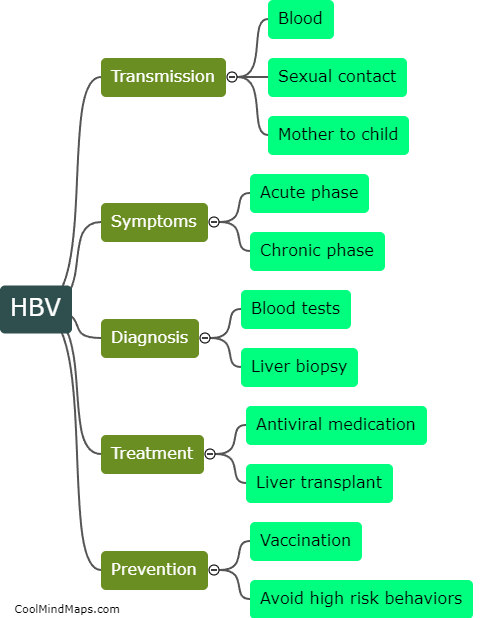
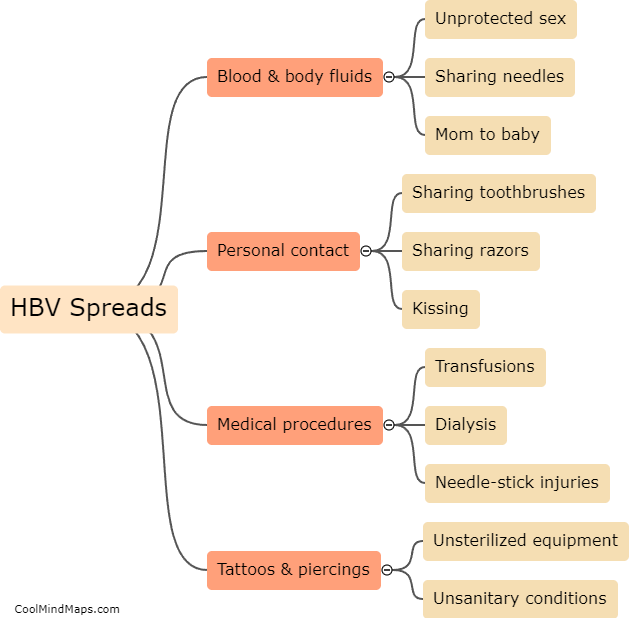
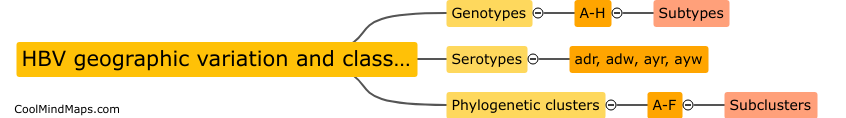
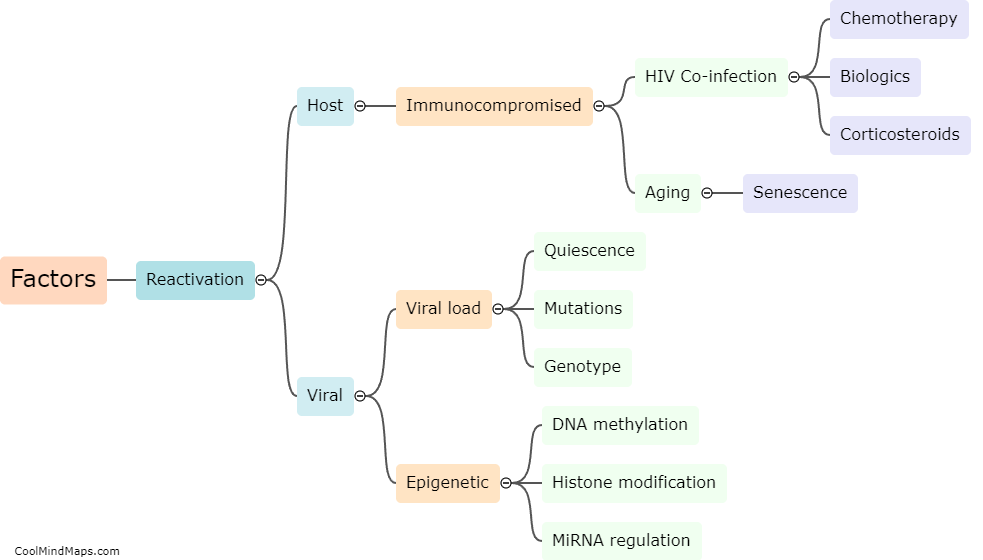
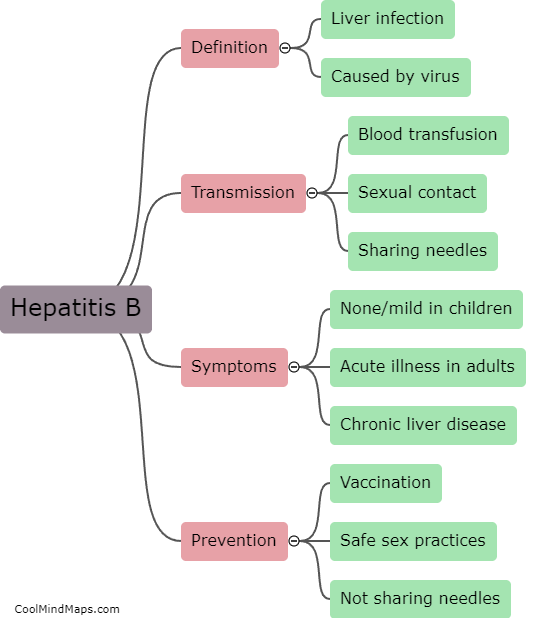
What is the mechanism of HBV replication?
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication is a complex process that involves reverse transcription of the viral RNA genome into DNA and amplification of the DNA in the host cell's nucleus. The replication of HBV is initiated by the viral polymerase, which reverse transcribes the viral pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) into DNA, forming an intermediate known as relaxed circular DNA (rcDNA). The rcDNA is then transported into the nucleus where it is converted into a covalently-closed circular DNA (cccDNA) molecule. The cccDNA serves as a template for HBV gene expression and replication. HBV replication requires host cell factors that are involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA replication, and transcription. The mechanism of HBV replication is complex and involves multiple steps that are regulated by both viral and host factors.

This mind map was published on 27 June 2023 and has been viewed 109 times.