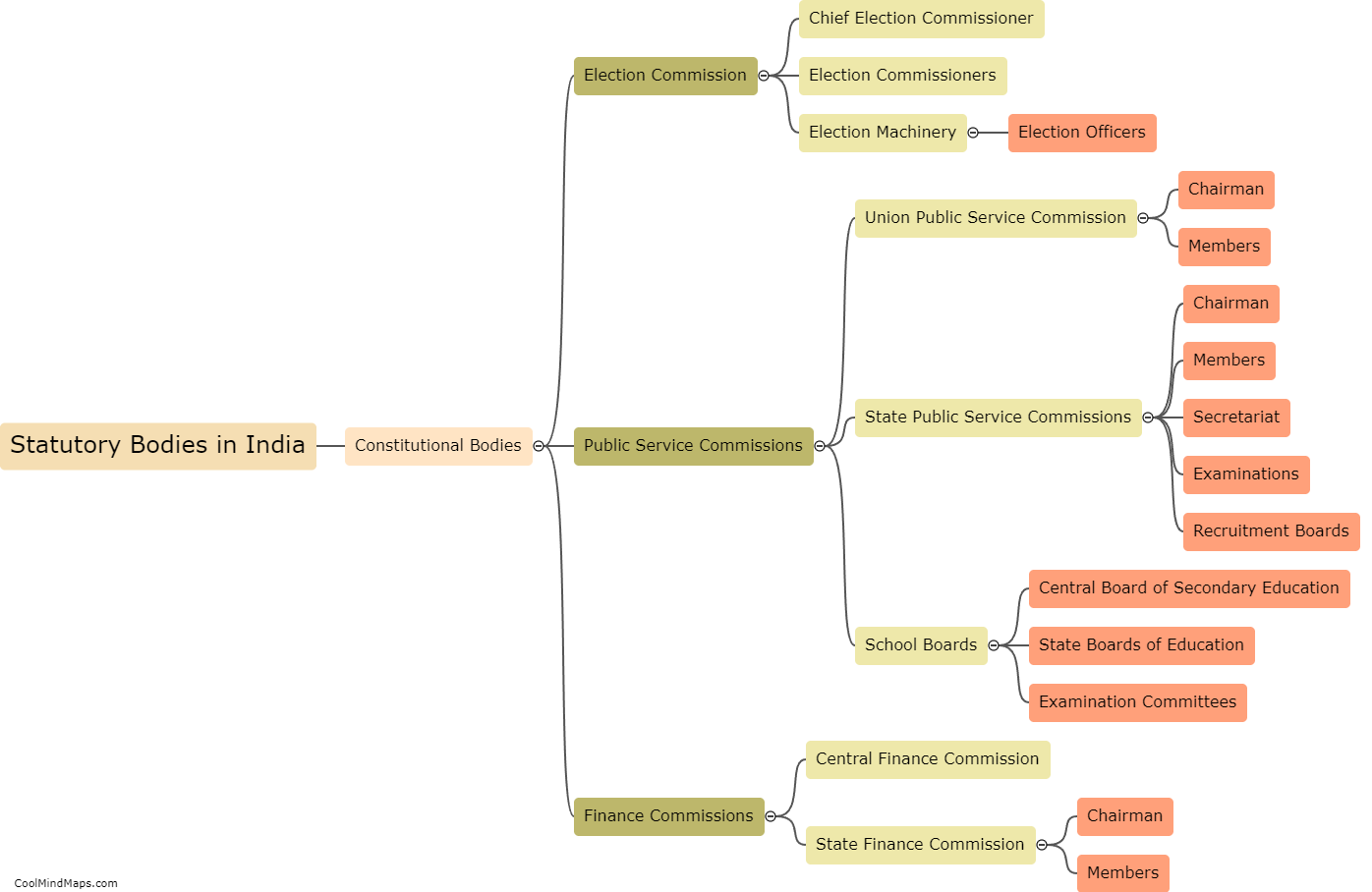
What are statutory bodies in India?
