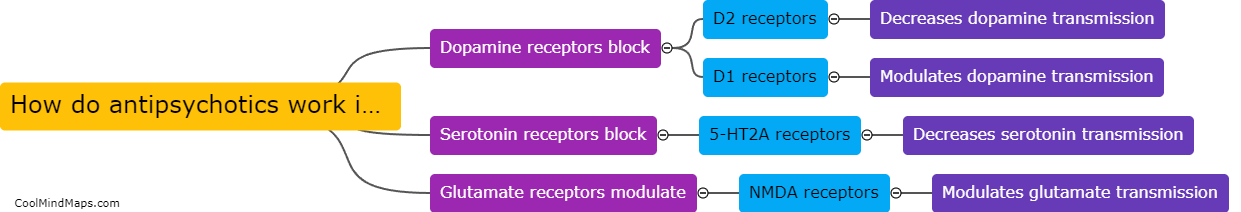
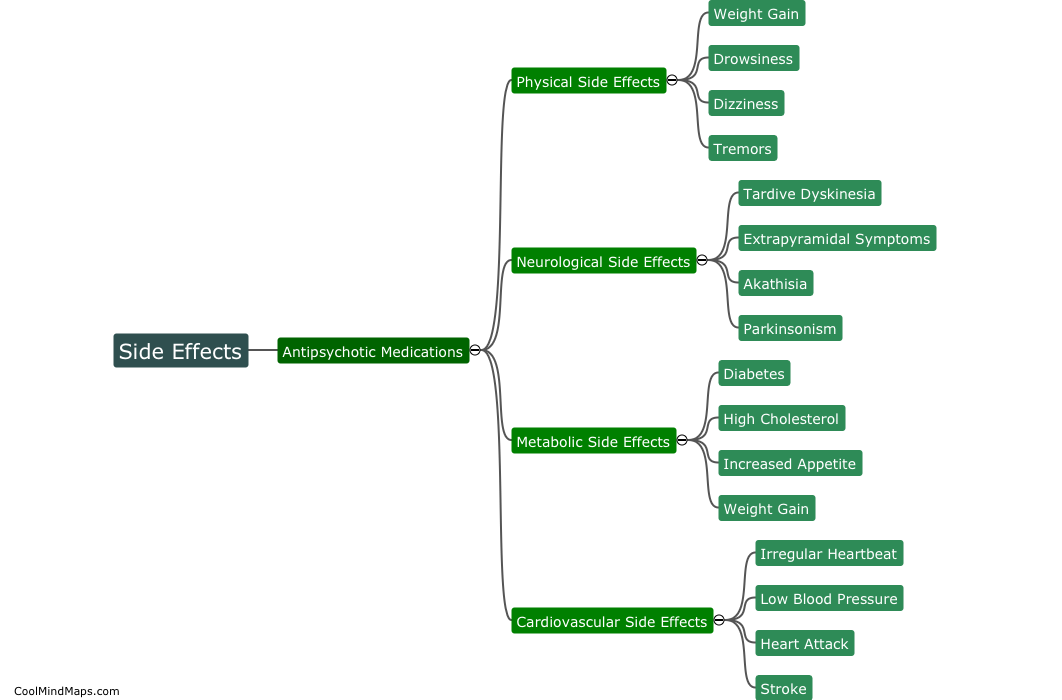
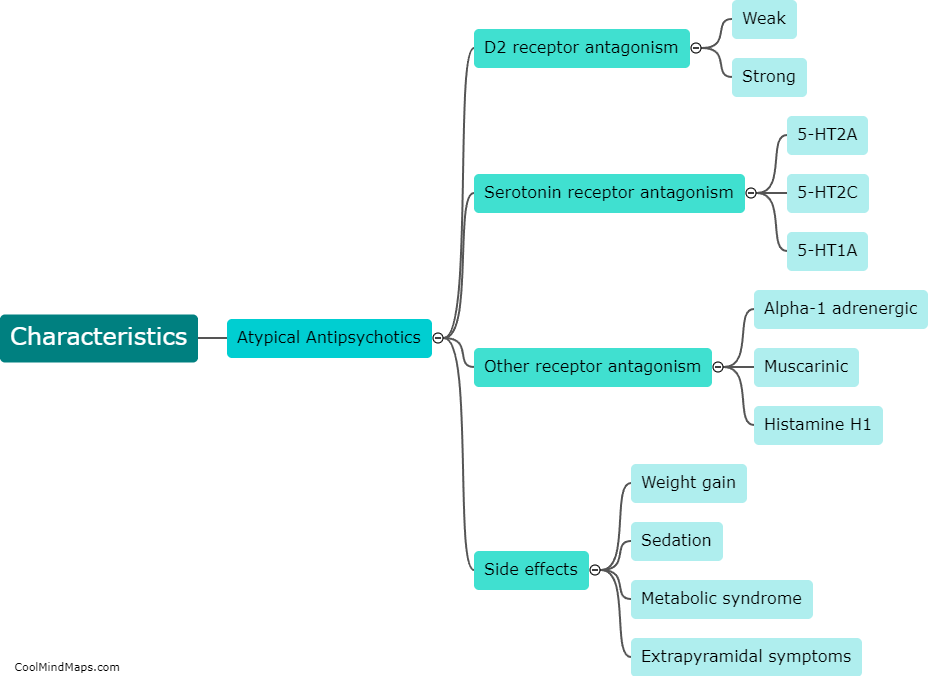
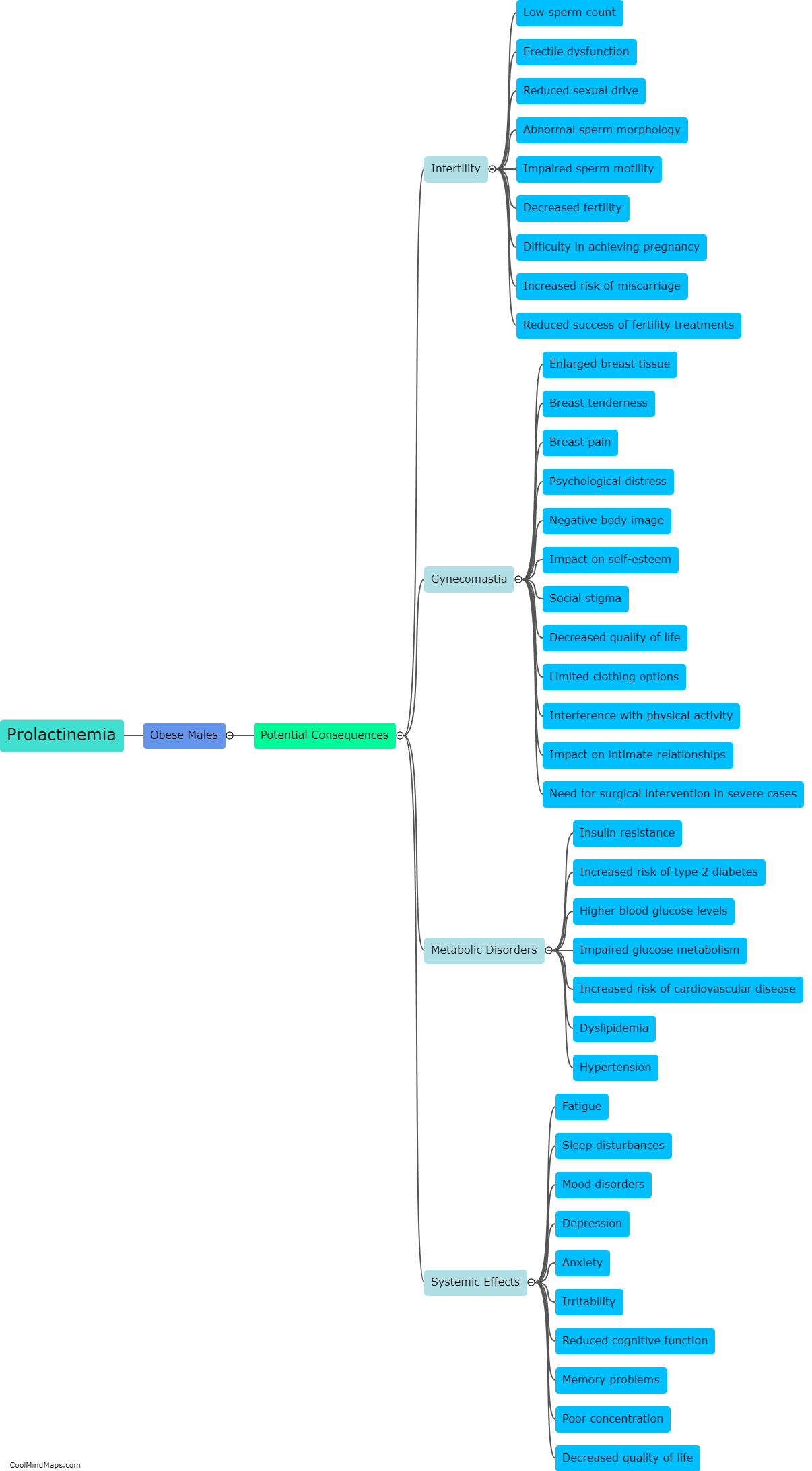
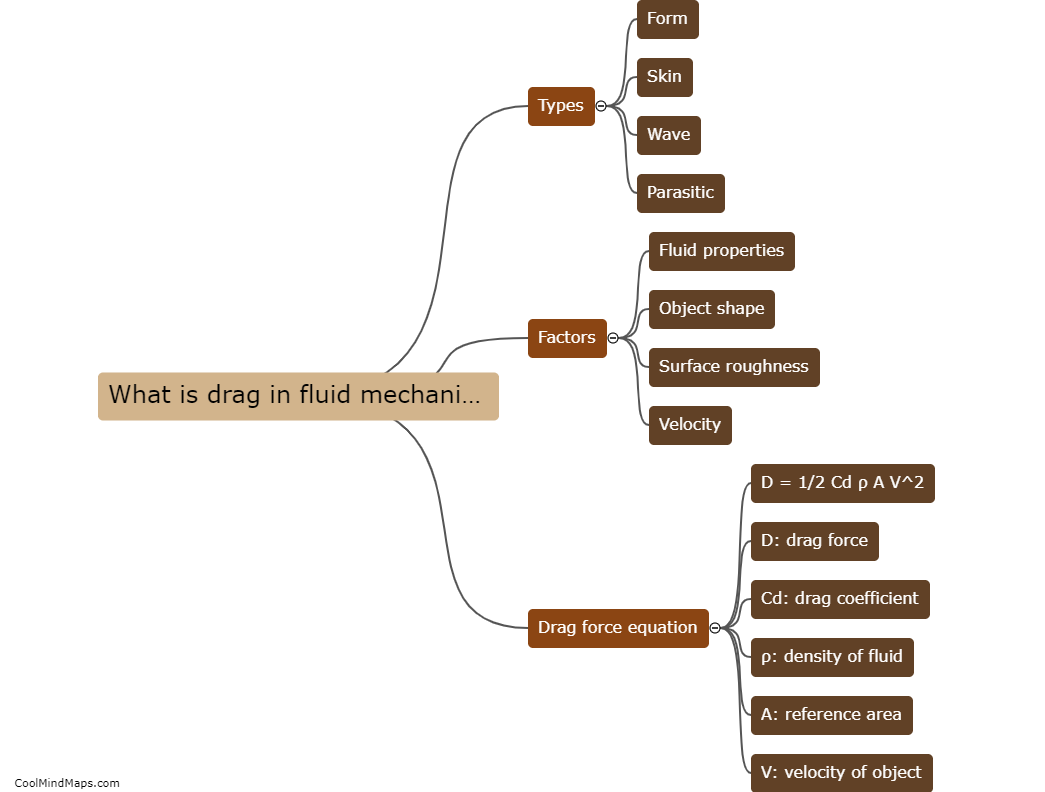
What is drag in fluid mechanics?
In fluid mechanics, drag refers to the force exerted by a fluid on an object moving through it, which opposes the motion of the object. It is a result of the interaction between the object and the fluid, and is influenced by several factors such as the shape and size of the object, its velocity, and the properties of the fluid. Drag can be categorized into two types: viscous drag and pressure drag. Viscous drag arises from the friction between the fluid and the surface of the object, while pressure drag occurs due to the pressure differences around the object. Understanding drag is crucial in various engineering fields, such as aerodynamics, hydrodynamics, and automotive design, as it affects the efficiency, performance, and stability of objects moving through fluids.
This mind map was published on 4 July 2023 and has been viewed 168 times.