How do rockets work as a propulsion system?
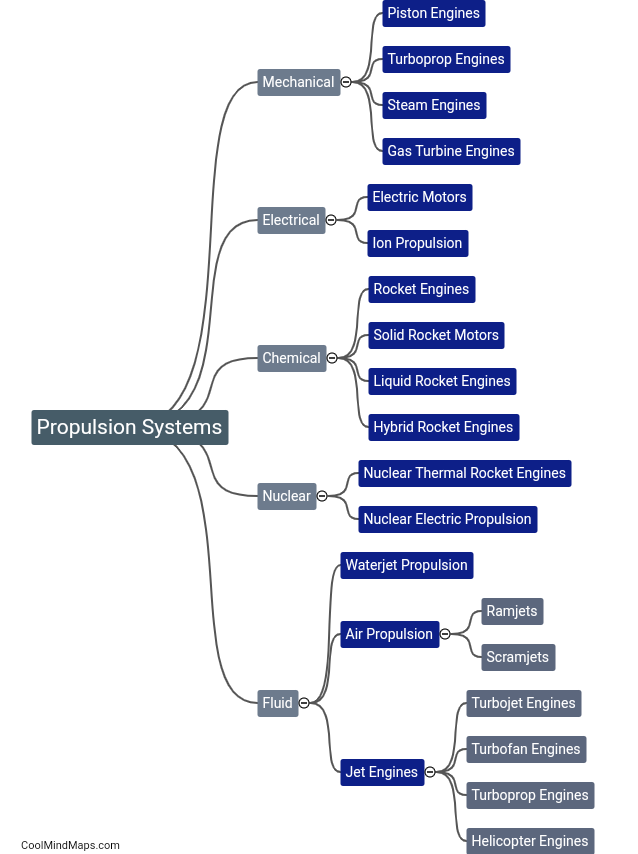
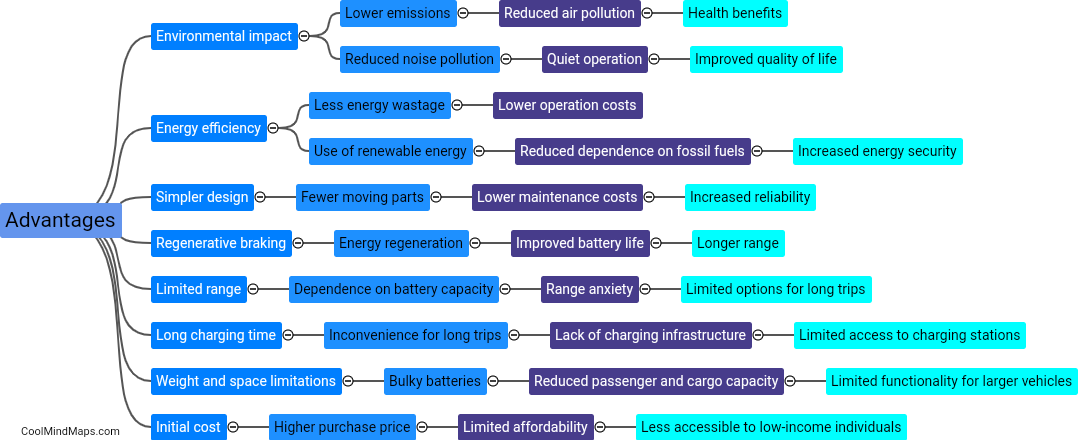
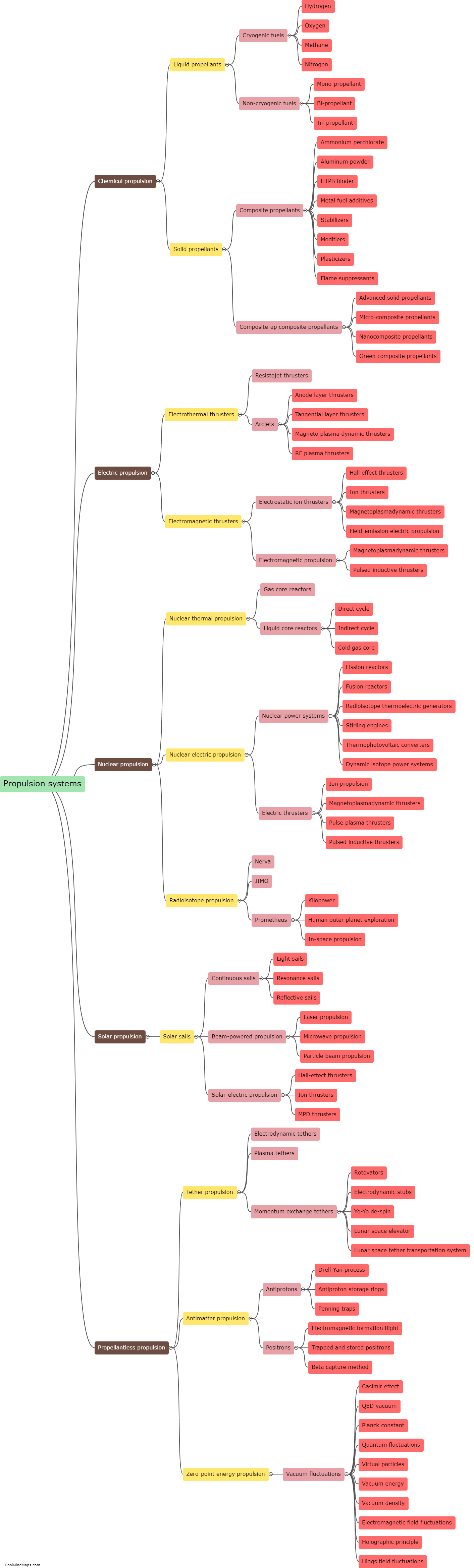
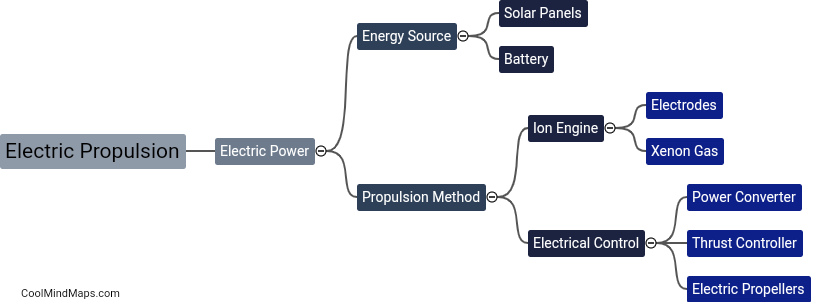
Rockets are a fascinating means of propulsion utilized in space exploration, military applications, and even as a source of entertainment. They function based on the principle of action and reaction, known as Newton's third law of motion. Inside a rocket, both liquid or solid propellants are combined in a combustion chamber and ignited. As the propellants burn, they release immense amounts of hot gas at high speeds, thus exerting an equal and opposite force on the rocket. This force, also known as thrust, propels the rocket forward. Additionally, the shape and design of the rocket, specifically the nozzle at its base, play a crucial role in converting the expanding gases' high pressure and temperature into high velocity exhaust, further enhancing the thrust. Throughout a rocket's journey, various stages may be deployed to optimize efficiency, shedding excess weight by detaching empty fuel tanks. Whether it's harnessing the power of chemical reactions or relying on the principles of physics, rockets continue to shape our understanding of space and push the boundaries of exploration.

This mind map was published on 30 July 2023 and has been viewed 134 times.