What is the role of DNA in immune system development?
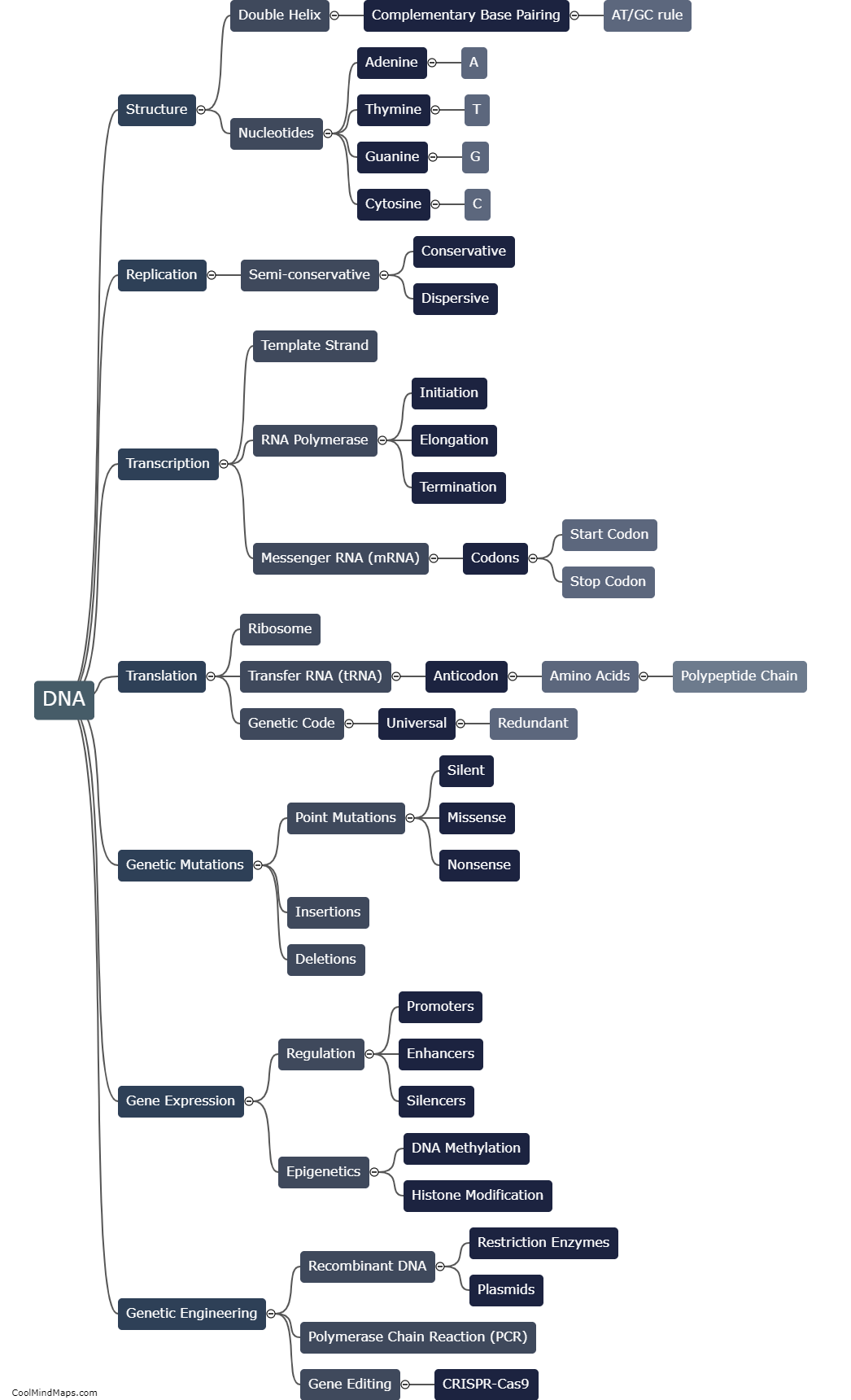
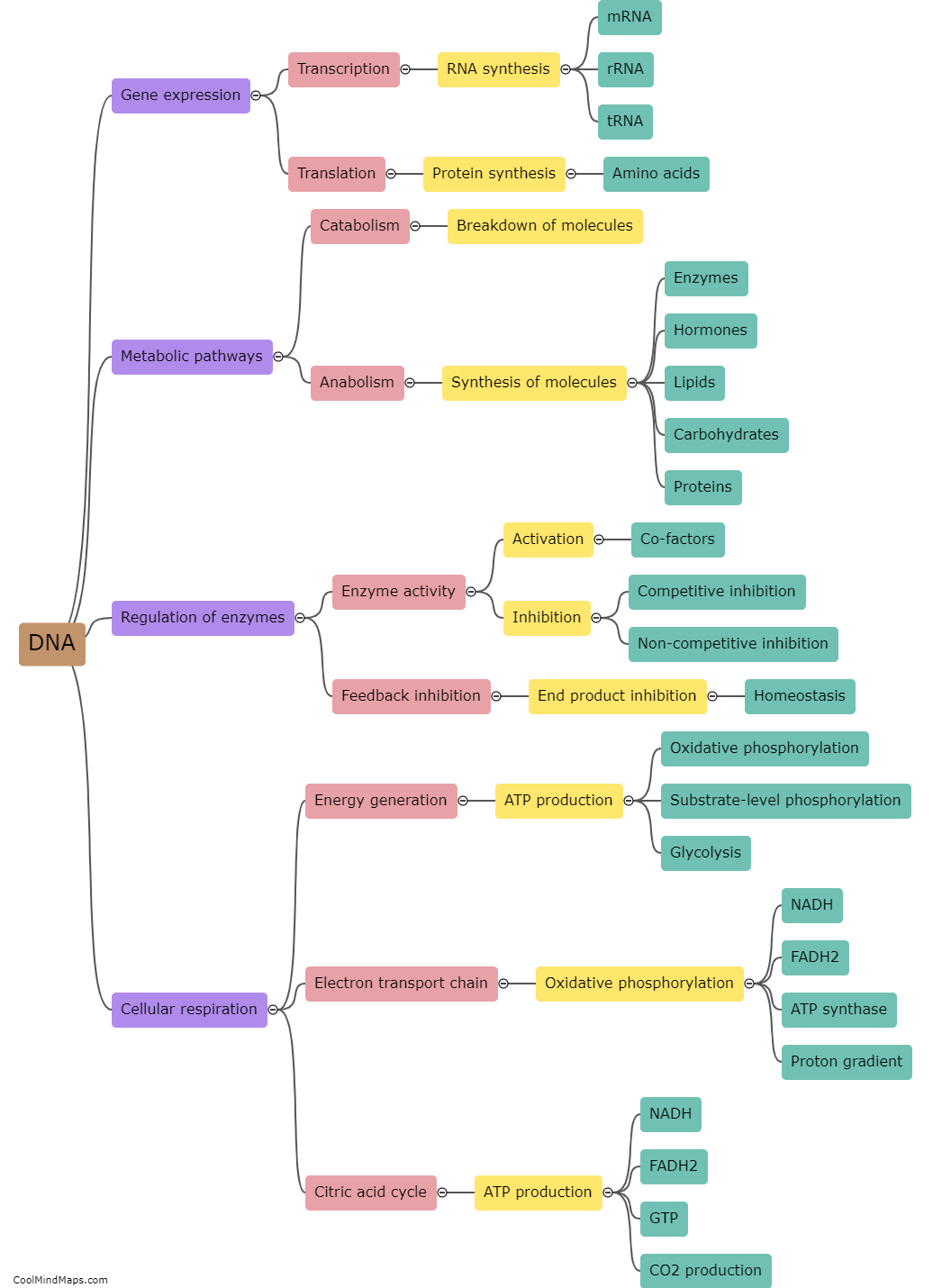
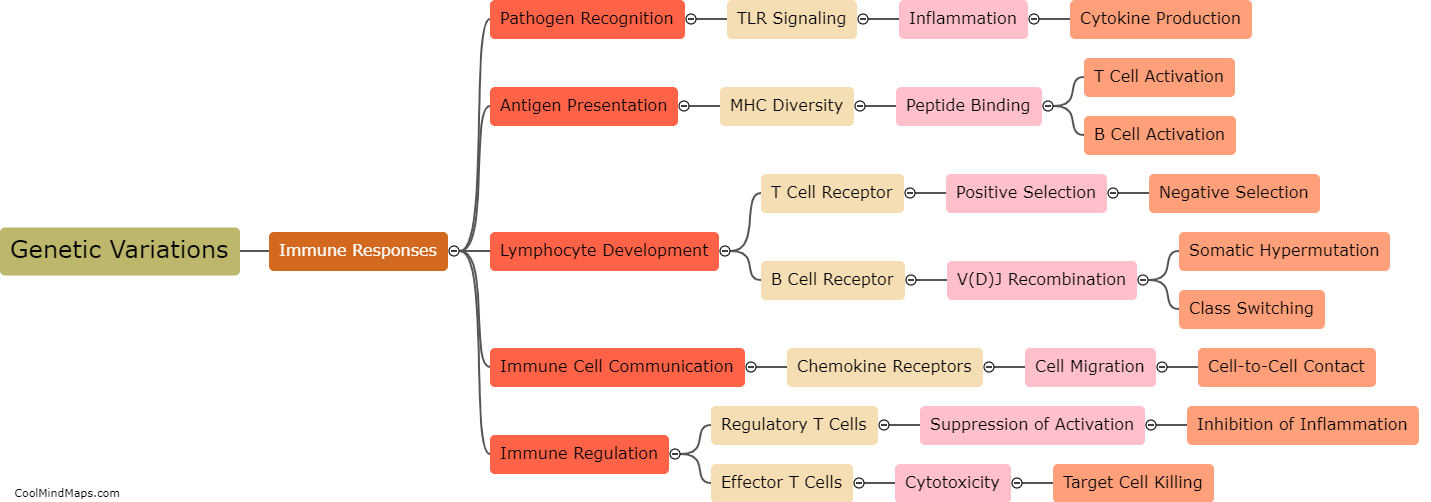
DNA plays a crucial role in immune system development through the genetic information it carries. The immune system relies on DNA to ensure the production of various immune cells and molecules. It starts with the genetic code that determines the structure and function of proteins involved in immune responses. Genes within the DNA sequence encode for these proteins, including antibodies, cytokines, and various cell surface receptors. DNA also contributes to the development of different immune cell types, such as B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells, through a process called V(D)J recombination, where DNA segments are rearranged to produce diverse receptors. Moreover, DNA methylation and chromatin modifications determine gene expression patterns, therefore influencing immune cell differentiation and function. Overall, DNA is an essential component in immune system development, enabling the body to mount effective responses against pathogens and maintain overall health.

This mind map was published on 22 November 2023 and has been viewed 85 times.