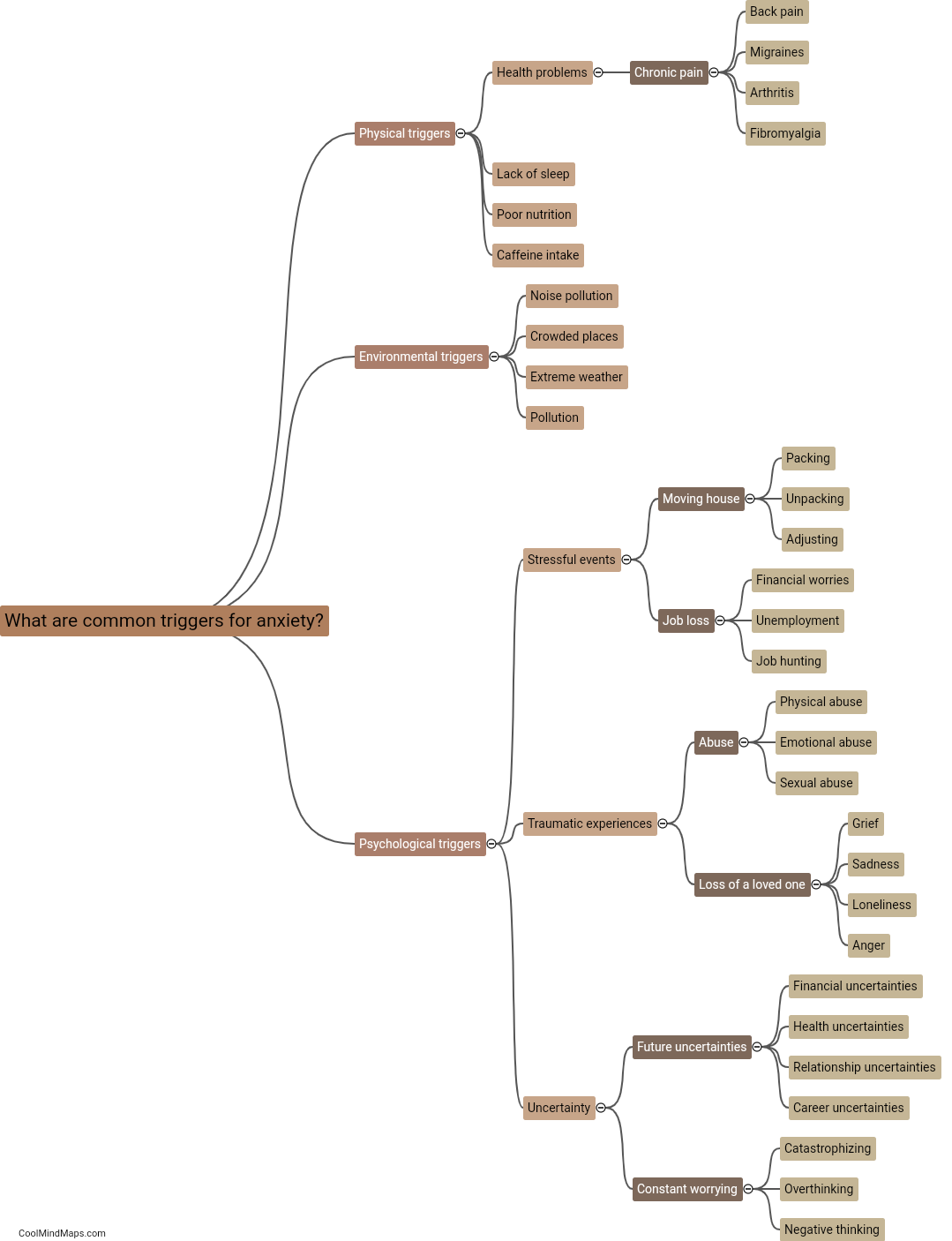
How does the central nervous system modulate chronic pain?
