How is the Indian constitution structured?
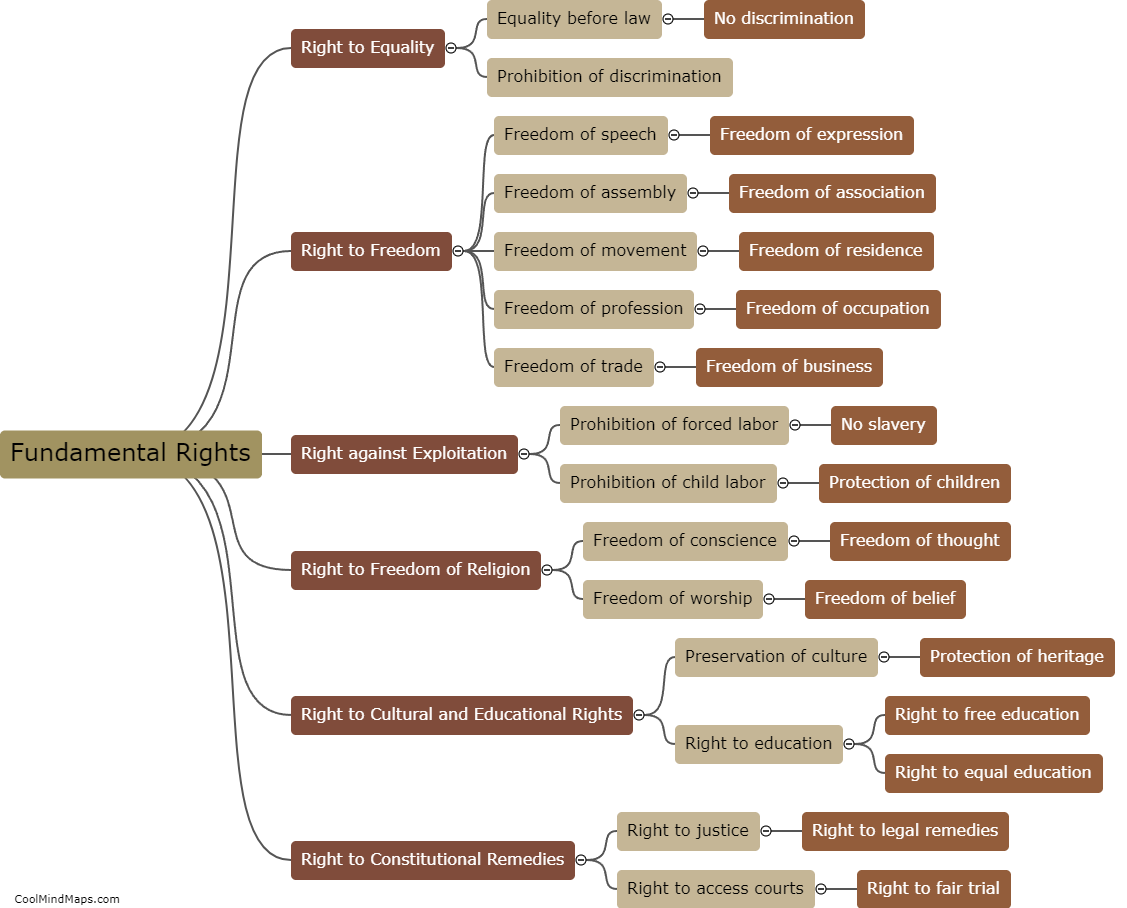
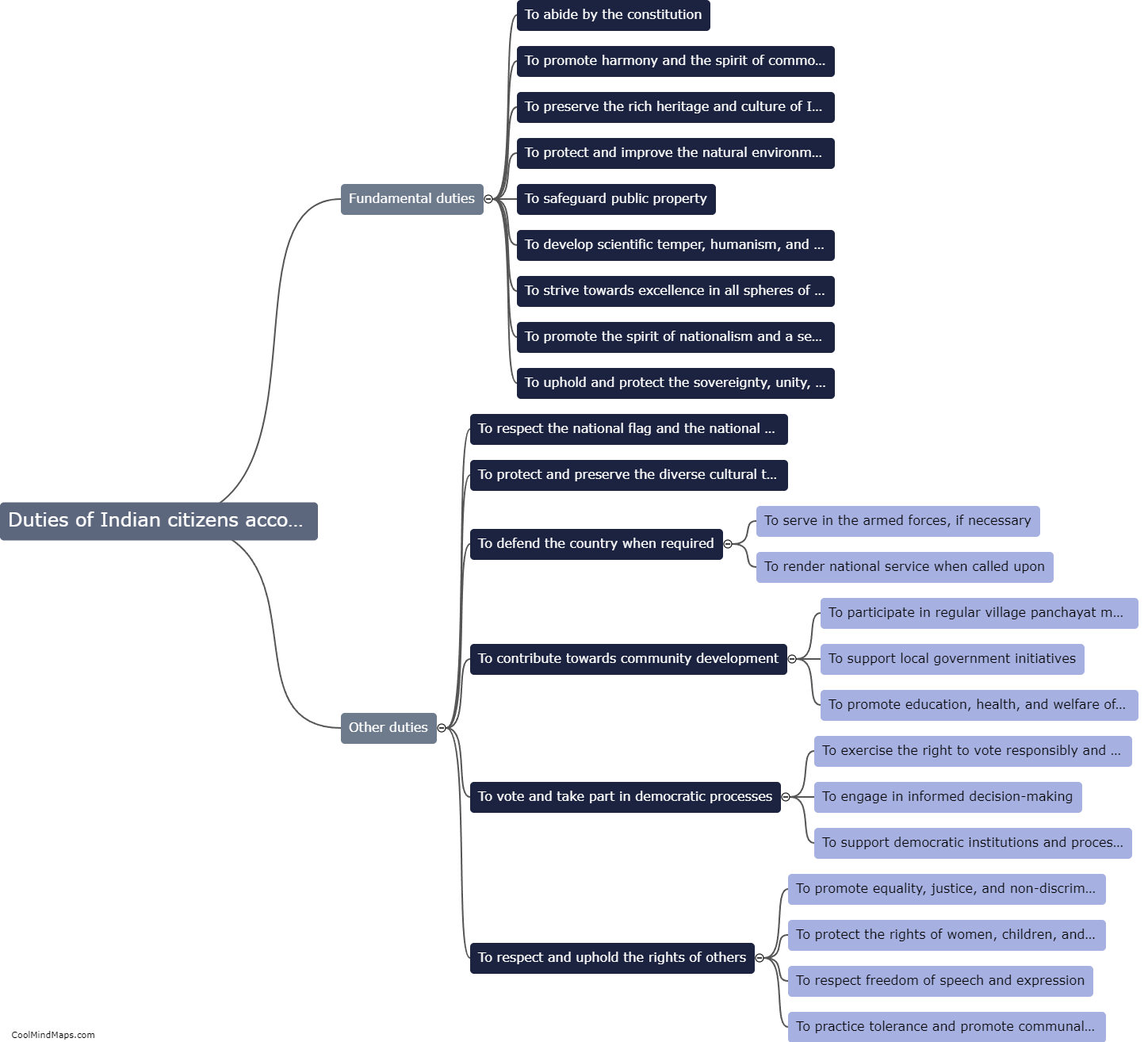
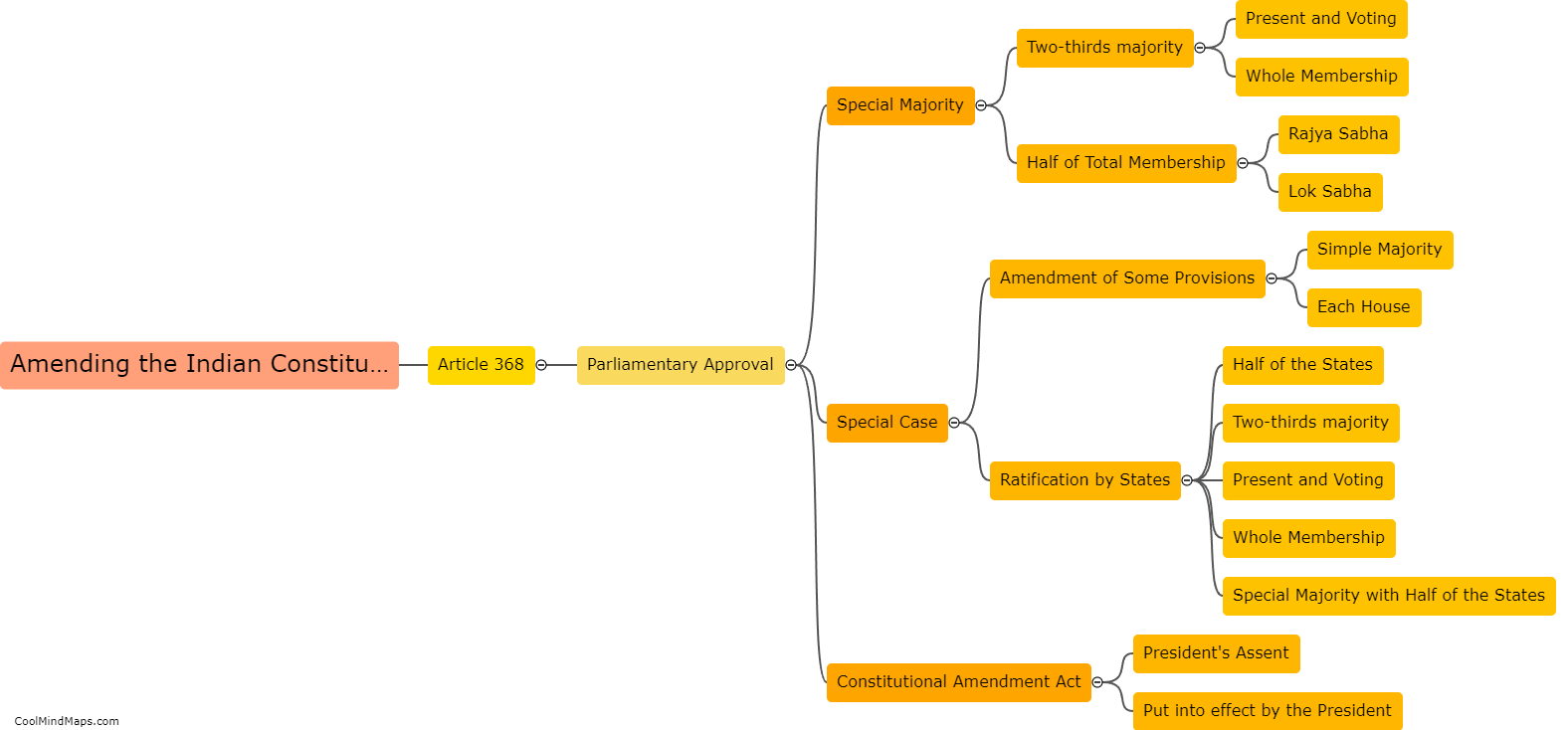
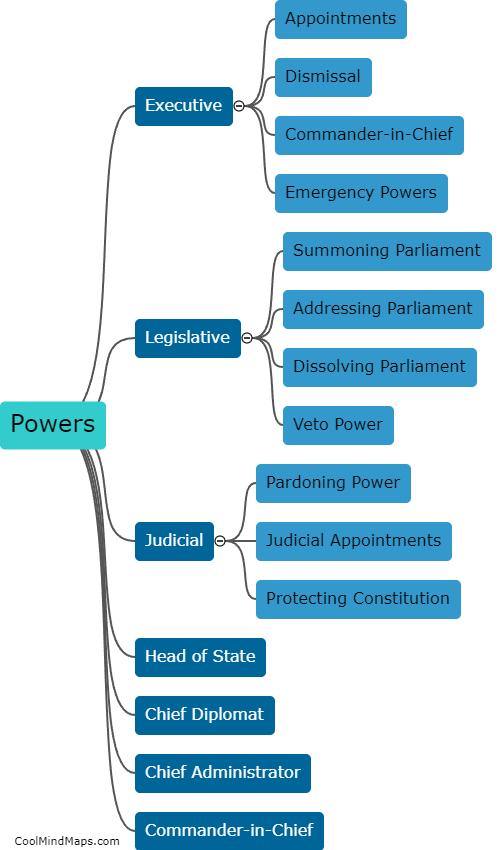
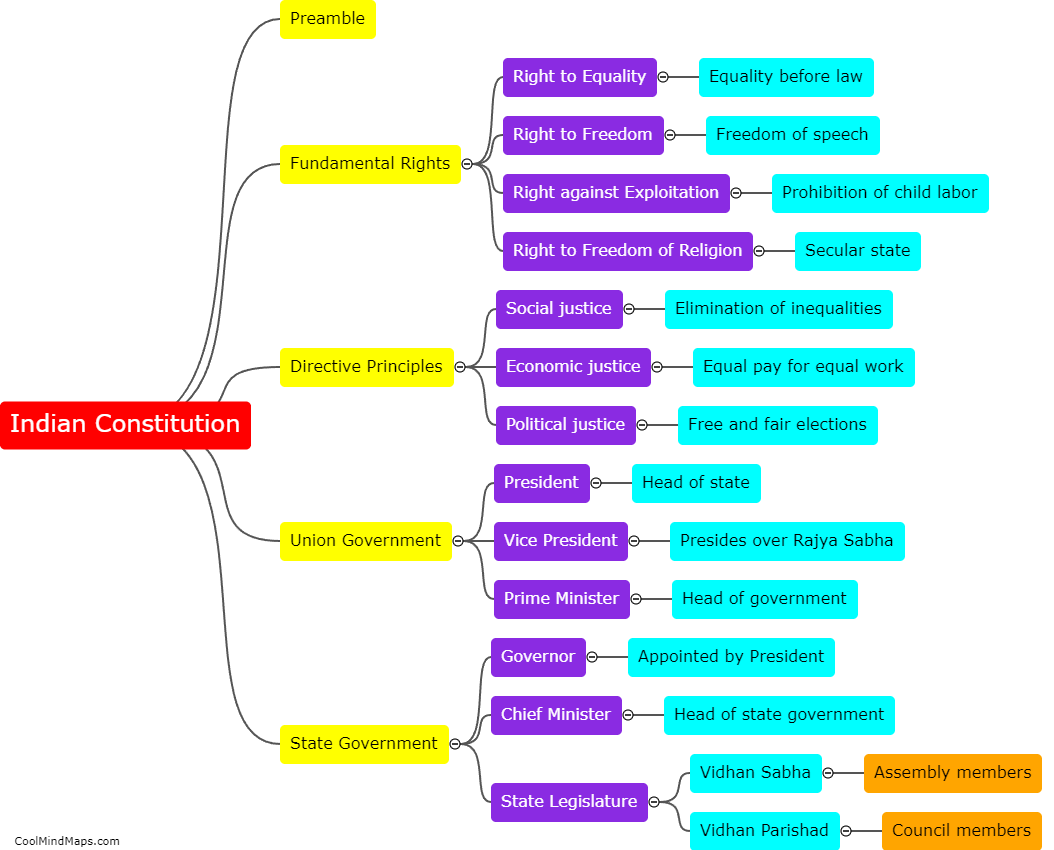
The Constitution of India, adopted on January 26, 1950, is a comprehensive and elaborate document that is the supreme law of the country. It serves as a framework for the governance and functioning of the Indian government. The Indian constitution is structured in a way that outlines the powers and functions of the three branches of government - the Legislature, the Executive, and the Judiciary. The legislative branch consists of the Parliament, which is further divided into the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the People). The executive branch comprises the President, who is the head of state, and the Prime Minister, who is the head of government. The judiciary, on the other hand, is independent and consists of the Supreme Court, High Courts, and other subordinate courts. Additionally, the constitution establishes fundamental rights, directive principles, and fundamental duties that safeguard the liberties and promote social justice for all citizens. The Indian constitution is considered one of the longest and most comprehensive constitutions in the world.
This mind map was published on 9 October 2023 and has been viewed 98 times.