How does photosynthesis work?
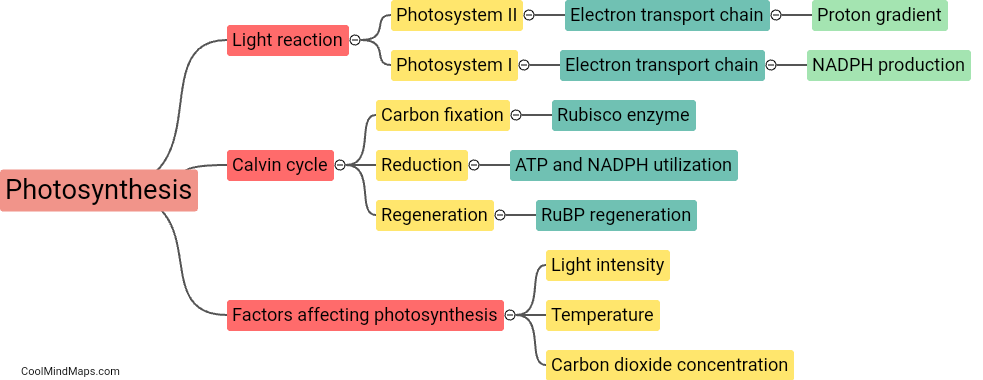
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in chloroplasts, specifically in the thylakoid membranes where chlorophyll pigments are concentrated. The process can be divided into two main stages - the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle). In the light-dependent reactions, sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll, energizing electrons and splitting water molecules, resulting in the release of oxygen and the creation of ATP and NADPH. Then, in the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose, using various enzymes and chemical reactions. Overall, photosynthesis is a vital process that not only produces oxygen but is also responsible for maintaining the Earth's atmospheric composition and providing a source of energy for numerous organisms.
This mind map was published on 2 September 2023 and has been viewed 119 times.