What are the steps of the Krebs cycle?
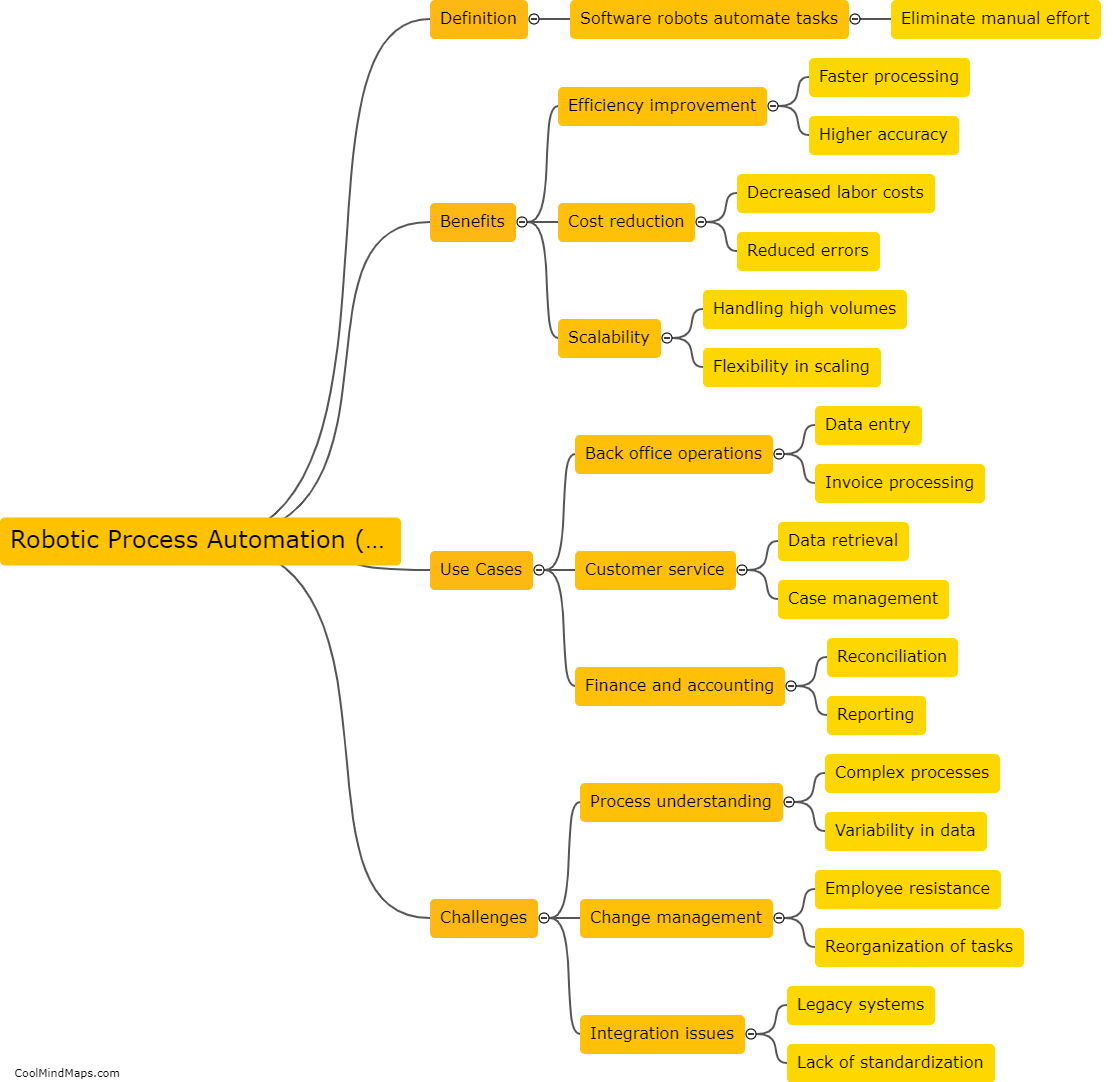
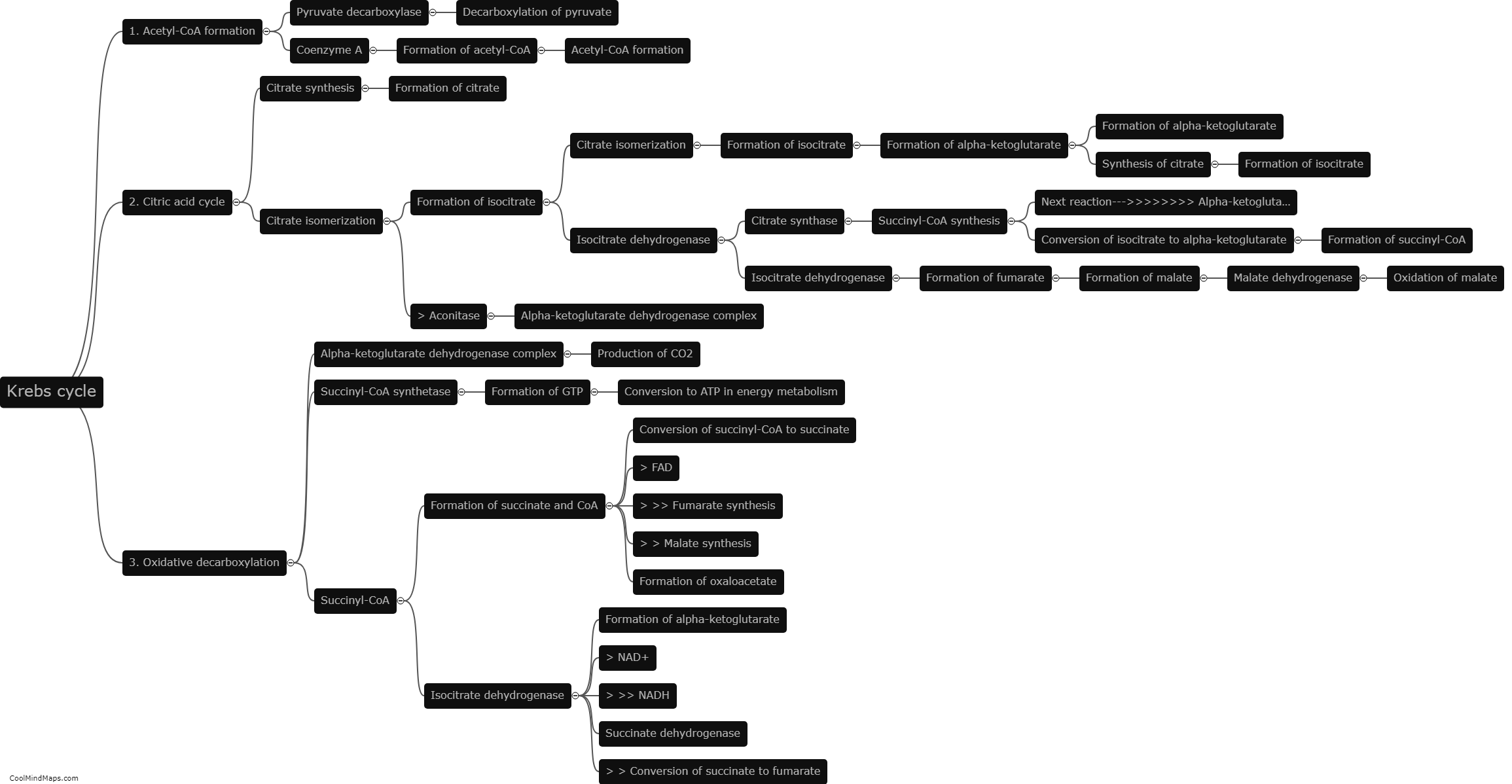
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle, is a vital part of cellular respiration. It takes place in the mitochondria and is responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP. The cycle begins with the entry of acetyl-CoA, a two-carbon compound derived from the breakdown of glucose and fatty acids, into the cycle. Acetyl-CoA then combines with a four-carbon compound to form a six-carbon compound called citrate. In subsequent steps, citrate undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions, including isomerization and decarboxylation, resulting in the regeneration of the four-carbon compound and the production of NADH and FADH2, which carry high-energy electrons. These electron carriers then transfer the electrons to the electron transport chain, leading to the production of ATP. Overall, the Krebs cycle is a cyclical process that extracts energy-rich electrons from carbon fuels and plays a crucial role in the energy metabolism of living organisms.
This mind map was published on 27 January 2024 and has been viewed 76 times.