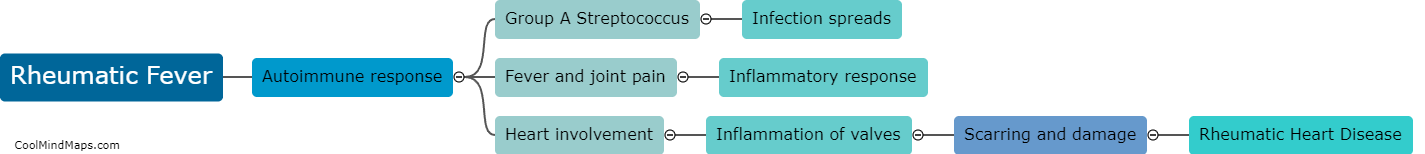
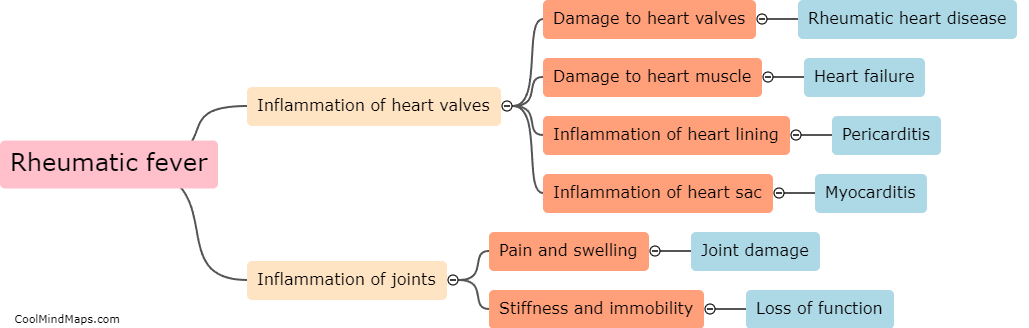
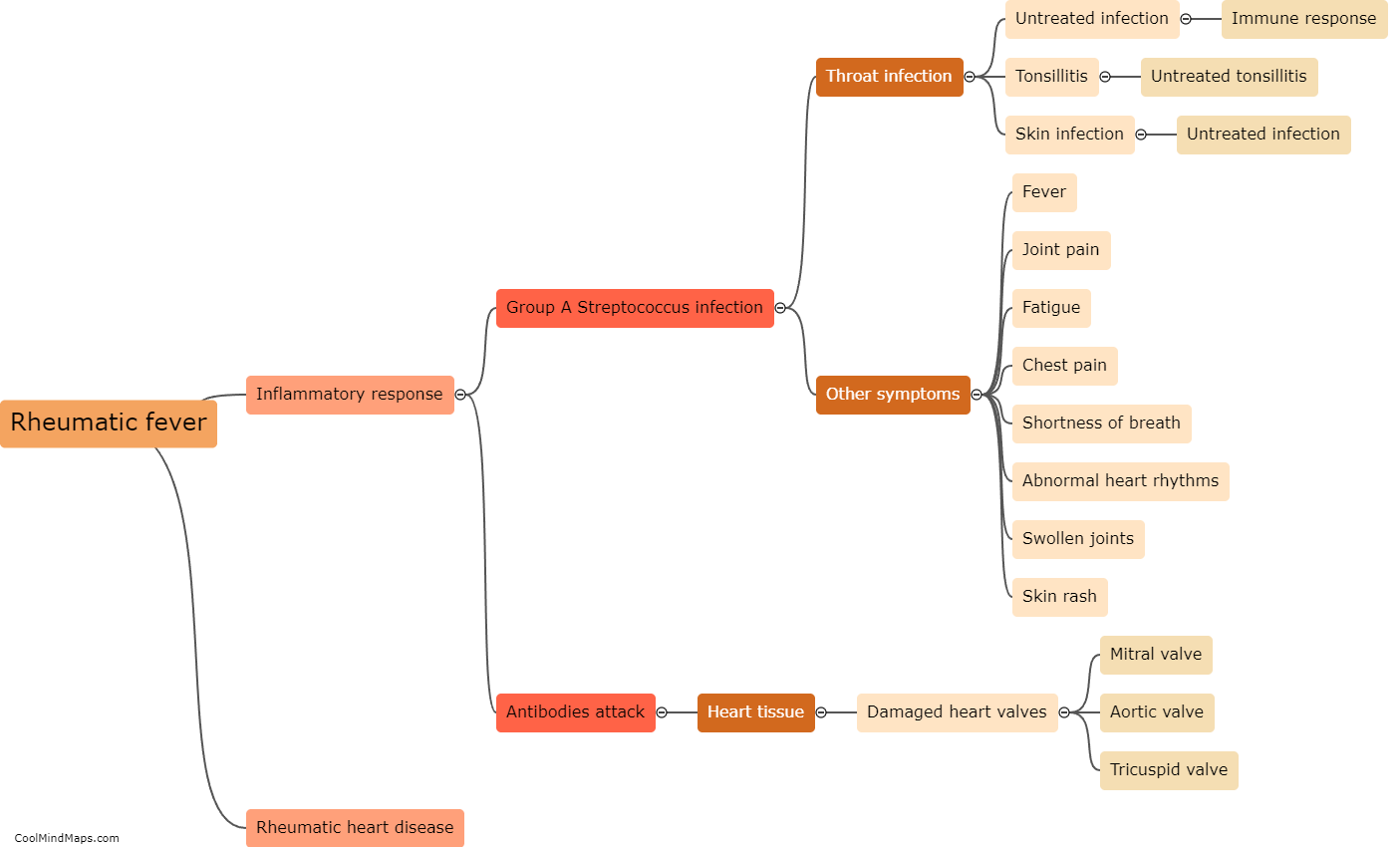
What is the progression from Rheumatic fever to Rheumatic heart disease?
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can occur after an untreated or inadequately treated Group A streptococcal infection, such as strep throat. If left untreated, rheumatic fever can lead to the development of rheumatic heart disease. The progression from rheumatic fever to rheumatic heart disease involves the inflammation of the heart valves, particularly the mitral valve, due to an autoimmune reaction triggered by the streptococcal bacteria. Over time, repeated episodes of rheumatic fever can cause scarring and thickening of the heart valves, which leads to valve dysfunction, such as stenosis or regurgitation. This can result in symptoms like heart murmurs, chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and ultimately, complications such as heart failure or infective endocarditis. Early diagnosis, prompt treatment of streptococcal infections with antibiotics, and regular follow-up can help prevent or slow down the progression to rheumatic heart disease.
This mind map was published on 17 October 2023 and has been viewed 91 times.