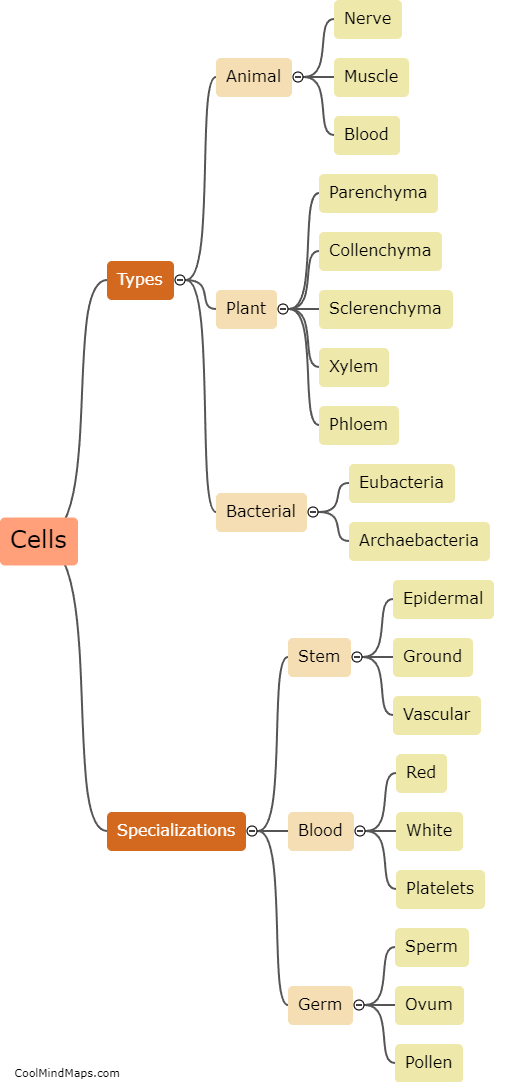
How do cells differ in structure and function?
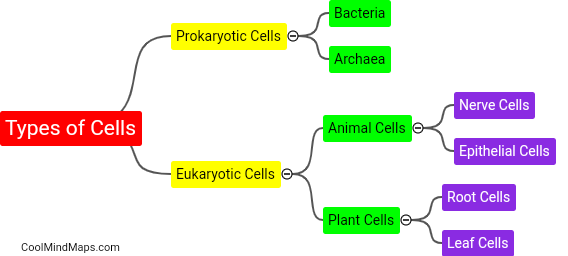
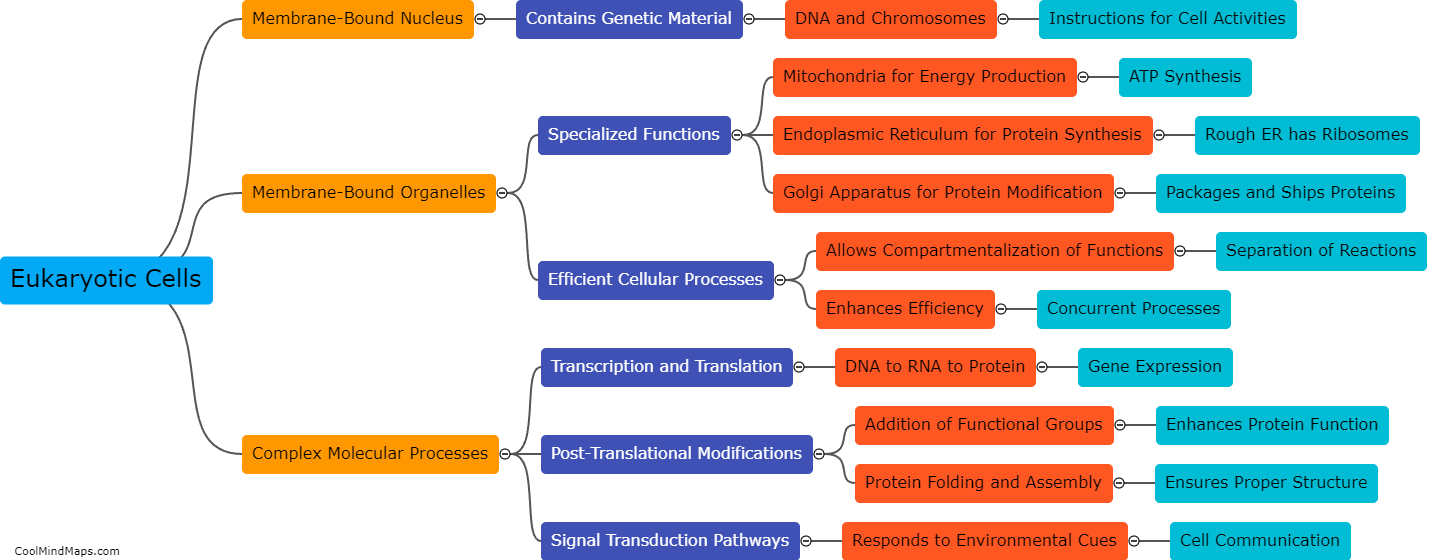
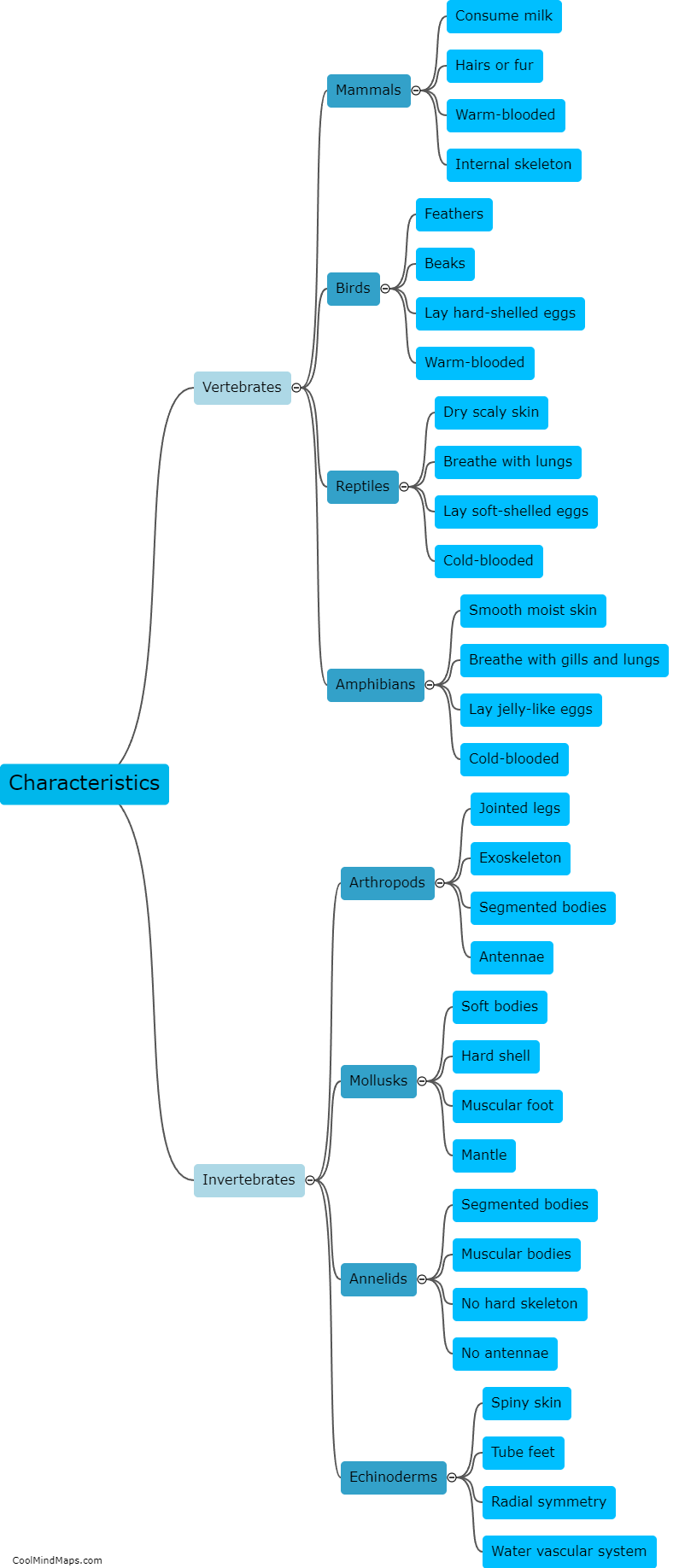
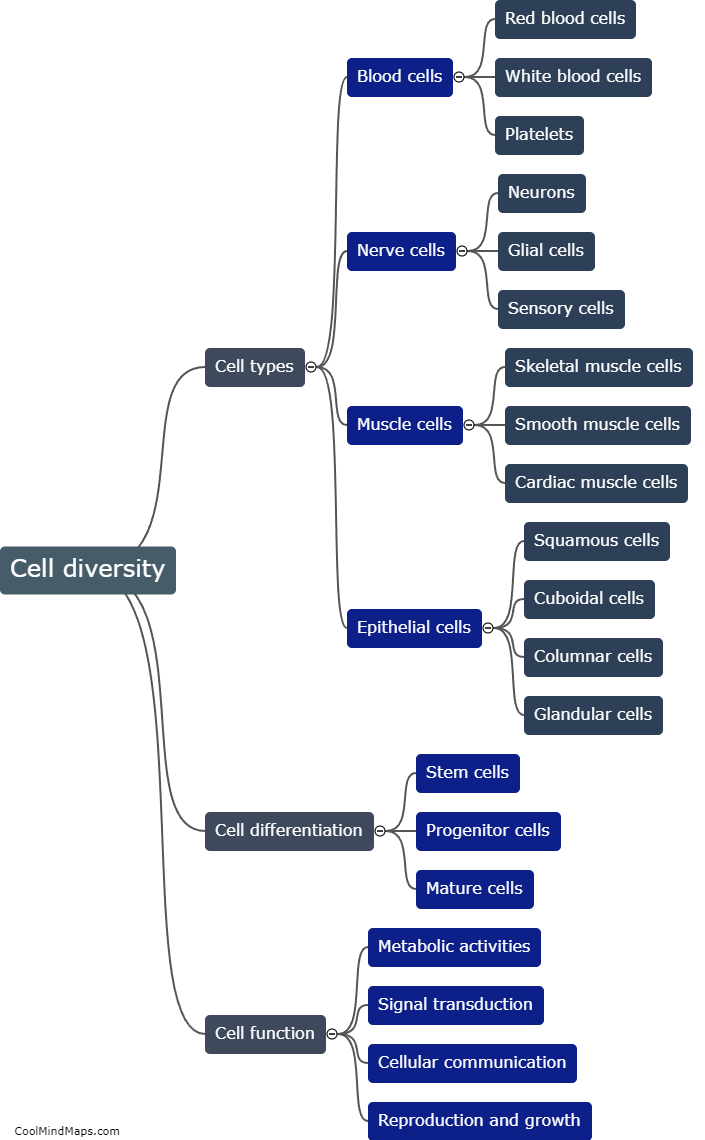
Cells differ in structure and function based on their specific roles in the body. Structurally, cells can vary in size, shape, and the presence of organelles. For example, muscle cells have long, cylindrical shapes to facilitate contraction, while red blood cells have a biconcave shape to increase their surface area for efficient oxygen transport. Functionally, cells are specialized to perform various tasks. Nerve cells, or neurons, transmit electrical signals, while white blood cells are responsible for immune defense. Additionally, cells can differ in their ability to divide. Some cells, like skin cells, have a high rate of division for tissue regeneration, while others, like neurons, have limited or no capacity for division. In summary, cells exhibit diversity in both structure and function to fulfill the wide range of tasks required for proper bodily function.

This mind map was published on 26 October 2023 and has been viewed 105 times.