What are the main principles of Ibn Sina's philosophy?
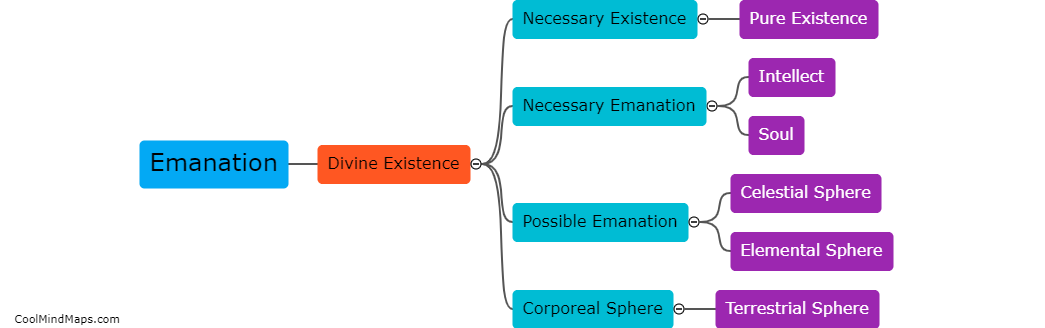
Ibn Sina, also known as Avicenna, was a prominent Persian philosopher and physician during the Islamic Golden Age. His philosophy encompassed various areas of knowledge including metaphysics, epistemology, ethics, and physics. One of the main principles of Ibn Sina's philosophy is his emphasis on the existence of a necessary being, which he referred to as the "First Cause" or "God." He argued that this necessary being is the origin of all existence and is the ultimate source of knowledge and truth. Another key principle is Ibn Sina's theory of knowledge, which combines rationalism and empiricism. According to him, true knowledge can be obtained through both reason and sensory perception, and he believed in the power of reason to uncover universal truths about reality. Additionally, Ibn Sina's philosophy stresses the importance of ethics and the attainment of individual happiness. He believed that individuals should strive to achieve a balance between the physical and spiritual aspects of their existence, by leading a virtuous life and cultivating moral virtues such as wisdom, moderation, and justice. Overall, Ibn Sina's philosophy is characterized by his unique amalgamation of Islamic theology, Aristotelian philosophy, and Neoplatonic elements.

This mind map was published on 28 January 2024 and has been viewed 148 times.