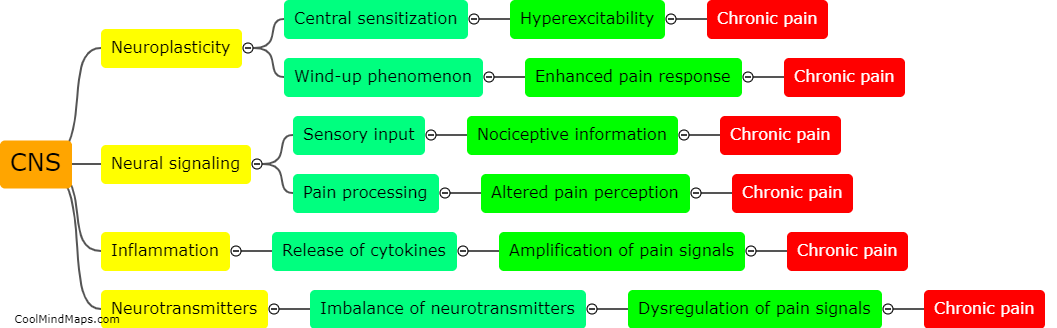
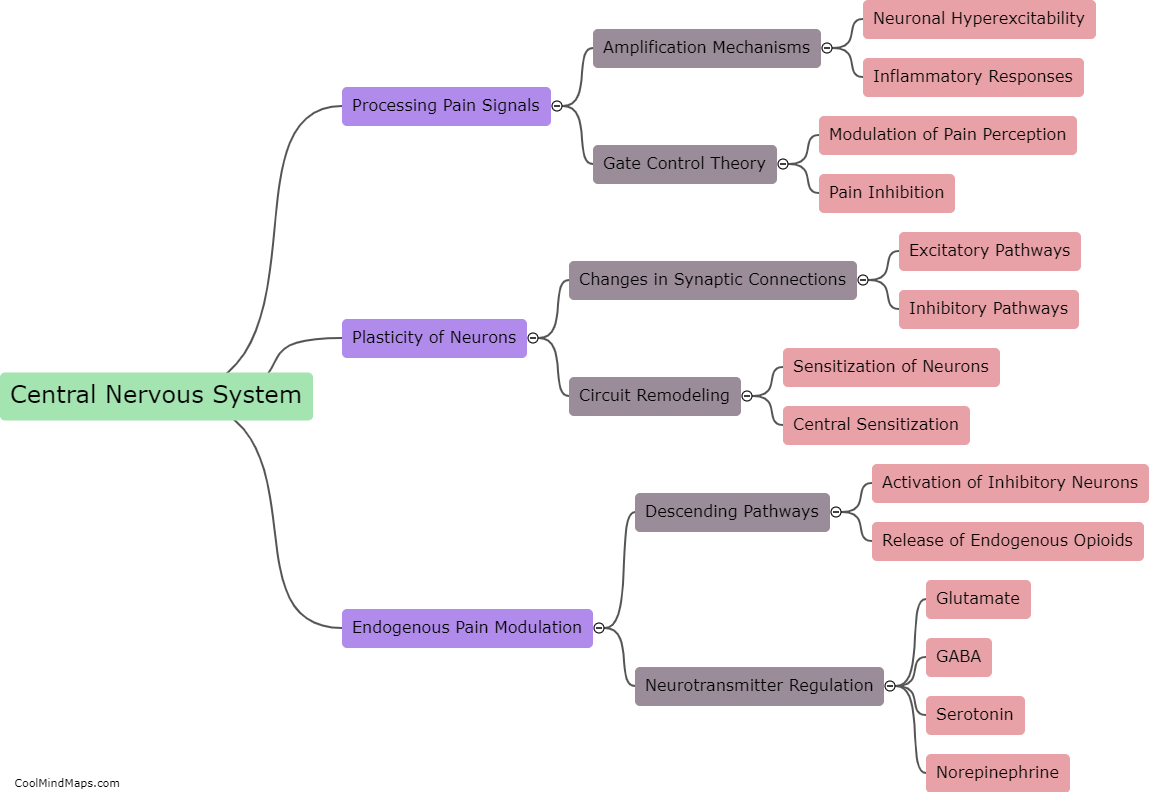
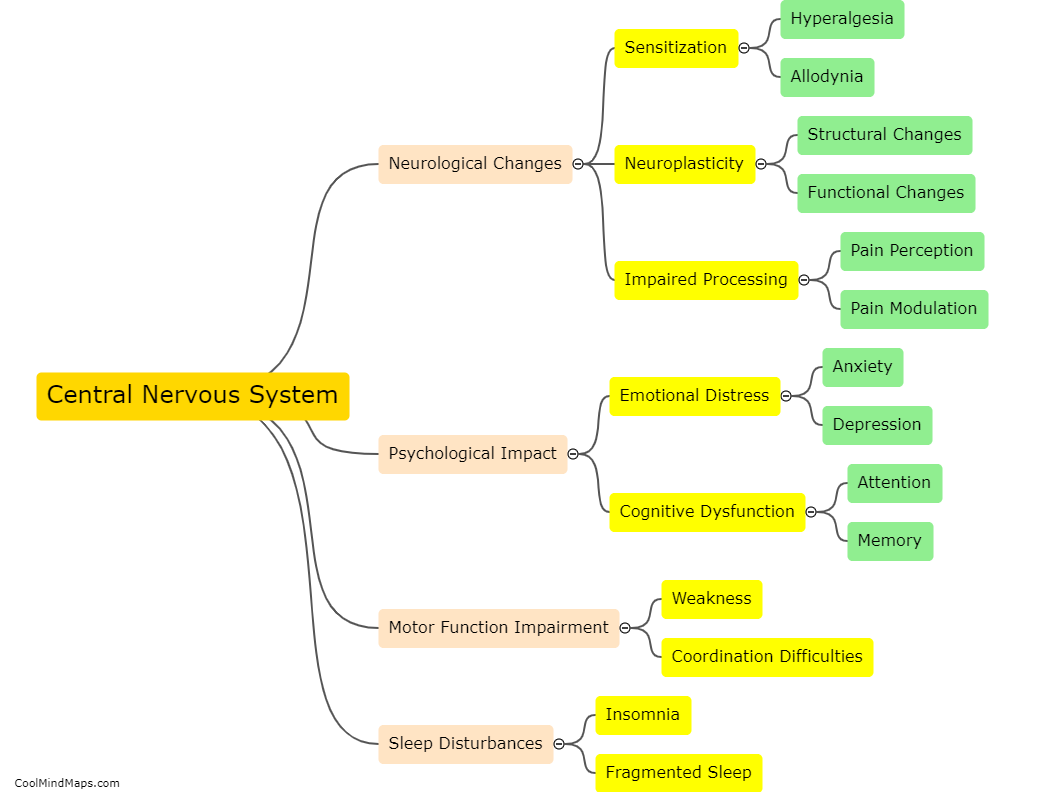
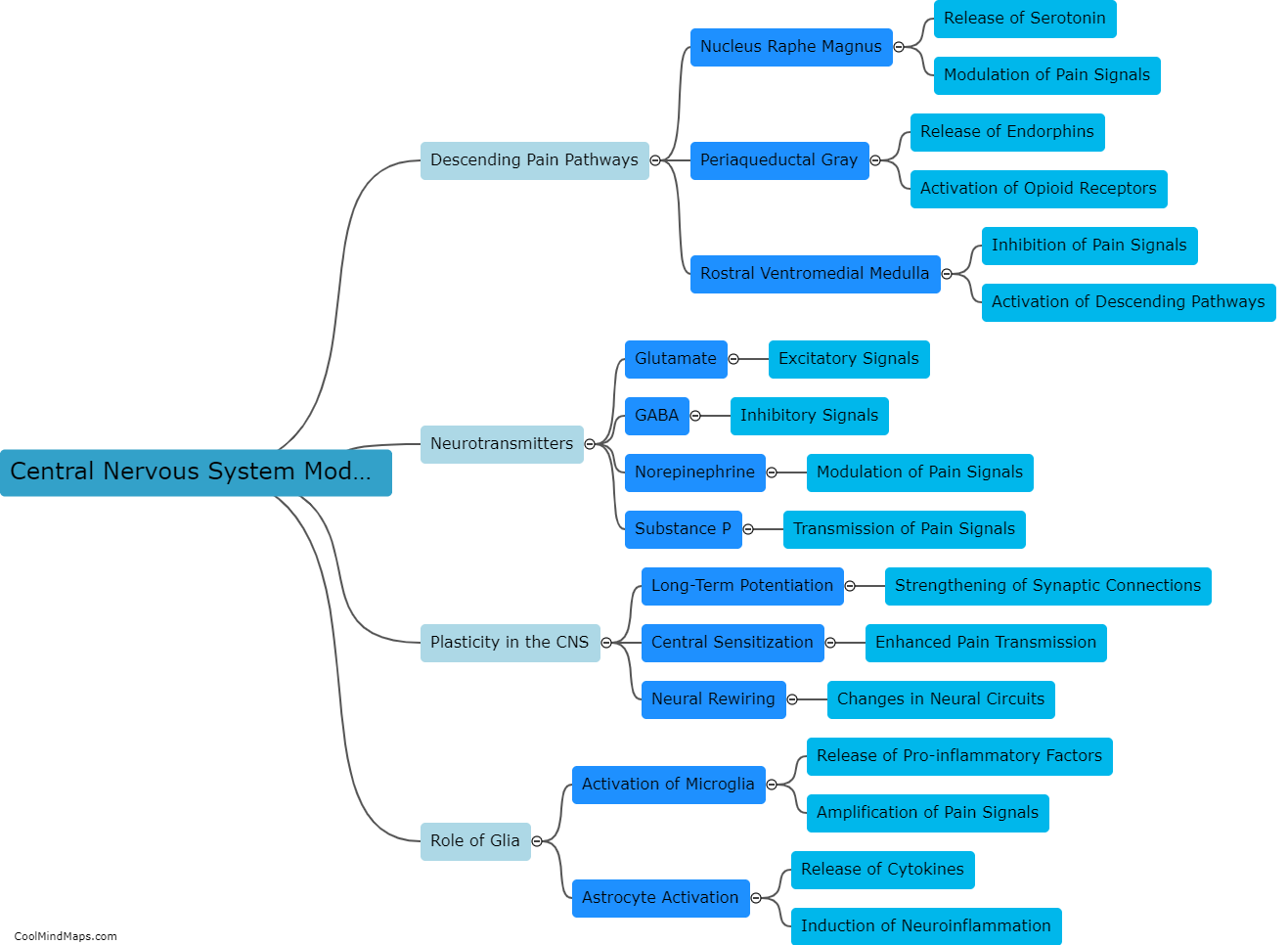
The central nervous system (CNS) plays a crucial role in modulating chronic pain. Chronic pain refers to persistent pain that lasts beyond the normal healing time and can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life. The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, which work together to process and interpret pain signals. In chronic pain, the CNS undergoes changes in its structure and function. These changes can result in amplified pain signals being transmitted to the brain, leading to heightened pain perception. Additionally, the CNS is involved in the release of neurotransmitters and the activation of various pain pathways, such as the descending pain modulation pathway. This pathway can further amplify or inhibit pain signals, thereby influencing the overall perception of chronic pain. Understanding how the CNS modulates chronic pain is vital in developing effective interventions and treatments to alleviate this debilitating condition.
This mind map was published on 2 December 2023 and has been viewed 86 times.