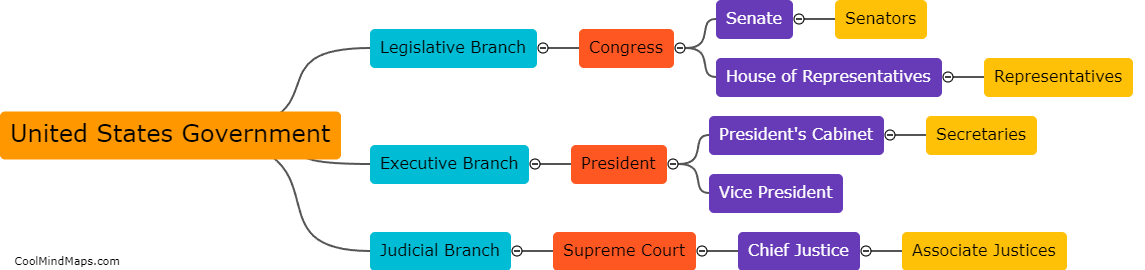
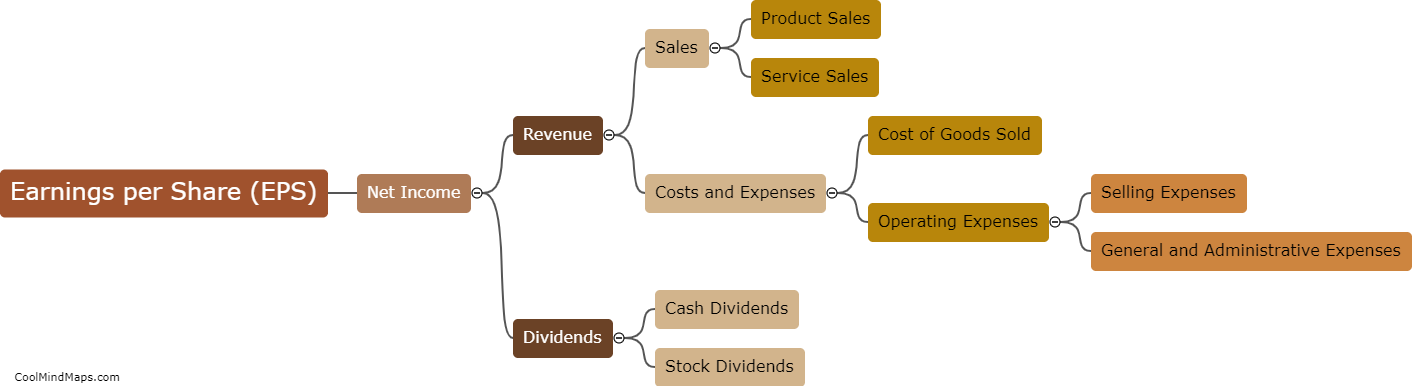
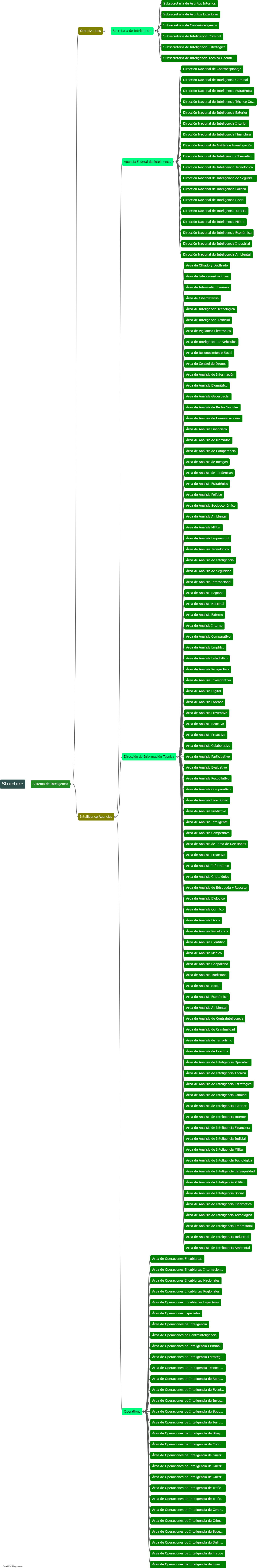
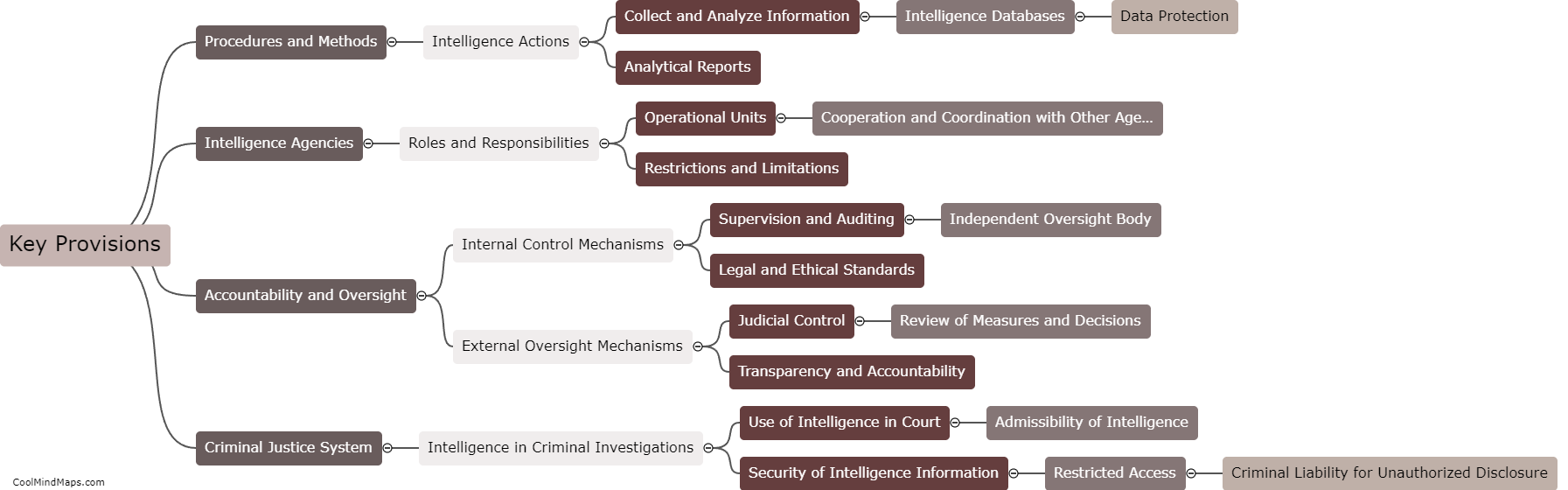
Statutory bodies in India refer to organizations that have been established by an Act of Parliament or State Legislature. These bodies are given specific powers and responsibilities to regulate and control various sectors and aspects of governance. They operate independently and are empowered to make decisions on policies, rules, and regulations within their designated domain. Examples of these bodies include the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), and Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI). Statutory bodies play a crucial role in implementing and enforcing laws, ensuring transparency, and safeguarding the interests of the public in their respective areas of operation.
This mind map was published on 7 September 2023 and has been viewed 98 times.