How does Theravada Buddhism differ from other Buddhist traditions?
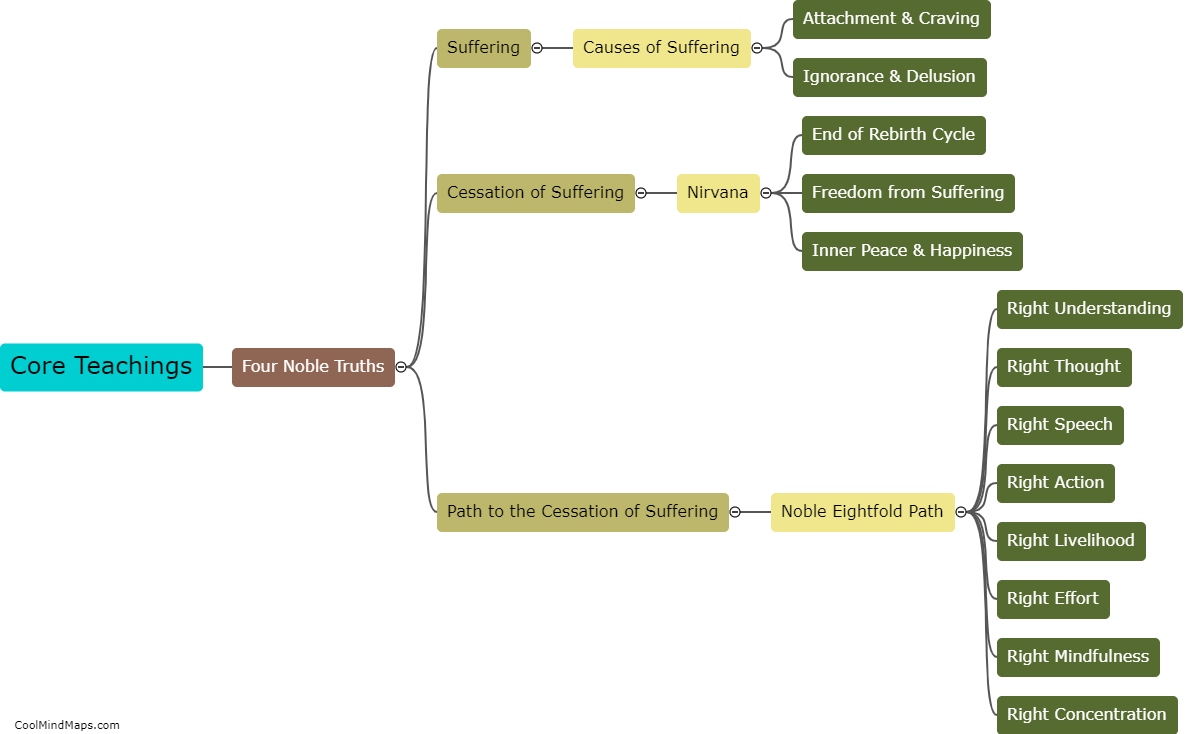
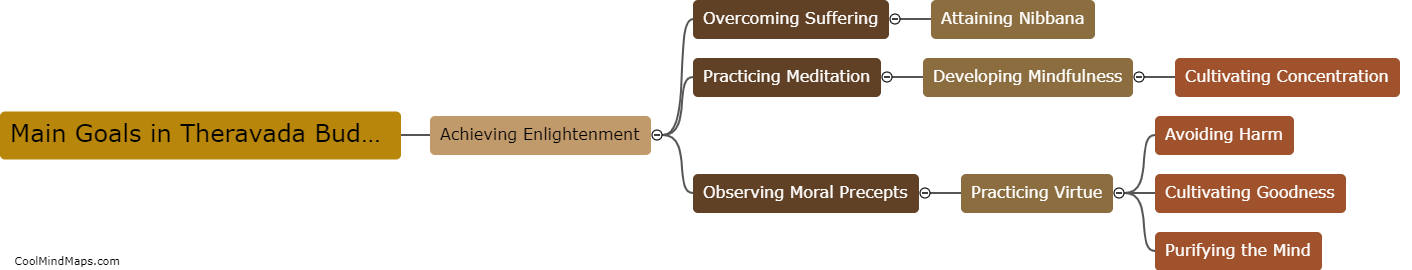
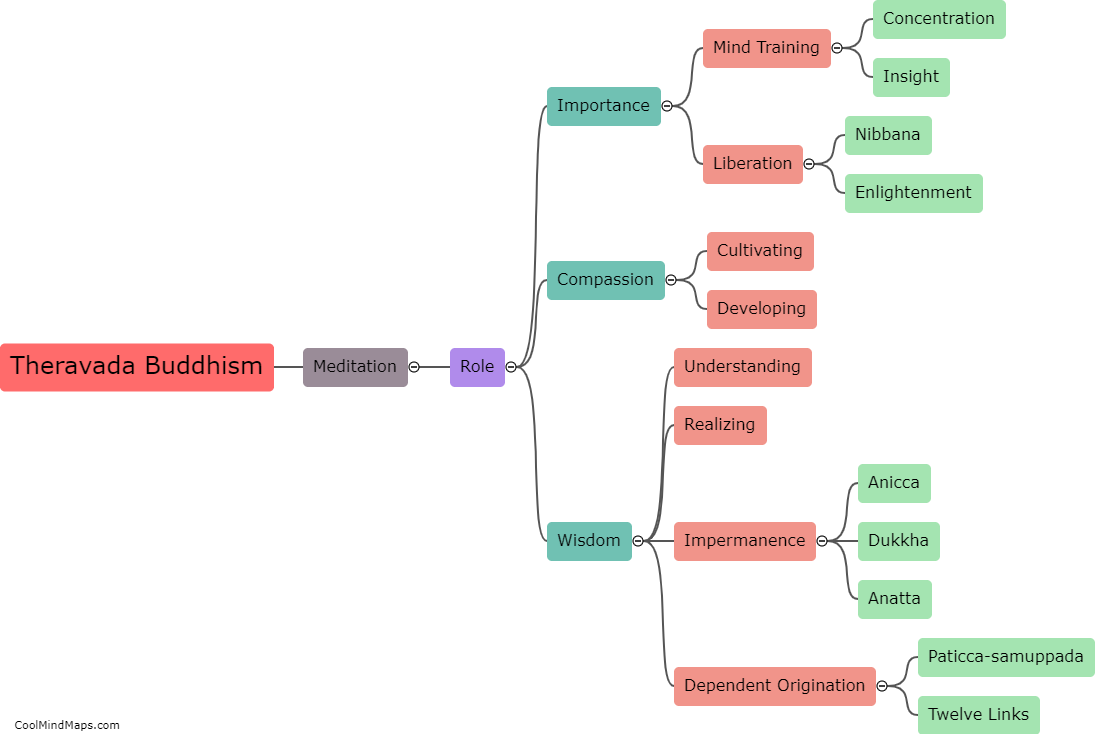
Theravada Buddhism, also known as the School of the Elders, is one of the oldest existing Buddhist traditions that originated in South Asia. It differs from other Buddhist traditions, such as Mahayana and Vajrayana, in several aspects. Firstly, Theravada focuses more on individual liberation and personal enlightenment, emphasizing the journey towards attaining Nirvana. In contrast, Mahayana Buddhism places greater emphasis on compassion and the aim of attaining Buddhahood to help others achieve enlightenment. Secondly, Theravada Buddhism strictly adheres to the original teachings and scriptures of the Buddha, known as the Pali Canon. Other traditions have their own additional sutras and scriptures. Lastly, Theravada places strong emphasis on monasticism as a path to enlightenment, while other traditions may incorporate lay practitioners more thoroughly into their practices. Overall, Theravada Buddhism maintains a more conservative and orthodox approach in comparison to other Buddhist traditions.
This mind map was published on 12 September 2023 and has been viewed 134 times.