How do web applications work?
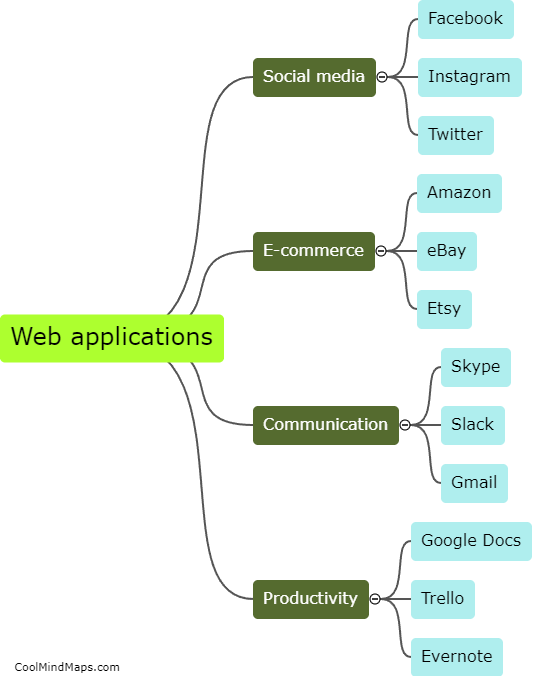
Web applications are software programs accessed through web browsers over the internet. They work by utilizing a combination of client-side and server-side components. The client-side consists of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which are loaded by the web browser and processed locally on the user's device. The user interacts with the application through the browser, which sends requests to the server-side. The server-side consists of a back-end framework, a database, and server-side programming languages like PHP, Python, or Ruby. The server processes the requests, retrieves data from the database, performs necessary computations, and sends back the response, typically in the form of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This response is then rendered by the browser, and the user sees the updated web application. This client-server architecture allows web applications to handle complex tasks, store and retrieve data, and provide dynamic and interactive experiences to users.

This mind map was published on 9 July 2023 and has been viewed 126 times.