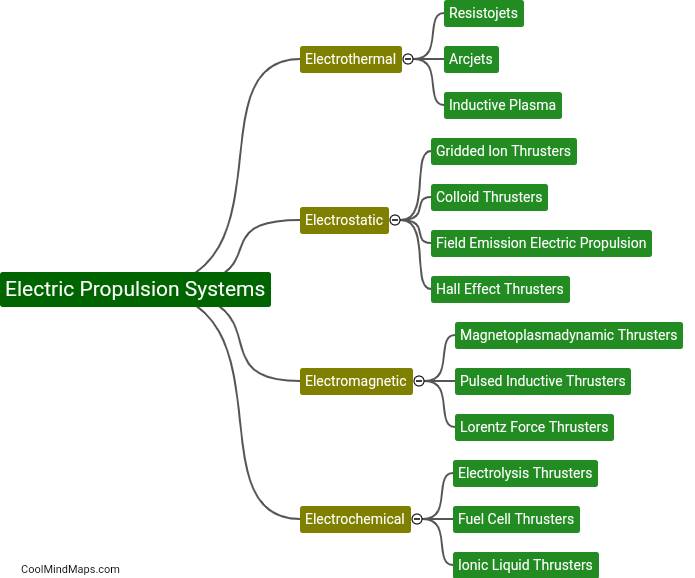
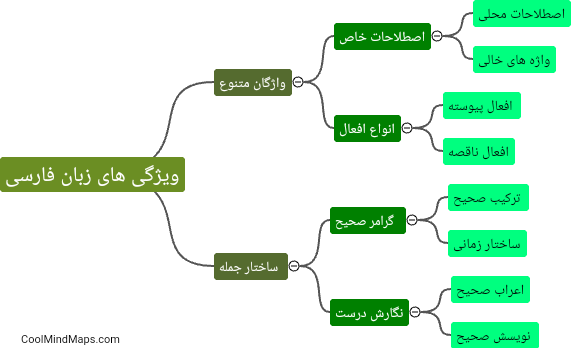
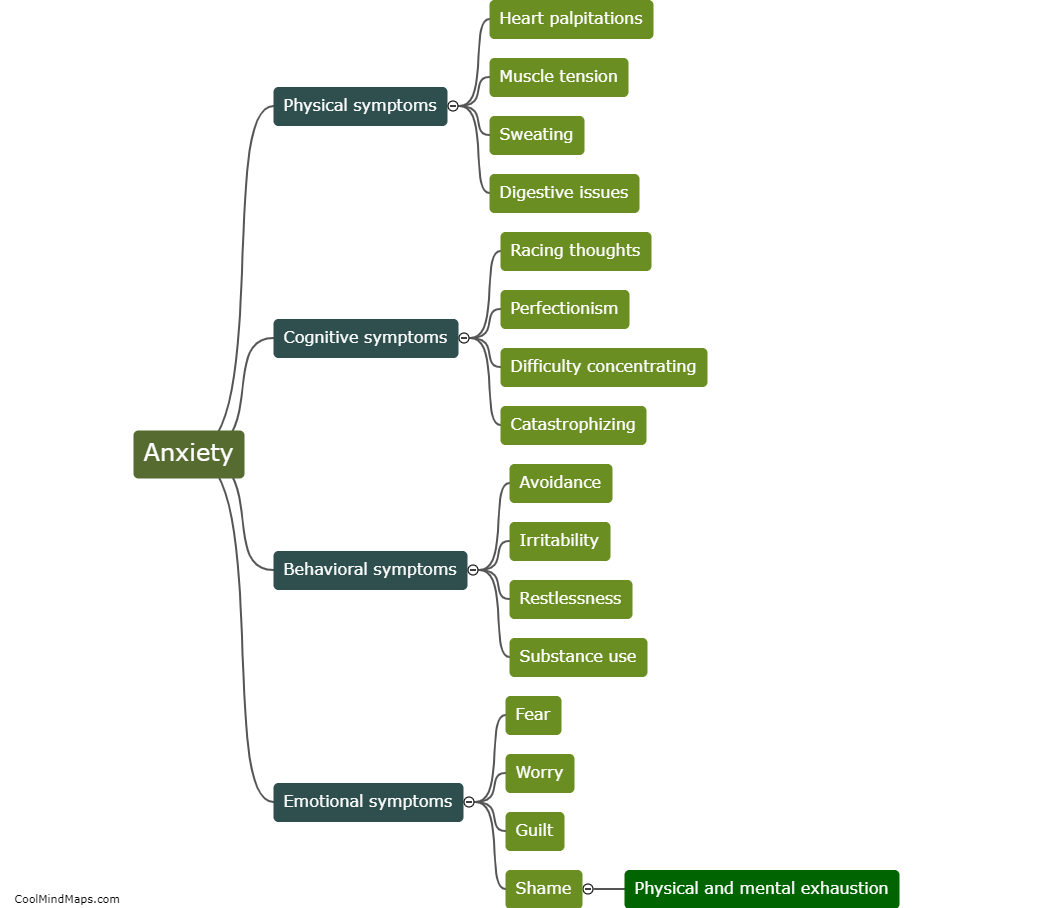
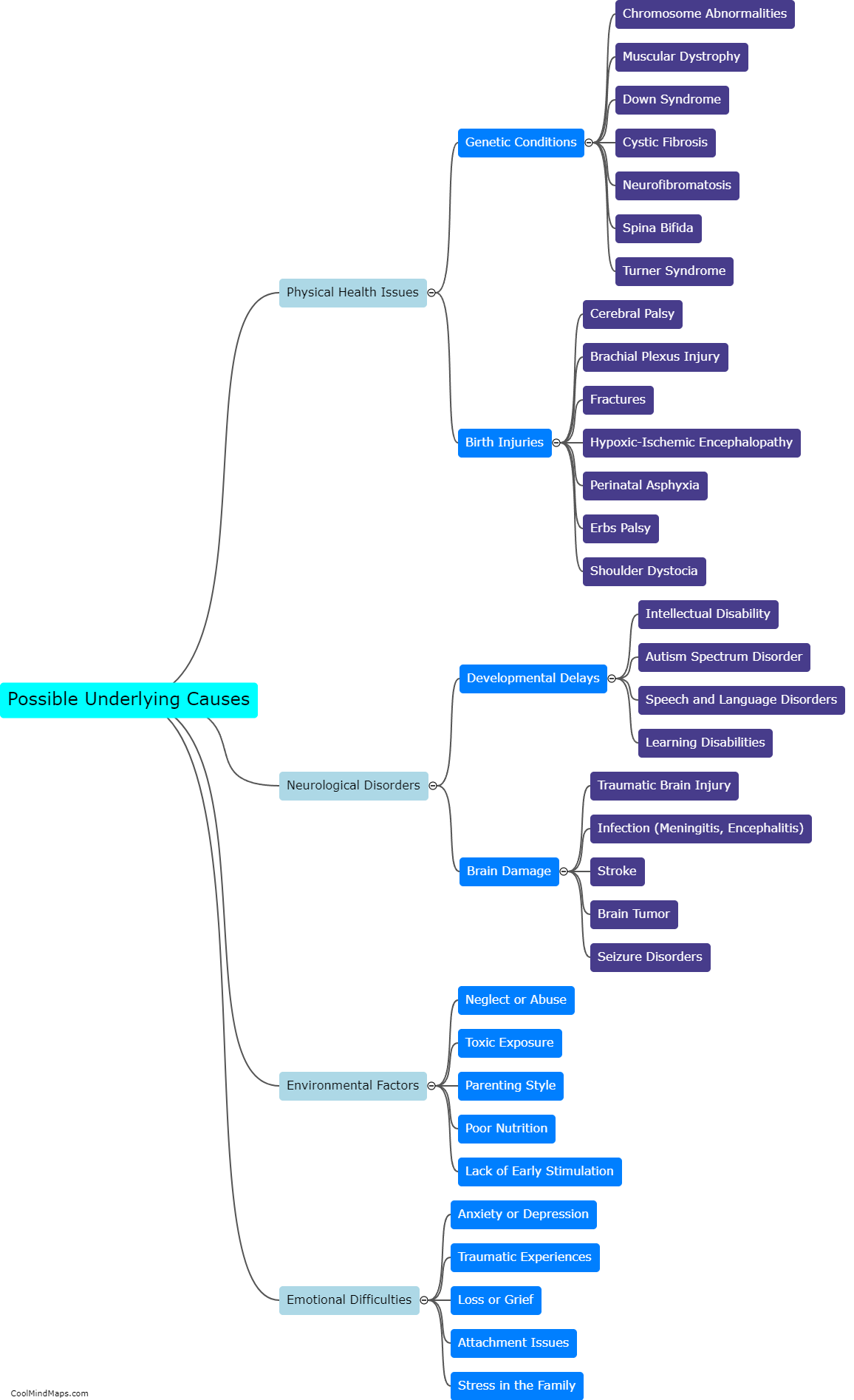
What is meant by Norton theorem?
The Norton theorem is a fundamental concept in electrical circuit analysis that allows for the simplification of complex circuits. It states that any linear circuit consisting of multiple sources and resistors can be replaced by a single current source in parallel with a resistor. The current source represents the Norton current, which is the short-circuit current flowing through a load connected across the output terminals, while the resistor represents the equivalent resistance seen by the load. By applying the Norton theorem, circuit analysis becomes more manageable, as the focus shifts from analyzing multiple sources and resistors to simply calculating the Norton current and equivalent resistance.

This mind map was published on 28 January 2024 and has been viewed 87 times.