How do hallucinogens affect the brain?
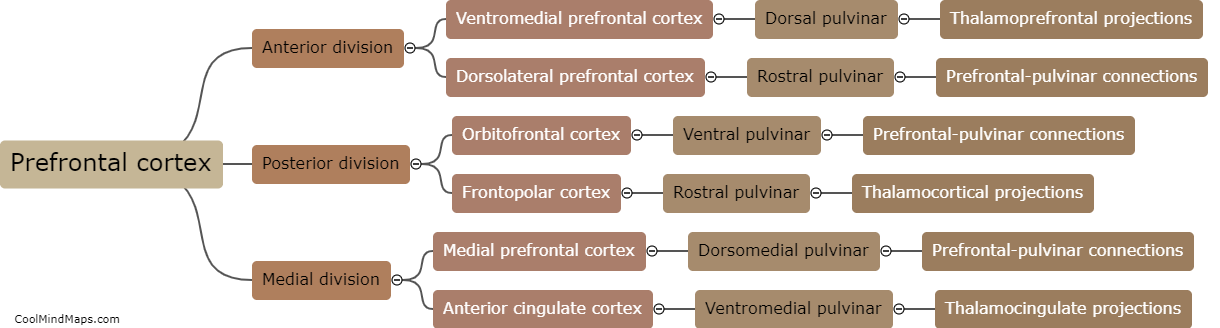
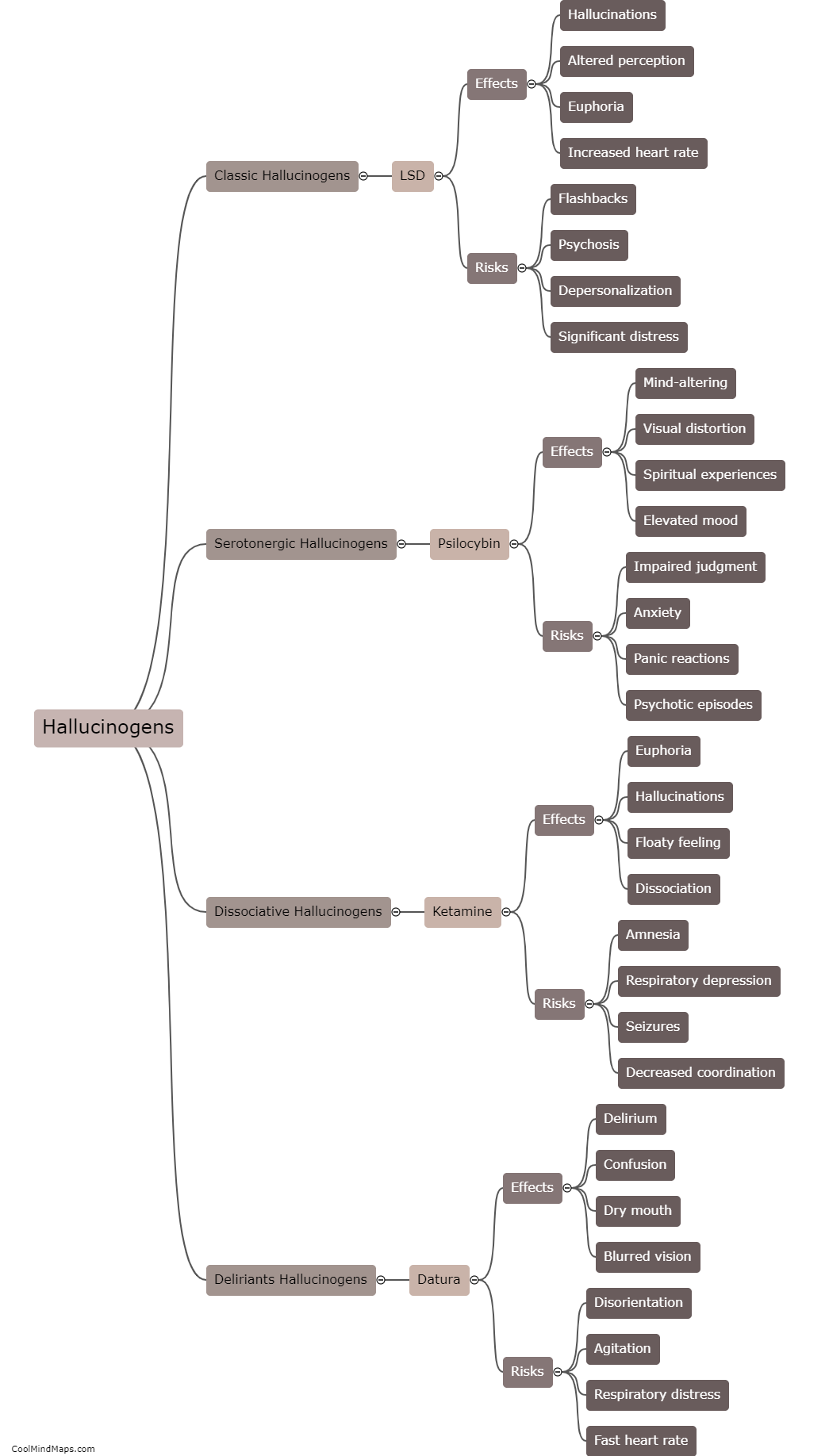
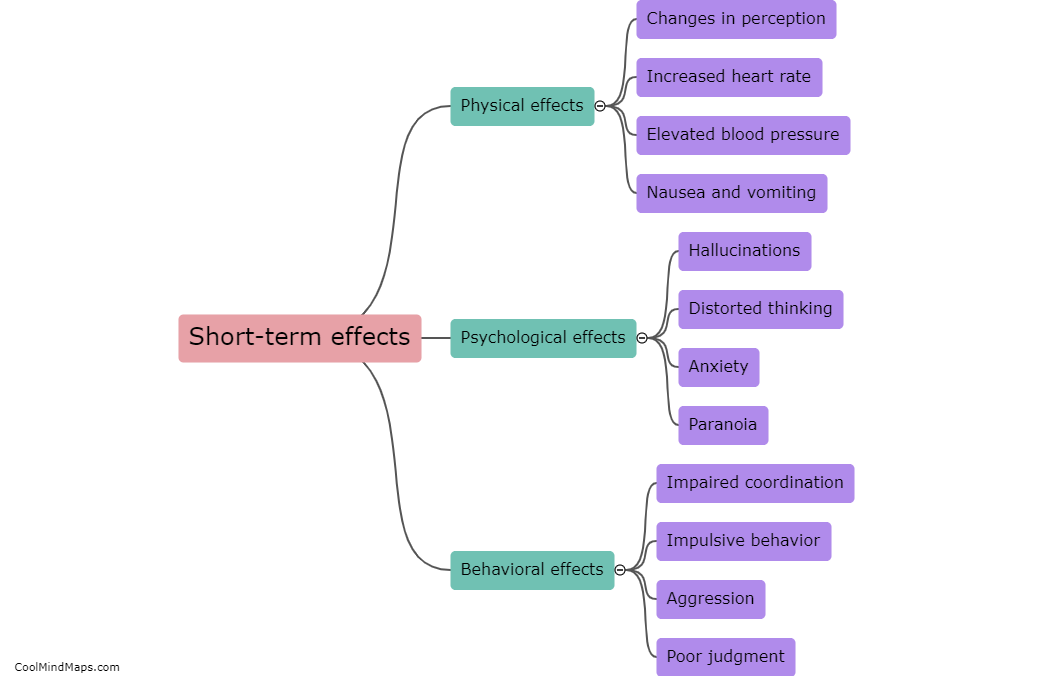
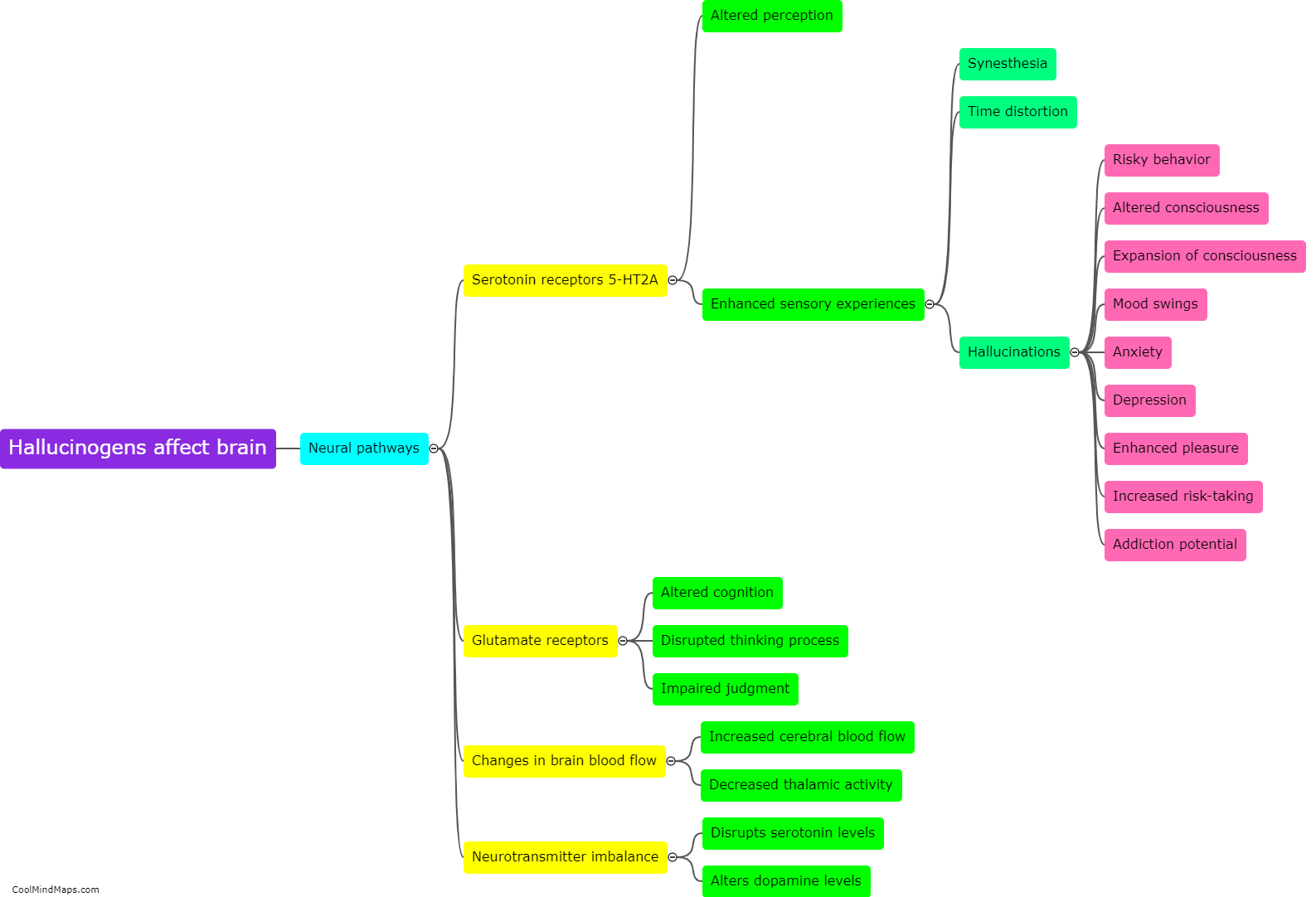
Hallucinogens, a class of psychoactive drugs that alter perception, thinking, and mood, have a profound impact on the brain. These substances, such as LSD, psilocybin, and DMT, work by stimulating serotonin receptors in various regions of the brain, primarily the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala, involved in cognition, emotions, and sensory processing. Hallucinogens cause an increase in neuronal activity, leading to distorted sensory perceptions, hallucinations, and intensified emotions. Furthermore, these substances disrupt the brain's default mode network, responsible for self-reflection and introspection, resulting in a loss of self-identity and ego dissolution commonly experienced during psychedelic trips. Research suggests that these alterations in brain connectivity and activity may have therapeutic potential for mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and addiction. However, the exact mechanisms and long-term effects of hallucinogen use on the brain still require further study.
This mind map was published on 5 December 2023 and has been viewed 92 times.