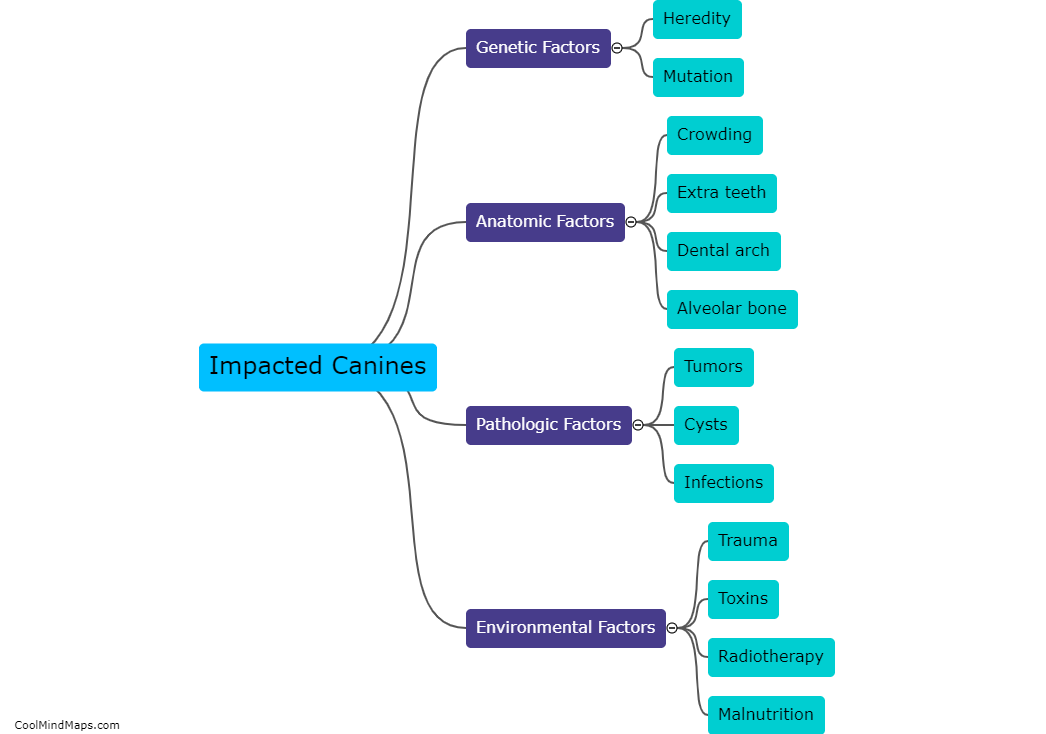
What are etiologic factors of impacted canines?
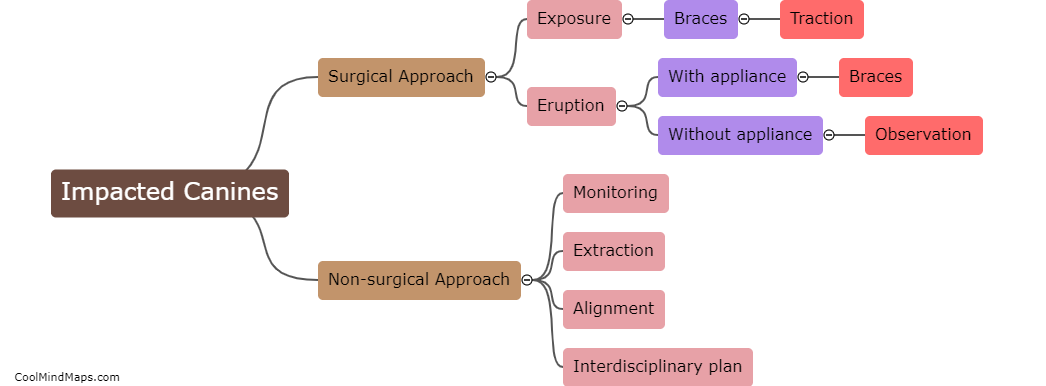
Etiologic factors of impacted canines can include genetic predisposition, inadequate space in the dental arch, early loss or delayed eruption of primary teeth, abnormal growths or cysts in the jawbone, and abnormalities in the positioning and orientation of adjacent teeth. These factors can prevent proper eruption of the canine tooth, leading to impaction and potential dental complications if left untreated. Treatment options typically involve orthodontic intervention to guide the tooth into its correct position.
This mind map was published on 1 May 2023 and has been viewed 92 times.