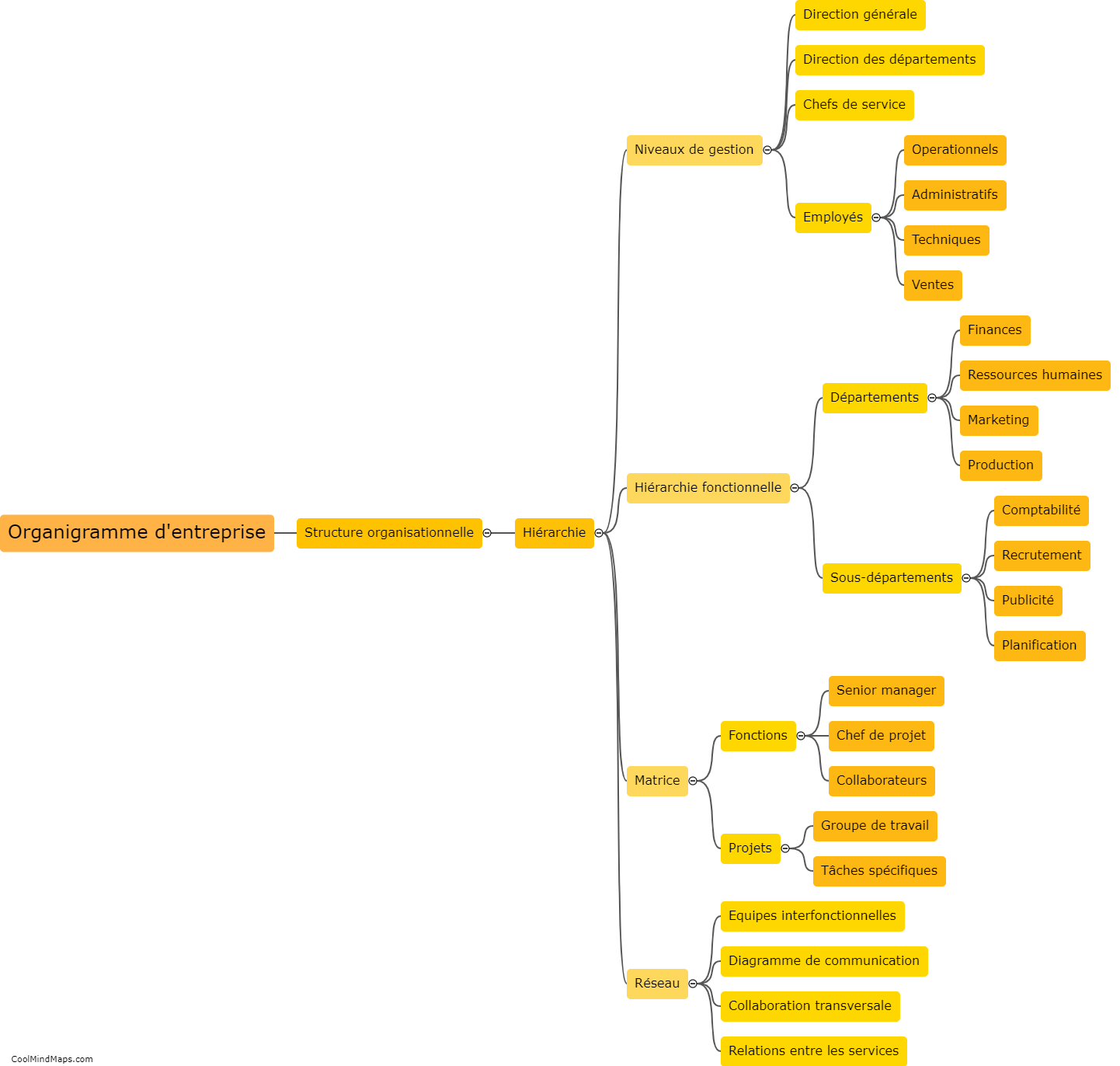
How do the different models explain the behavior of electrons?
The behavior of electrons is explained by different models in the field of quantum mechanics. The Bohr model, proposed by Niels Bohr, describes electrons as orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. Electrons transition between these energy levels by either absorbing or emitting photons. However, this model fails to fully explain the behavior of electrons in complex atoms. The Schrödinger model, which utilizes wave mechanics, describes electrons as standing waves or electron clouds. According to this model, electrons do not follow fixed paths but occupy regions of space with certain probabilities. The Quantum Mechanical model, a more advanced approach, combines wave mechanics with the concept of particle-like properties of electrons. It describes electrons as both waves and particles, characterized by their wave functions or probability distributions. This model provides a better understanding of electron behavior, including the possibility of electron tunneling and the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. Overall, these models have contributed to our understanding of the behavior of electrons, but they are constantly evolving as new discoveries are made in the realm of quantum mechanics.

This mind map was published on 21 September 2023 and has been viewed 120 times.