What is the mechanism of TNF inhibitors in paradoxical psoriasis?
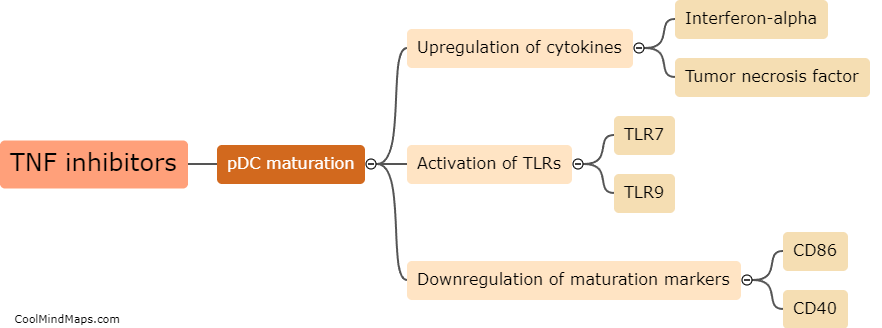
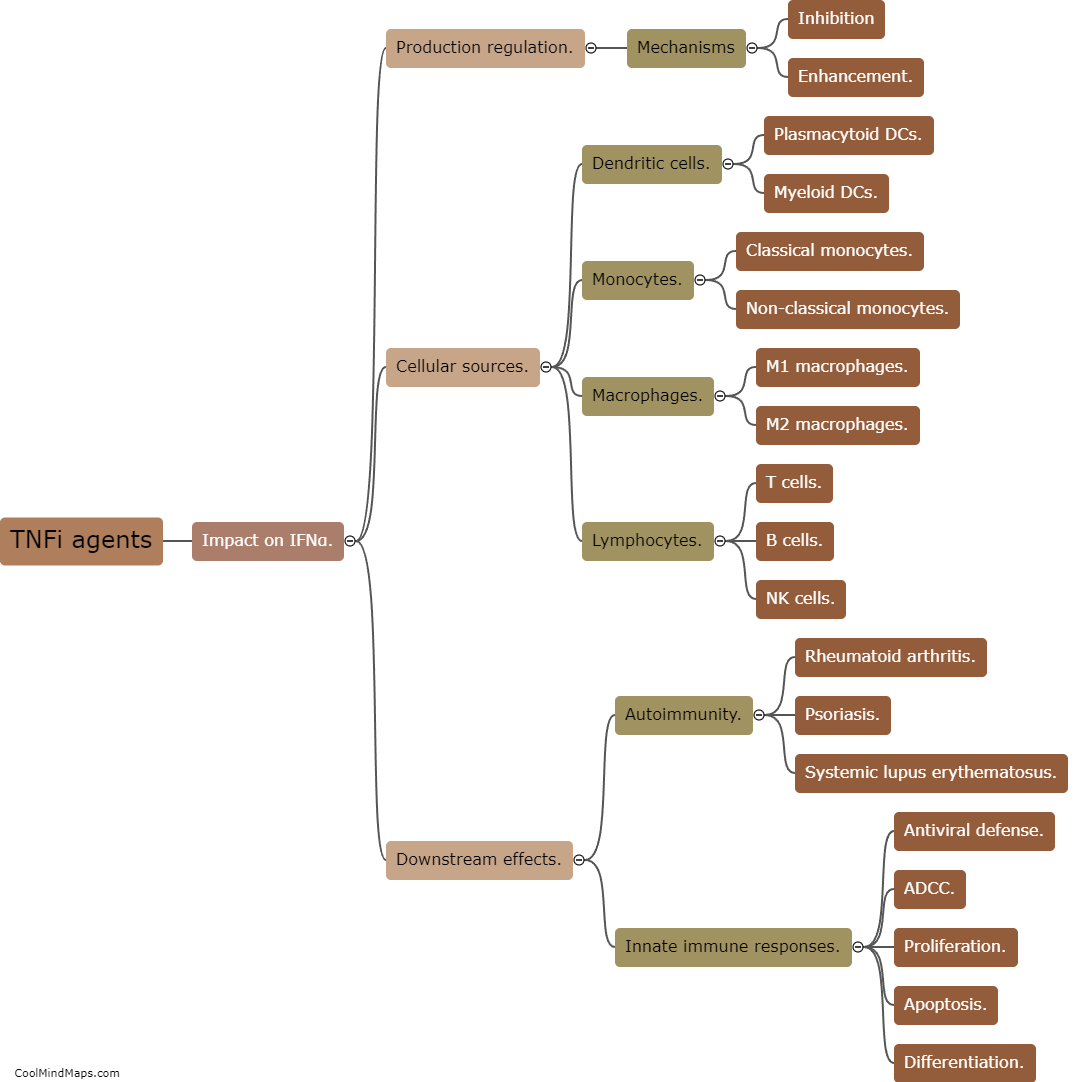
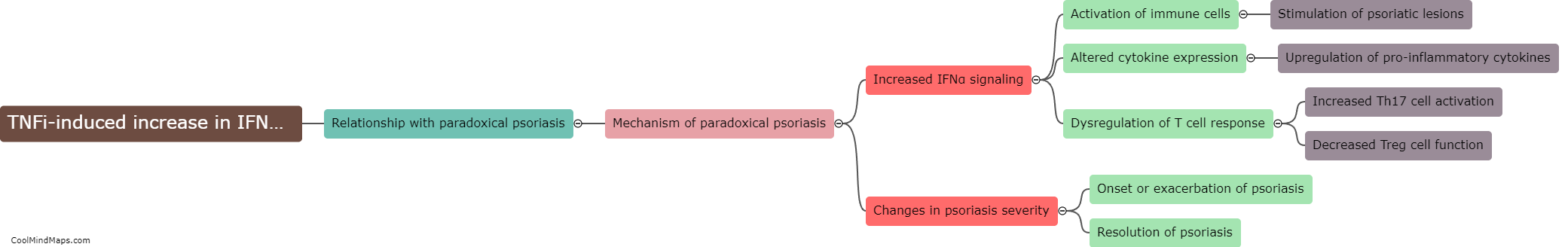
TNF inhibitors, a class of drugs commonly used to treat inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis, work by blocking the action of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a pro-inflammatory cytokine. Paradoxical psoriasis refers to the occurrence of new-onset psoriasis or exacerbation of existing psoriasis in patients receiving TNF inhibitors for unrelated conditions. The exact mechanism of paradoxical psoriasis in response to these drugs is not fully understood. However, it is believed that the inhibition of TNF may disrupt the delicate balance between various cytokines and immune cell interactions, leading to an increase in other pro-inflammatory mediators such as interleukin-17 (IL-17). This dysregulated immune response triggers the development or worsening of psoriasis lesions. Further research is needed to gain a deeper understanding of the precise mechanism underlying paradoxical psoriasis and to develop strategies to manage this side effect effectively.

This mind map was published on 12 July 2023 and has been viewed 106 times.