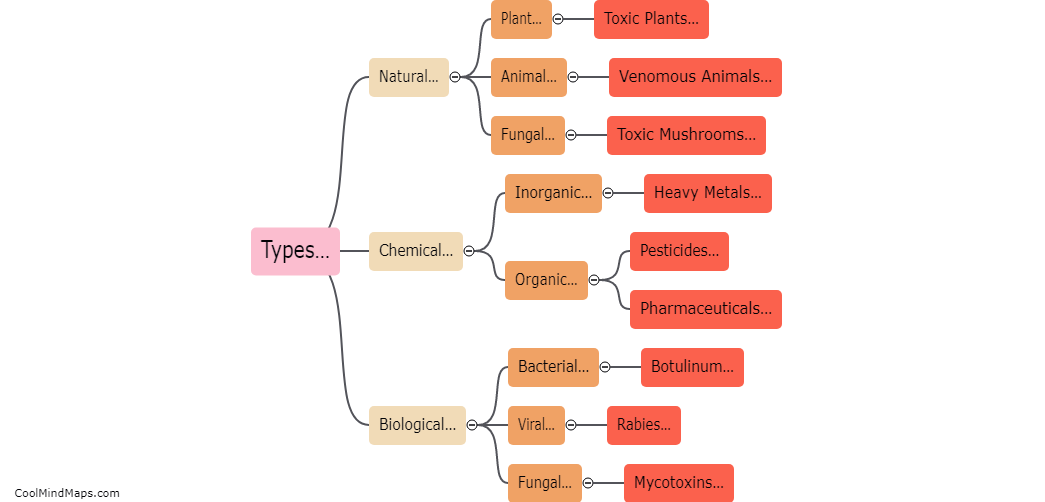
How does poison affect the human body?
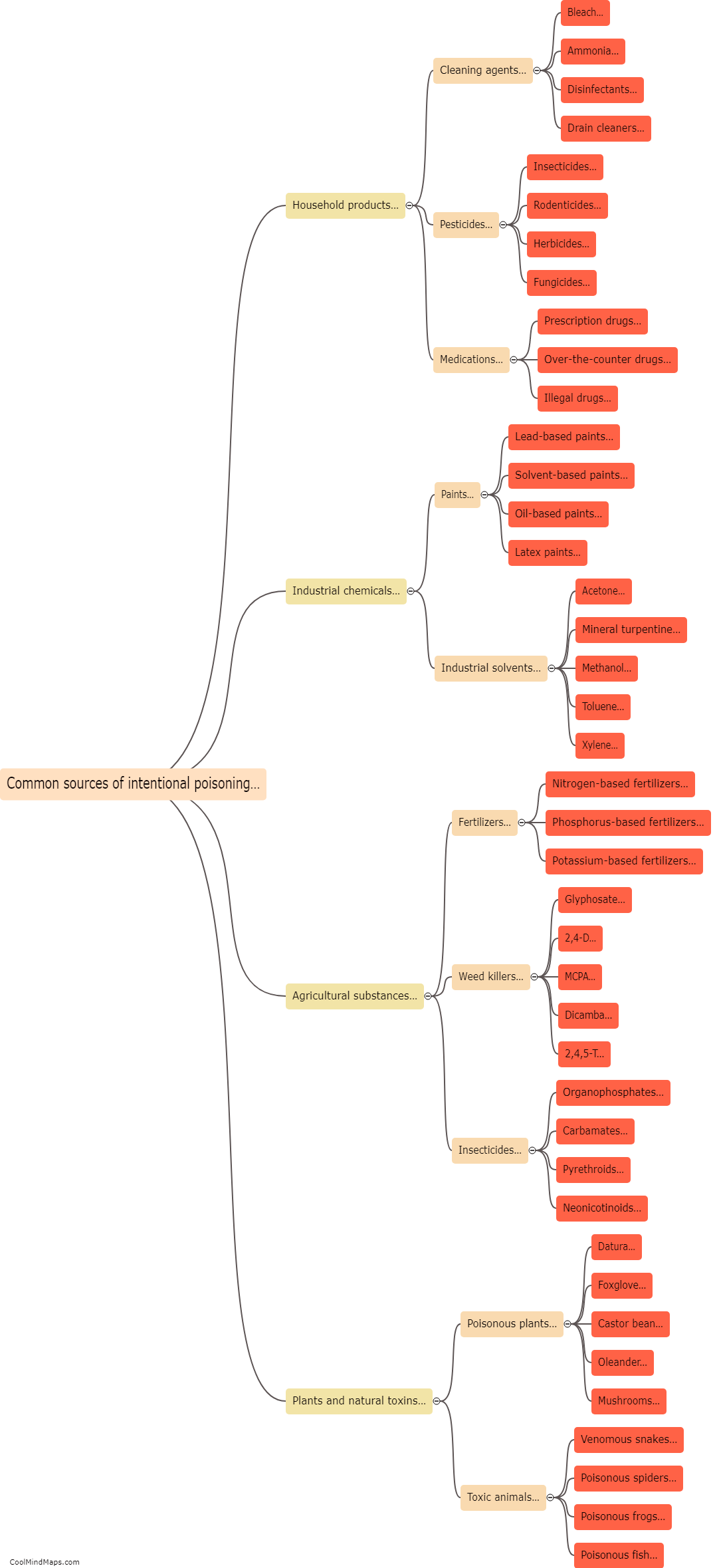
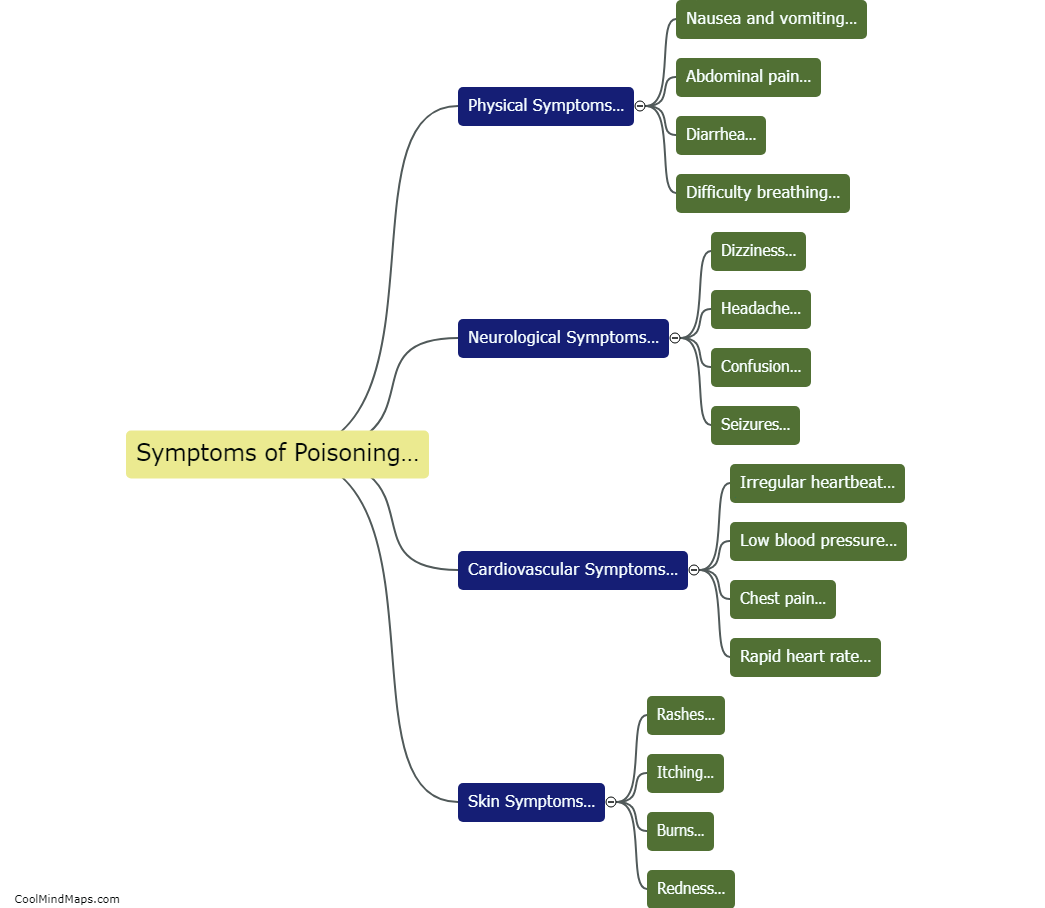
When poison enters the human body, it can have a wide range of detrimental effects on various organs and systems. The exact impact depends on the type and amount of poison involved. For example, certain toxins may cause immediate symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or difficulty breathing. Others may act slowly over time, accumulating within the body and causing chronic illnesses or organ damage. Poisonous substances can interfere with the normal functioning of cells, disrupt vital chemical reactions, or inhibit enzymes, leading to imbalances that can be fatal. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention in case of suspected poisoning, as timely intervention can help mitigate the damage and potentially save a life.

This mind map was published on 3 December 2023 and has been viewed 100 times.